(Press-News.org) People selectively underestimate how rich the world’s richest people are, according to a study. Increasing income inequality in many countries is driven by steep gains among the top 1% of earners. In the United States, support for policies that would redistribute wealth has not increased since the 1970s, even as the share of incomes held by the top 1% of Americans jumped from 10% to 19%. Barnabas Szaszi and colleagues conducted four studies to explore how well people understand the wealth held by others. In one study, 990 US residents recruited online were asked to estimate the minimum annual household income thresholds of various percentiles of American earners. Participants underestimated the income thresholds of the top 1% of earners but were more accurate when estimating income thresholds for lower percentiles. These results were replicated in a survey of 834 US citizens who were incentivized to guess accurately with the promise of cash rewards for accurate answers. In two additional studies, participants were shown photos and income figures for members of a fictional society, which allowed the authors to manipulate the extent to which wealth was concentrated in the top 1%. Participants underestimated the average income of the top 20% but not the lower quintiles. According to the authors, underestimation of the incomes held by the upper end of the income distribution could be caused in part by a phenomenon known as “scope insensitivity” in which people become less attuned to specific amounts, replacing specific amounts in their minds with a catch-all category such as “rich.” For example, a billionaire earning one more million does not register the way a person earning $50,000 a year suddenly earning a million dollars would.
END
People underestimate the income of the top 1%
2024-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ChatGPT and cultural bias
2024-09-17
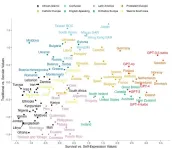
A study finds that ChatGPT expresses cultural values resembling people in English-speaking and Protestant European countries. Large language models, including ChatGPT, are trained on data that overrepresent certain countries and cultures, raising the possibility that the output from these models may be culturally biased. René F Kizilcec and colleagues asked five different versions of OpenAI’s GPT to answer 10 questions drawn from the World Values Survey, an established measure of cultural values used for decades to collect data from countries around the world. The ten questions place respondents ...
National political dialogue focused on power and morals
2024-09-17
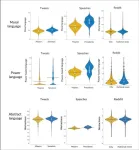
A study of political speeches, social media posts from politicians, and Reddit discussions among everyday users finds a higher prevalence of abstract, moralized, and power-centric language in national versus local politics. Political dialogue and debate in the United States has largely shifted from the local to the national in recent years, in part due to the decline of local news media. However, national discussions lack the concrete common ground that comes from shared place-based knowledge. Danica Dillion and colleagues studied how this shift is affecting ...
Police body-camera footage as data
2024-09-17
A study uses body-worn camera footage as a source of data on police-community interactions. Nicholas Camp and colleagues analyzed transcripts from 615 police stops made in California by Oakland Police Department police officers before and after a procedural justice training, which focused on officer communication in routine traffic stops. The training included findings by the authors in a previous study that showed officers used more respectful language with White drivers than with Black drivers during traffic stops. The training ...
Intimate partner violence: Preserving patient privacy saves lives
2024-09-17
Historically, South Carolina has had some of the highest rates of intimate partner violence, or IPV, in the U.S. IPV encompasses any physical or sexual violence, stalking and psychological aggression by a current or previous partner or spouse.
“There is an epidemic of intimate partner violence in South Carolina,” said Leslie A. Lenert, M.D., associate provost of Data Science and Informatics and director of the Biomedical Informatics Center at the Medical University of South Carolina.
To address that epidemic, Lenert partnered with clinical psychologist Alyssa A. Rheingold, Ph.D., family physician Vanessa Diaz, M.D., and health services ...
Moving particle simulation-aided soil plasticity analysis for earth pressure balance shield tunnelling
2024-09-17
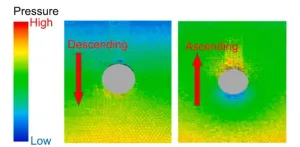
Infrastructures often suffer severe damage due to geotechnical hazards of both natural kinds such as floods or earthquakes and man-made ones like underground construction work and excavations. The fields of civil engineering and disaster risk management have extensively studied methods to prevent these risks and are still looking for more effective ways of avoiding large-scale deformations associated with said hazards. The advent of computer-aided simulations has provided researchers with particle-based methods such as moving particle ...
Identifying body-scan postures suitable for people with hyperactivity tendency
2024-09-17
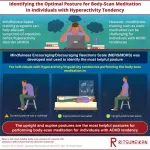
ADHD is a developmental condition of brain with symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity or impulsivity. People with ADHD lack the ability of self-control and experience anxiety, depression, academic failure, and low self-confidence. These symptoms can be alleviated by a holistic approach such as mindfulness-based stress reduction and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy. These practices encourage patients to pay attention to the present moment with purpose and without judgment. However, these practices involving meditation require sitting in certain postures which can be challenging for patients with high ADHD tendency.
To address this, ...
Indiana University selects Symplectic Elements as faculty activity reporting system
2024-09-17
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that Indiana University has selected Symplectic Elements as its new faculty activity management and reporting system.
This strategic decision marks a significant advancement toward the university’s goals of streamlining the management and reporting of the work and accomplishments of its faculty.
Indiana University is internationally known for outstanding research and its world-class degree programs, from business and health to STEM and the arts at its flagship campus in Bloomington, the expanding ...
Stephenson Prize for Innovation in Pancreatic Cancer Research launched with $150 million gift to City of Hope
2024-09-17
LOS ANGELES — City of Hope®, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations in the U.S. and ranked among the nation’s top 5 cancer centers by U.S. News & World Report, has received a historic $150 million gift from entrepreneurs and philanthropists A. Emmet Stephenson Jr. and his daughter Tessa Stephenson Brand to immediately fund pancreatic cancer research.
The centerpiece of this gift is the $1 million Stephenson Prize, one of the largest ...
New understanding of the limits on nano-noise
2024-09-17
Thanks to nanoscale devices as small as human cells, researchers can create groundbreaking material properties, leading to smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient electronics. However, to fully unlock the potential of nanotechnology, addressing noise is crucial. A research team at Chalmers University of Technology, in Sweden, has taken a significant step toward unraveling fundamental constraints on noise, paving the way for future nanoelectronics.
Nanotechnology is rapidly advancing, capturing ...
Graphite oxidation experiments reveal new type of oscillating chemical reaction
2024-09-17
A reaction that puzzled scientists for 50 years has now been explained by researchers at Umeå University. Rapid structural snapshots captured how graphite transforms into graphite oxide during electrochemical oxidation, revealing intermediate structures that appear and disappear over time. The researchers describe this as a new type of oscillating reaction.
Oscillating chemical reactions are fascinating to watch and important for developing an understanding of how complex systems work, both in chemistry and in nature. Classical visual examples of such reactions show how the colors of a solution change back and forth, cycling ...