(Press-News.org) Trachomatous trichiasis, a potentially blinding condition where inward-turned eyelashes scratch the front of the eye, can successfully be treated by either of the two most common types of eyelid surgery, according to findings from a large comparison trial funded by the National Institutes of Health. In light of previous, smaller studies, which suggested that one of the commonly used surgery types had poorer outcomes, this study provides reassurance that either technique can treat the condition. The study, published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, was supported by the National Eye Institute (NEI), part of NIH.
“Some studies have reported post-operative trichiasis rates of 30% or higher for patients with trachomatous trichiasis following surgery, and repeat surgeries are more difficult,” said Emily Gower, Ph.D., University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “This trial sought to determine if we could decrease the risk of post-operative trichiasis by modifying the surgical procedure. We found that existing approaches result in better outcomes.”
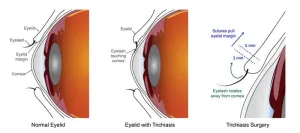
Trachomatous trichiasis affects approximately 1.7 million people worldwide, mostly in poor and rural areas of Africa. The condition arises after repeated or chronic eye infections with the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis, which is spread by person-to-person contact. Trachoma is very common in hot, dry areas of the world, and repeat infections can eventually lead to scarring and malformation of the eyelid. This malformation causes the edge of the eyelid to draw inward, so that eyelashes scratch the eye. If left untreated, trichiasis can result in corneal clouding, and eventually blindness.
The most common and effective treatment for trichiasis is surgery to correct the in-turning of the eyelid, which typically is performed in one of two different ways. A few smaller studies indicated that one of the surgery methods, posterior lamellar tarsal rotation (PLTR), might be more effective, so some programs in Africa began retraining surgeons to perform that method. Additionally, previous analysis of eyelids treated with the other surgery, bilamellar tarsal rotation (BLTR), suggested that placing the surgical incision slightly further from the edge of the eyelid (5 millimeters above the lid margin instead of 3 mm) might lead to fewer recurrences, but this change had not previously been tested. The current study directly compared these three surgery approaches and evaluated the risk of post-operative trichiasis.
The study, which took place in southern Ethiopia, enrolled 4,914 patients with trichiasis in one or both eyes (6,940 eligible eyes). The participants were randomized to receive BLTR at 3 mm incision height, BLTR at 5 mm incision height, or PLTR. Researchers rechecked the patients for post-operative trichiasis at six weeks and again at 12-18 months. On average, approximately 17% of eyelids had post-operative trichiasis. There was no difference in risk of post-operative trichiasis between the two methods with a 3 mm incision height, while those who received the 5 mm incision height BLTR were significantly more likely to have post-operative trichiasis. The results indicate that the current standard surgeries – either method at 3 mm – are better options for trichiasis treatment than the 5 mm method.
The study was funded by NEI grant UG1EY025992 and carries clinical trial registration number NCT03100747.
Reference:
Gower EW, Sisay A, Bayissasse B, Seyum D, Weaver J, Munos B, Keil AP, Bankoski A, Sullivan KM, Kana H, Admassu F, Tadesse D, and Merbs SL. “The impact of modified incision height and surgical procedure on trichiasis surgery outcomes: Results of the Maximizing Trichiasis Surgery Success (MTSS) Randomized Trial.” PLOS NTD. Sep 17, 2024. https://journals.plos.org/plosntds/article?id=10.1371/journal.pntd.0012034
NEI leads the federal government’s efforts to eliminate vision loss and improve quality of life through vision research…driving innovation, fostering collaboration, expanding the vision workforce, and educating the public and key stakeholders. NEI supports basic and clinical science programs to develop sight-saving treatments and to broaden opportunities for people with vision impairment. For more information, visit https://www.nei.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit https://www.nih.gov/.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
END
Two common surgeries equally effective for treating blinding condition of the eyelid
NIH-funded study supports no change to surgical technique for trichiasis management
2024-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NIH grant supports research into environmental factors regarding male fertility
2024-09-17
DETROIT — A grant from the National Institutes of Health will support ongoing research at Wayne State University investigating the consequences environmental factors may have on fertility in males.
The five-year, $3,082,404 grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences of the National Institutes of Health is led by Richard Pilsner, Ph.D., professor and the Robert J. Sokol, M.D., Endowed Chair of Molecular Obstetrics and Gynecology in the C.S. Mott Center for Human Growth and Development in the department of Obstetrics/Gynecology at Wayne State, and faculty member in the Institute of Environmental ...
