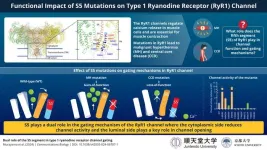
The type 1 ryanodine receptor (RyR1) is an important calcium release channel in skeletal muscles essential for muscle contraction. It mediates calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a calcium-storing organelle in muscle cells, a process vital for muscle function. Mutations in the RyR1 gene can affect the channel's function in extremely contrasting ways leading to severe muscle diseases such as malignant hyperthermia (MH) and central core disease (CCD). MH is an inherited disease that causes high fever and muscle contractures in response to inhalational anesthetics in patients with gain-of-function RyR1 variants. CCD is one of the inherited myopathies that leads to muscle weakness and myopathy due to loss-of-function RyR1 variants. These effects emphasize the critical role of RyR1 and the optimal functioning of the calcium channels for muscle health.
While recent research has focused on the large cytoplasmic region of RyR1, where many disease-associated mutations are found, the specific role of the fifth transmembrane segment (S5) in channel gating and the pathogenesis of muscle diseases was not well understood. Fortunately, in a new pioneering study published on 18 September 2024, in Communications Biology researchers from Japan addressed this knowledge gap by investigating how mutations in the S5 segment of the RyR1 contribute to MH and CCD. The research team comprising Associate Professor Takashi Murayama with Associate Professor Nagomi Kurebayashi from Juntendo University and Associate Professor Haruo Ogawa with Graduate student Yuya Otori from Kyoto University, set out to unravel how S5 mutations lead to muscle disorders. “The S5 segment is crucial for pore formation in the RyR1 channel. However, we found numerous disease-associated mutations in S5 reported in the literature, which motivated us to study the role of S5 segment in regulating the RyR1 channel,” explains Associate Prof. Takashi Murayama.
Researchers utilized HEK293 cells (a commonly used human embryonic kidney cell line) engineered to express RyR1 proteins with specific mutations. They measured caffeine-induced calcium release to assess the effects of mutations on calcium release dynamics. Further, they monitored resting cytoplasmic and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) calcium levels using Fluo-4 AM (green-fluorescent calcium indicator) and R-CEPIA1er (a genetically encoded calcium indicator), respectively. [3H]Ryanodine binding assays were performed to evaluate the binding affinity and activity of RyR1 channels. Additionally, the depolarization-induced calcium release (DICR) platform was used to assess calcium release in the RyR1 channel.
The study focused on mutations in the S5 and S5-S6 regions of RyR1, identifying three mutations linked to MH and eight associated with CCD. For MH mutants, they observed increased caffeine sensitivity, elevated resting cytoplasmic calcium levels, and reduced ER calcium levels. Ryanodine binding and DICR assays confirmed enhanced channel activity. In contrast, CCD mutants exhibited a loss-of-function phenotype, marked by reduced caffeine sensitivity, minimal calcium release, suppressed ryanodine binding, and reduced DICR. Notably, some CCD mutants displayed no detectable channel activity despite confirmed expression, indicating severely impaired channel function. The structure of the RyR1 channel and the mentioned mutations can be visualized in a video created by the authors on YouTube.
Next, the results were interpreted with respect to the RyR1 structures. The researchers identified several potential interactions between the residues responsible for the disease-associated mutations, and the other transmembrane segments. Notably, the importance of these interactions was validated by mutating the interaction partners. Highlighting their research findings, Associate Prof. Haruo Ogawa mentions, “We discovered a novel regulatory mechanism of the RyR1, in which the S5 segment plays a dual role in channel gating, and elucidated molecular mechanisms of channel alterations by disease-associated mutations.”
This study clarifies how mutations in S5 impact channel function, thereby improving the understanding of calcium signaling in muscle physiology. Explaining the potential implications of their current research, Associate Profs. Murayama and Ogawa share, “Our research findings provide new insights for the development of novel drugs to cure muscle diseases caused due to RyR1 mutations.”
We certainly hope that this study paves the way for revolutionizing the management of severe muscle disorders.
Reference
Authors
Takashi Murayama1, Yuya Otori2, Nagomi Kurebayashi1, Toshiko Yamazawa3, Hideto Oyamada4, Takashi Sakurai1, and Haruo Ogawa2
Title of original paper
Dual role of the S5 segment in type 1 ryanodine receptor channel gating
Journal
Communications Biology
DOI
10.1038/s42003-024-06787-1
Affiliations
1Department of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology, Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine
2Department of Structural Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kyoto University
3Core Research Facilities, The Jikei University School of Medicine
4Pharmacological Research Center, Showa University
About Associate Professor Takashi Murayama
Dr. Takashi Murayama is an Associate Professor in the Department of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology at Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. He earned his Doctor of Philosophy degree from Juntendo University. With over 106 publications and extensive experience in the field, Dr. Murayama focuses on ryanodine receptor physiology, cell biology, and molecular biology. His current research aims to develop therapeutics for ryanodine receptor-related diseases, highlighting his expertise in calcium signaling and molecular biological techniques. His significant contributions and extensive publication record underscore his role as a leading researcher in the field of excitation-contraction coupling.
About Associate Professor Haruo Ogawa
Dr. Haruo Ogawa is an Associate Professor at the Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kyoto University. He earned his Doctor of Philosophy degree from Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Japan. He is a leading expert in structural biology of membrane proteins and has made outstanding achievements in structural studies of ryanodine receptors and ion pump proteins. Specifically, his atomic structure of the world's first ion pump, published in Nature in 2000 has over 2000 citations. With research interests including the structure-function relationship of membrane proteins, he aims to elucidate the transmission of extracellular signals into the cell through membrane proteins.
END