(Press-News.org) Big data and artificial intelligence are transforming how we think about health, from detecting diseases and spotting patterns to predicting outcomes and speeding up response times.
In a new study analyzing two million Google Street View images from New York City streets, a team of New York University researchers evaluated the utility of this digital data in informing public health decision-making. Their findings, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), show how relying on street view images alone may lead to inaccuracies and misguided interventions, but combining it with other knowledge grows its potential.
“There’s a lot of excitement around leveraging new data sources to gain a holistic view of health, including bringing in machine learning and data science methods to extract new insights,” said Rumi Chunara, associate professor of biostatistics at NYU School of Global Public Health, associate professor of computer science at NYU Tandon School of Engineering, and the study’s senior author.
“Our study highlights the potential of digital data sources such as street view images in enhancing public health research, while also pointing out the limitations of data and the complex dynamics between the environment, individual behavior, and health outcomes,” said Miao Zhang, a PhD student at NYU Tandon School of Engineering and the study’s first author.
A street-level view of health
In recent years, researchers have begun using street view images to connect an area’s environment and infrastructure with outcomes such as mental health, infectious diseases, or obesity—a task that would be challenging to measure by hand.
“We know that a city’s built environment can shape our health, whether it's the availability of sidewalks and greenspaces for walking, or groceries stores carrying healthy foods,” said Chunara. “Some studies show that the availability of sidewalks correlates with lower obesity rates—but is that the whole story?”
“Our motivation for this study was to dive deeper into these associations to see if there are potential factors driving them,” said Zhang.
Chunara, Zhang, and their colleagues analyzed more than two million Google Street View images of every New York City street, using artificial intelligence to assess the availability of sidewalks and crosswalks in the images. They then compared this information with localized data on obesity, diabetes, and physical activity from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to see if the built environment predicted health outcomes.
The researchers found that neighborhoods with more crosswalks had lower rates of obesity and diabetes. However, no significant link was found between sidewalks and health outcomes, in contrast to earlier research.
“This may be because a lot of the sidewalks in New York City are in places that people don't use—along a highway, on a bridge, or in a tunnel—so sidewalk density may not reflect neighborhood walkability as accurately as crosswalks,” said Zhang.
They also surfaced issues with the accuracy of the AI-generated labels for the street view images, cautioning that they may not match the “ground truth” and be a reliable measure on their own. When comparing existing data on New York City’s sidewalk availability with the labeled street view images, they found that many were incorrectly labeled as having or not having sidewalks, which may have been due to cars or shade obscuring them in photos.
If you build it, will they come?
While crosswalks were linked to lower rates of obesity and diabetes, the researchers applied a public health lens to determine what could explain this association. Their analyses of the CDC data revealed that physical activity—not just crosswalks, as measured in street view images—accounted for the decrease in obesity and diabetes. In one test, they found that increasing physical activity could result in a four times larger decrease in obesity and 17 times greater decrease in diabetes than could be achieved through installing more crosswalks.
“We saw that physical activity delivers the benefits of crosswalks, so it’s important to take such mechanisms into account, especially when they act on different levels like the built environment versus individuals,” said Zhang.
Based on their findings, the researchers conclude that public health decision-making shouldn’t rely on new data sources alone, but must also consider domain knowledge. When analyzing street view images, incorporating computer science knowledge—for instance, how image processing techniques can improve accuracy or how to correct for bias in algorithms—and public health knowledge—what drives the associations between built environment and health outcomes—are critical. Layering this expertise over big data can inform how programs are designed and implemented to improve public health.
In this case, building more sidewalks and crosswalks would be less effective at improving health outcomes than the same increase in physical activity, such as through local exercise classes for the community.
“While growing amounts of digital data can be useful in informing decision-making, our results show that simply using associations from new data sources may not lead to the most useful interventions or best allocation of resources,” added Chunara. “A more nuanced approach using big data in conjunction with expertise is needed to make the best use of this new data.”
Salman Rahman and Vishwali Mhasawade of NYU Tandon were also study authors. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (award 1845487).
END
Can Google street view data improve public health?
Study finds big data alone won’t solve public health problems, but pairing street view images with expertise holds promise
2024-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mapping out matter’s building blocks in 3D
2024-09-17
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Deep inside what we perceive as solid matter, the landscape is anything but stationary. The interior of the building blocks of the atom’s nucleus — particles called hadrons that a high school student would recognize as protons and neutrons — are made up of a seething mixture of interacting quarks and gluons, known collectively as partons.
A group of physicists has now come together to map out these partons and disentangle how they interact to form hadrons. Based at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility and known as the HadStruc Collaboration, these ...
Cancer patients want financial screening early in care, study finds
2024-09-17
Patients want providers to reach out early and often to ask about financial needs
First study seeking cancer patient input on how they want to be screened
Findings show how to best deploy policies to screen cancer patients for financial concerns
CHICAGO --- Patients with cancer want their care team to assess them early in treatment about their concerns related to costs of care, reports a Northwestern Medicine study. It is the first time a study has sought cancer patients’ input on how they want to be screened for financial needs.