Children’s National Hospital selected to lead next-generation BARDA Accelerator Network Special Populations Hub
2024-09-17
WASHINGTON (September 17, 2024) – Children’s National Hospital, widely recognized for its expertise and innovation in pediatric care, has been chosen by the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) to lead the Special Populations Hub in the next generation of the BARDA Accelerator Network. BARDA, is part of the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response (ASPR) within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
The next generation of the BARDA Accelerator Network builds on lessons learned from the first iteration of the network ...
What happens to patients when their GP retires or relocates?
2024-09-17
Norway introduced its Regular GP Scheme was introduced in 2001. This gave all citizens the right to choose a GP in their home municipality and facilitates personal continuity between the doctor and the patient.
These types of long-term doctor-patient relationships are associated with reduced use of emergency health services and lower mortality, both internationally and in Norway.
A widely discussed Norwegian study from 2022 showed that patients who had the same GP for more than fifteen years had a 25 per cent lower risk of dying compared to patients who had the same GP for one year or less.
However, there has been an increasing shortage of GPs in recent years. As of July 2024, just over ...
Cancer cells may be using lipids to hide from the immune system
2024-09-17
Cancer cells seldom start off stealthy. Quite to the contrary, they announce their presence to the immune system by planting chemical red flags right on their membranes. Once alerted, the body’s defenses can swoop in, destroying rogue cells before they can do much damage. Lying at the heart of this early warning system are lipids, fatty compounds previously seen by cancer biologists primarily as a fuel source for burgeoning tumors.
But now, a new study in Nature demonstrates that one particular lipid type is actually ...
NASA completes spacecraft to transport, support Roman Space Telescope
2024-09-17
The spacecraft bus that will deliver NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope to its orbit and enable it to function once there is now complete after years of construction, installation, and testing.
Now that the spacecraft is assembled, engineers will begin working to integrate the observatory’s other major components, including the science instruments and the telescope itself.
“They call it a spacecraft bus for a reason — it gets the telescope to where it needs to be ...
University of Health Sciences earns $5.3 million from NIH to boost cancer research, support emerging scientists
2024-09-17
A $5.3 million National Institutes of Health grant awarded to the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences will support advanced cancer research in Oklahoma. The Centers of Biomedical Research Excellence (COBRE) grant is designed to build research capacity and help early-career researchers establish independently funded laboratories.
This is the third and final phase of the COBRE grant, which was first awarded in 2012, followed by phase two in 2017. The grant has supported and paralleled the growth of OU Health Stephenson Cancer Center, Oklahoma’s ...
Central America could play troubling new role in cocaine trade
2024-09-17
COLUMBUS, Ohio – For many decades, the coca plant – the main ingredient in cocaine – has been grown almost exclusively in South America. But a new study shows that nearly half of northern Central America appears to be highly suitable for cultivating this lucrative cash crop.
Findings showed that 47% of Honduras, Guatemala and Belize have the right climate and soil for commercial coca growing. Most of southern Central America was not suitable.
It’s not a hypothetical concern. Researchers began ...
SwRI and UTSA will create synthetic process for antibiotic drug discovery
2024-09-17
SAN ANTONIO — September 17, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) is collaborating with The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) to explore and develop a novel platform or chemical process for synthesizing antibiotic compounds with a $125,000 grant. The project, one of two winning proposals this cycle, is supported by the Connecting through Research Partnerships (Connect) program designed to foster collaboration between SwRI and UTSA.
“SwRI and UTSA will work together to combat the growing threat antimicrobial resistance poses to global health by developing a proof-of-concept platform to potentially create a whole ...
Norwegian Afghanistan veterans more prone to anger
2024-09-17
From 2001 to 2021, roughly 9200 Norwegian soldiers served in Afghanistan. The vast majority of them have managed well in the years that have followed. According to a new survey conducted by the Norwegian Armed Forces Joint Medical Services, however, a significant number of the veterans struggle with mental health issues.
“All Norwegian veterans who served in Afghanistan were invited to participate in a large health survey in 2020,” says Associate Professor Andreas Espetvedt Nordstrand at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology ...
Black hole pairs may unveil new particles
2024-09-17
In a paper published in Physical Review Letters this week, physicists from Amsterdam and Copenhagen argue that close observations of merging black hole pairs may unveil information about potential new particles. The research combines several new discoveries made by UvA scientists over the past six years.
Gravitational waves that are emitted by the merger of two black holes carry detailed information about the shape and evolution of the orbits of the components. A new study by physicists Giovanni Maria Tomaselli and Gianfranco Bertone from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
[Press-News.org] Two common surgeries equally effective for treating blinding condition of the eyelidNIH-funded study supports no change to surgical technique for trichiasis management