(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA—At this moment, the world has few tools to combat deadly filoviruses, such as Ebola and Marburg viruses. The only approved vaccine and antibody treatments protect against just one filovirus species.
Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) are working to guide the development of new antivirals by leading some clever enemy reconnaissance. These researchers use high-resolution imaging techniques to examine a virus's molecular structure—and uncover where a virus is vulnerable to new therapies.
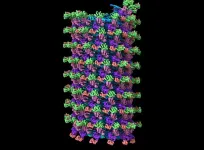
In a new Cell study, scientists in LJI's Center for Vaccine Innovation share the first detailed, complete images of a viral structure called the Ebola virus nucleocapsid. This breakthrough may accelerate the development of antivirals that target this viral structure to combat several filoviruses at once.
"A universal antiviral is the dream for stopping any kind of viral disease," says LJI Staff Scientist Reika Watanabe, Ph.D. who led the Cell study as a first author. "This study brings us a step closer to finding a universal antiviral."
Inspecting the enemy
Ebola virus relies on its nucleocapsid structure to protect and replicate its own genetic material inside host cells—and suppress host cellular immunity. Thanks to the nucleocapsid, Ebola can turn infected host cells into virus-making factories.
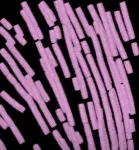
For the study, Watanabe achieved a first in science—by harnessing an imaging technique called cryo-electron tomography, she glimpsed Ebola's nucleocapsid structure at work inside actual infected cells.
At first glance, the Ebola virus nucleocapsid looks like a coiled telephone cord. Watanabe revealed the stages of coiling and compression of the coil. She also discovered that the nucleocapsid's cylindrical shape is made up of three layers. Each layer plays a different role as the virus replicates in host cells. Before LJI’s imaging studies, the existence of the outer layer was entirely unknown.
Watanabe's work also shows how this outer layer is composed, and how it provides a flexible tether between the nucleocapsid and the viral membrane.
"We found that the core protein adopts different forms in the distinct layers of the nucleocapsid to play different roles. ," says LJI Professor, President & CEO Erica Ollmann Saphire, Ph.D., MBA, who served as study senior author.
Watanabe's further investigations revealed how the proteins in these layers make contact with each other during assembly in host cells—and how the Ebola virus rearranges these proteins when nucleocapsids help form new viral particles.
"This study solves several puzzles in the field," says Saphire.
Targeting Ebola virus—and more
As Watanabe explains, targeting the nucleocapsid spells game over for the virus. "If you don't have a nucleocapsid, nothing can happen. That's the core of the virus," she says.
In fact, the Ebola virus nucleocapsid plays such a critical role in infection that Watanabe suspects the nucleocapsid's overall structure may have stayed the same as filoviruses evolved. Scientists call this kind of crucial structural feature "conserved" when it is shared across related species.
Indeed, all pathogenic filovirus species known so far, including Ebola and Marburg virus, share a conserved nucleocapsid structure, says Watanabe. She's now leading further research to study nucleocapsid assembly more closely in Marburg virus.
Additional authors of the study, "Intracellular Ebola Virus nucleocapsid assembly revealed by in situ cryo-electron tomography," include Dawid Zyla, Diptiben Parekh, Connor Hong, Ying Jones, Sharon L. Schendel, Willian Wan, and Guillaume Castillon.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH, grant R21AI180801).
About La Jolla Institute
La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) is dedicated to understanding the intricacies and power of the immune system so that we may apply that knowledge to promote human health and prevent a wide range of diseases. Since its founding in 1988 as an independent, nonprofit research organization, the Institute has made numerous advances leading toward its goal: life without disease. Visit lji.org for more information.
END
LJI discovery paves the way for antivirals against Ebola virus and its deadly relatives
Scientists capture first look at key viral structure within infected host cells
2024-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
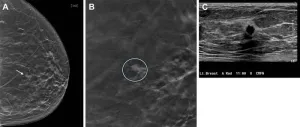
Advanced 3D mammography detects more breast cancers, fewer false positives
2024-09-17
New Haven, Conn. — The newer, 3D form of breast screening, known as digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), is more effective at detecting breast cancer than traditional 2D digital mammography (DM). That’s the conclusion of an analysis of 13 years’ worth of screening data conducted by Yale Cancer Center researchers. The data also suggests that 3D mammograms could reduce the incidence of advanced cancer diagnoses.
“Most of the time, women will do better with 3D mammograms since their ...
How an MBA can empower entrepreneurs
2024-09-17
Many leading entrepreneurs have questioned the value of investing in an MBA if you want to run a successful start-up. But a recent survey conducted with members of the INSEAD community shows that going to business school can help ensure that any entrepreneurial scheme has a better chance of achieving greater impact and long-term success.
According to the INSEAD Alumni Entrepreneurship Report 2024, 73 percent of the INSEAD students and graduates surveyed embarked on entrepreneurial activities following their time at the global business school. More than ...