The financial impact of treatment, referred to as financial toxicity, includes direct costs, such as how much ...
Black women have a higher risk of dying from all types of breast cancer, meta-analysis reveals
2024-09-17
Breast cancer is the most diagnosed cancer among U.S. women and the second leading cause of cancer death. Black women who develop breast cancer are around 40% more likely to die of the disease than white women, but it was unclear until now whether this disparity exists across all types of breast cancer. Now, a meta-analysis led by Mass General Brigham researchers shows that Black women have a higher risk of dying from breast cancer for all tumor subtypes, and the size of this disparity varies from 17-50% depending on the type of breast cancer.
These findings, ...
‘Good complexity’ can make hospital networks more cybersecure
2024-09-17
In May, a major cyberattack disabled clinical operations for nearly a month at Ascension, a health care provider that includes 140 hospitals across the U.S. Investigators tracked the problem to malicious ransomware that had infected an employee’s computer.
Health care systems offer juicy targets for cybercrime because of the valuable personal, financial, and health data they hold. A 2023 survey of health information technology and IT security professionals reported that 88% of ...
Up to one-third of antibody drugs are nonspecific, study shows
2024-09-17
Integral Molecular, a leader in antibody discovery and characterization, has published new research in the journal mAbs, revealing that as many as one-third of antibody-based drugs exhibit nonspecific binding to unintended targets. A serious concern, off-target drug binding is a significant cause of adverse events in patients, with the potential to even cause death. Analysis of antibody off-target binding across different phases of clinical development suggests this to be a major cause of drug attrition. Early specificity testing could improve drug approvals and patient safety.
Learn how antibody developers can use the Membrane Proteome Array™ to assess specificity ...
Shrinking the pint can reduce beer sales by almost 10%
2024-09-17
Reducing the serving size for beer, lager and cider reduces the volume of those drinks consumed in pubs, bars and restaurants, and could be a useful alcohol control measure, according to research published September 17th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine. Theresa Marteau and colleagues at the University of Cambridge, UK, found that over a short intervention period, venues that removed the pint and offered two third pints instead, sold 10% less beer by volume compared with when pints were available.
When wine by the glass is offered in smaller servings, the amount sold ...
Unhealthy behaviors contribute to more coronary artery disease deaths in the poor
2024-09-17
Lower socioeconomic status is associated with higher rates of death from coronary artery disease compared to higher socioeconomic status, and more than half of the disparities can be explained by four unhealthy behaviors. Dr. Yachen Zhu of the Alcohol Research Group, U.S., and Dr. Charlotte Probst of the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Canada, report these findings in a new study published September 17th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine.
Coronary artery disease, also known as coronary heart disease or ischemic heart disease, occurs when the arteries supplying the heart cannot deliver enough oxygen-rich blood due to plaque buildup, and is a major cause of death in the ...
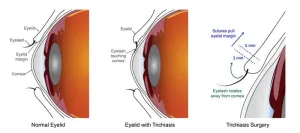
Two common surgeries equally effective for treating blinding condition of the eyelid
2024-09-17
Trachomatous trichiasis, a potentially blinding condition where inward-turned eyelashes scratch the front of the eye, can successfully be treated by either of the two most common types of eyelid surgery, according to findings from a large comparison trial funded by the National Institutes of Health. In light of previous, smaller studies, which suggested that one of the commonly used surgery types had poorer outcomes, this study provides reassurance that either technique can treat the condition. The study, published in PLOS Neglected ...
NIH grant supports research into environmental factors regarding male fertility
2024-09-17
DETROIT — A grant from the National Institutes of Health will support ongoing research at Wayne State University investigating the consequences environmental factors may have on fertility in males.
The five-year, $3,082,404 grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences of the National Institutes of Health is led by Richard Pilsner, Ph.D., professor and the Robert J. Sokol, M.D., Endowed Chair of Molecular Obstetrics and Gynecology in the C.S. Mott Center for Human Growth and Development in the department of Obstetrics/Gynecology at Wayne State, and faculty member in the Institute of Environmental ...
Children’s National Hospital selected to lead next-generation BARDA Accelerator Network Special Populations Hub
2024-09-17
WASHINGTON (September 17, 2024) – Children’s National Hospital, widely recognized for its expertise and innovation in pediatric care, has been chosen by the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) to lead the Special Populations Hub in the next generation of the BARDA Accelerator Network. BARDA, is part of the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response (ASPR) within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
The next generation of the BARDA Accelerator Network builds on lessons learned from the first iteration of the network ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Can Google street view data improve public health?Study finds big data alone won’t solve public health problems, but pairing street view images with expertise holds promise