How can climate adaptation succeed in the long run?
2024-09-17
(Press-News.org)
Invitation for Members of the Press
How can climate adaptation succeed in the long run?
On the basis of nine case studies from around the world, the Hamburg Climate Futures Outlook 2024 identifies the conditions for successfully and sustainably adapting to the impacts of climate change. A study recently released by the University of Hamburg’s Cluster of Excellence for climate research (CLICCS) demonstrates the urgent need for developing new adaptation strategies while also reducing climate-harmful emissions – and offers corresponding practical recommendations.
As in past installments, the experts assessed ten key social processes that are relevant for deep decarbonization and adhering to the 1.5-degree target. In addition, the study shows how the combination of climate change and natural climate variations is already affecting ecosystems and economies and entails greater risks for the future.
To accompany the release of the “Hamburg Climate Futures Outlook 2024. Conditions for Sustainable Climate Change Adaptation,” you are warmly invited to a presentation of the main findings. There will be ample time for your questions.
Online Press Conference
Thursday, September 19, 2024, 10 a.m. (EST)
With
Prof. Anita Engels, sociology, CLICCS, University of Hamburg, Germany
Prof. Jochem Marotzke, meteorology, CLICCS, Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Germany
Prof. Beate Ratter, geography, CLICCS, University of Hamburg, Helmholtz Centre Hereon, Germany
Prof. Gabriela Di Giulio, public health and environment, University of São Paulo, Brazil
Host
Dr. Eduardo Gresse, CLICCS, University of Hamburg
Venue: Virtual, ZOOM videocall
Registration: Please register by mailing Stephanie Janssen (stephanie.janssen@uni-hamburg.de) by Sept. 18, 2024. You will receive a link to the conference well in advance.
Organizer: Cluster of Excellence “Climate, Climatic Change, and Society (CLICCS)”, University of Hamburg
Please note that you need to have ZOOM installed on your device; otherwise, the University’s security system will unfortunately not allow you to participate.
Press contact:
Stephanie Janssen
University of Hamburg
Cluster of Excellence Climate, Climatic Change, and Society (CLICCS)
Public Relations / Outreach
+49 40 42838-7596
Email: stephanie.janssen@uni-hamburg.de
Franziska Neigenfind
University of Hamburg
Cluster of Excellence Climate, Climatic Change, and Society (CLICCS)
Public Relations / Outreach
+49 40 42838-6173
Email: franziska.neigenfind@uni-hamburg.de
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-17
WASHINGTON—Consuming moderate amounts of coffee and caffeine regularly may offer a protective effect against developing multiple cardiometabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease and stroke, according to new research published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Researchers found that regular coffee or caffeine intake, especially at moderate levels, was associated with a lower risk of new-onset cardiometabolic multimorbidity (CM), which refers to the coexistence of at least two cardiometabolic diseases.
The prevalence of individuals with multiple ...
2024-09-17
New York, NY (September 17, 2024) – A new four-year, $3.26 million grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), a part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), establishes the first Undiagnosed Diseases Network (UDN) site in the New York metropolitan area. Patients of all ages with difficult-to-diagnose diseases can apply to have their cases studied intensively by the new Mount Sinai Center for Undiagnosed Diseases using state-of-the-art genomic approaches as soon as the beginning of 2025.
These funds expand the work of the Undiagnosed Diseases Program, previously ...
2024-09-17
New York, NY. September 17. The Lupus Research Alliance (LRA) is pleased to announce the recipients of the 2024 Career Development and Postdoctoral Awards to Promote Diversity in Lupus Research. Launched in 2021, the Diversity in Lupus Research (DLR) Awards aim to foster the development and productivity of exceptional early-career and postdoctoral scientists from underrepresented minority groups in science.
Lupus is a debilitating autoimmune disease that disproportionately affects Black, Hispanic, Indigenous, and Asian/Pacific Islander people. The LRA inaugurated the DLR Awards three years ...
2024-09-17
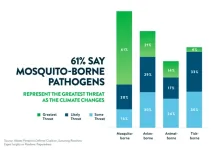
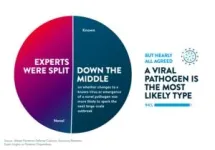
Survey reveals that infectious disease experts see the need to address gaps in surveillance programs to identify emerging pathogens, public health funding and testing infrastructure capabilities
They point to viral pathogens and mosquito-borne pathogens as likely to spark outbreaks as humans, animals and viruses overlap; and new viruses are as concerning as changes to existing viruses
Experts believe robust tracking of changing insect range, animal habitats and their migrations and extreme weather events are important to understanding infectious diseases and changing risk patterns
ABBOTT PARK, Ill., ...
2024-09-17
In a new study, MIT physicists propose that if most of the dark matter in the universe is made up of microscopic primordial black holes — an idea first proposed in the 1970s — then these gravitational dwarfs should zoom through our solar system at least once per decade. A flyby like this, the researchers predict, would introduce a wobble into Mars’ orbit, to a degree that today’s technology could actually detect.
Such a detection could lend support to the idea that primordial black holes are a primary source of dark matter throughout the universe.
“Given decades of precision ...
2024-09-17
Images
A key step toward reusing CO2 to make sustainable fuels is chaining carbon atoms together, and an artificial photosynthesis system developed at the University of Michigan can bind two of them into hydrocarbons with field-leading performance.
The system produces ethylene with efficiency, yield and longevity well above other artificial photosynthesis systems. Ethylene is a hydrocarbon typically used in plastics, so one direct application of the system would be to harvest carbon dioxide that would otherwise be vented into the atmosphere for making plastics.
"The performance, or the activity and stability, is about five to six times better than what is typically reported ...
2024-09-17
Doctors and pharmacists treating people with blood thinners can reduce the rate of inappropriate dosing — as well as blood clots and strokes that can result from it — using an electronic patient management system, a study suggests.
The online dashboard, developed by the United States Veterans Health Administration in 2016, was designed to highlight and optimize the treatment of patients with direct oral anticoagulants, or DOACs, the most commonly prescribed blood thinners.
Researchers led by Michigan Medicine used the tool to assess over 120,000 cases in which patients with atrial fibrillation or venous thromboembolism, blood clots in the veins, were treated with ...
2024-09-17
UPTON, N.Y. — The Blavatnik Family Foundation and the New York Academy of Sciences have recognized chemical engineer Juan Jimenez as a Finalist in the 2024 Blavatnik Regional Awards for Young Scientists. Jimenez’s catalysis science research at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory opens doors for turning climate change-driving gases into industrially useful materials.
The yearly honor is awarded to distinguished early career researchers at institutions in ...
2024-09-17
NEW YORK – September 17, 2024 – The Blavatnik Family Foundation and The New York Academy of Sciences today announced the three Laureates and six Finalists of the 2024 Blavatnik Regional Awards for Young Scientists. The Awards honor outstanding postdoctoral scientists from academic research institutions across New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut.
The Blavatnik Regional Awards jury, consisting of distinguished scientists and engineers, selected one Laureate in each category who will receive a $30,000 unrestricted prize and two Finalists in each category who will be awarded $10,000 ...
2024-09-17
People selectively underestimate how rich the world’s richest people are, according to a study. Increasing income inequality in many countries is driven by steep gains among the top 1% of earners. In the United States, support for policies that would redistribute wealth has not increased since the 1970s, even as the share of incomes held by the top 1% of Americans jumped from 10% to 19%. Barnabas Szaszi and colleagues conducted four studies to explore how well people understand the wealth held by others. In one study, 990 US residents ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How can climate adaptation succeed in the long run?