Ten-year study shows tomosynthesis improves breast cancer detection
2024-09-17
OAK BROOK, Ill. – According to a new 10-year study, screening for breast cancer with digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) increases cancer detection rates and significantly reduces the rate of advanced cancers compared to conventional 2D digital mammography. The findings were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Mammography is considered the gold standard in breast cancer screening for the general population. However, conventional 2D mammography, in which a low-dose X-ray system produces pictures of the inside of the breast from two angles, fails to detect approximately 20% of breast cancers. It is ...
How can climate adaptation succeed in the long run?
2024-09-17
Invitation for Members of the Press
How can climate adaptation succeed in the long run?
On the basis of nine case studies from around the world, the Hamburg Climate Futures Outlook 2024 identifies the conditions for successfully and sustainably adapting to the impacts of climate change. A study recently released by the University of Hamburg’s Cluster of Excellence for climate research (CLICCS) demonstrates the urgent need for developing new adaptation strategies while also reducing climate-harmful emissions – and offers corresponding practical recommendations.
As in past installments, the experts assessed ten key social processes that are relevant for deep ...
Moderate coffee and caffeine consumption is associated with lower risk of developing multiple cardiometabolic diseases, new study finds
2024-09-17
WASHINGTON—Consuming moderate amounts of coffee and caffeine regularly may offer a protective effect against developing multiple cardiometabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease and stroke, according to new research published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Researchers found that regular coffee or caffeine intake, especially at moderate levels, was associated with a lower risk of new-onset cardiometabolic multimorbidity (CM), which refers to the coexistence of at least two cardiometabolic diseases.
The prevalence of individuals with multiple ...
New four-year, $3.26 million grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke establishes the Mount Sinai Center for Undiagnosed Diseases
2024-09-17
New York, NY (September 17, 2024) – A new four-year, $3.26 million grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), a part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), establishes the first Undiagnosed Diseases Network (UDN) site in the New York metropolitan area. Patients of all ages with difficult-to-diagnose diseases can apply to have their cases studied intensively by the new Mount Sinai Center for Undiagnosed Diseases using state-of-the-art genomic approaches as soon as the beginning of 2025.
These funds expand the work of the Undiagnosed Diseases Program, previously ...
Lupus Research Alliance announces recipients of 2024 Diversity in Lupus Research Awards
2024-09-17
New York, NY. September 17. The Lupus Research Alliance (LRA) is pleased to announce the recipients of the 2024 Career Development and Postdoctoral Awards to Promote Diversity in Lupus Research. Launched in 2021, the Diversity in Lupus Research (DLR) Awards aim to foster the development and productivity of exceptional early-career and postdoctoral scientists from underrepresented minority groups in science.
Lupus is a debilitating autoimmune disease that disproportionately affects Black, Hispanic, Indigenous, and Asian/Pacific Islander people. The LRA inaugurated the DLR Awards three years ...
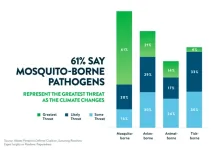
New survey from Abbott finds epidemiologists believe viral and mosquito-borne pathogens are priority concerns for disease outbreaks
2024-09-17
Survey reveals that infectious disease experts see the need to address gaps in surveillance programs to identify emerging pathogens, public health funding and testing infrastructure capabilities
They point to viral pathogens and mosquito-borne pathogens as likely to spark outbreaks as humans, animals and viruses overlap; and new viruses are as concerning as changes to existing viruses
Experts believe robust tracking of changing insect range, animal habitats and their migrations and extreme weather events are important to understanding infectious diseases and changing risk patterns
ABBOTT PARK, Ill., ...
A wobble from Mars could be sign of dark matter, MIT study finds
2024-09-17
In a new study, MIT physicists propose that if most of the dark matter in the universe is made up of microscopic primordial black holes — an idea first proposed in the 1970s — then these gravitational dwarfs should zoom through our solar system at least once per decade. A flyby like this, the researchers predict, would introduce a wobble into Mars’ orbit, to a degree that today’s technology could actually detect.
Such a detection could lend support to the idea that primordial black holes are a primary source of dark matter throughout the universe.
“Given decades of precision ...
In step toward solar fuels, durable artificial photosynthesis setup chains two carbons together
2024-09-17
Images
A key step toward reusing CO2 to make sustainable fuels is chaining carbon atoms together, and an artificial photosynthesis system developed at the University of Michigan can bind two of them into hydrocarbons with field-leading performance.
The system produces ethylene with efficiency, yield and longevity well above other artificial photosynthesis systems. Ethylene is a hydrocarbon typically used in plastics, so one direct application of the system would be to harvest carbon dioxide that would otherwise be vented into the atmosphere for making plastics.
"The performance, or the activity and stability, is about five to six times better than what is typically reported ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
[Press-News.org] LJI discovery paves the way for antivirals against Ebola virus and its deadly relativesScientists capture first look at key viral structure within infected host cells