Keck Hospital of USC named a 2024 top performer by Vizient, Inc.
Hospital receives a 5-star rating, the highest possible, for excellence in delivering high-quality care
2024-09-18
(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES — Keck Hospital of USC has been named a top performer in the 2024 Bernard A. Birnbaum, MD, Quality Leadership award by Vizient, Inc., a leading health care performance improvement company.
The top performer designation acknowledges the hospital’s excellence in delivering high-quality care as measured by the annual Vizient Quality and Accountability Study.
Keck Hospital was among 14 top performers out of 115 comprehensive academic medical centers nationally and achieved a five-star rating, the highest possible. This is the second time the hospital has been named a top performer in this category.
“Being named a Vizient top performer for the second time is a tremendous honor and reflects our continual efforts to provide superior clinical outcomes for our patients,” said Stephanie Hall, MD, MHA, chief medical officer of Keck Medical Center, which includes Keck Hospital. “The hospital uses a rigorous quality and accountability framework to guide and benchmark our performance across many markers of patient care, which has led to this success.”
The Vizient Quality and Accountability Study evaluates hospitals in six domains: safety, mortality, effectiveness, efficiency, patient centeredness and equity of care. The study factors in data from Vizient and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as well as a national survey of patients’ perspectives of hospital care known as the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems Survey (HCAHPS).
“This latest distinction achieved by Keck Hospital of USC is made possible by our culture of shared goals, collaboration and adaptability in an ever-changing health care environment, and is a testament to our staff’s unwavering commitment to deliver nationally recognized high-quality, equitable care,” said Marty Sargeant, MBA, CEO of Keck Medical Center.
The Vizient recognition period spans from July 1, 2023, through June 30, 2024.
This distinction is the third national quality designation Keck Hospital has received in 2024. The hospital also earned an “A” Hospital Safety Grade from The Leapfrog Group, an independent national watchdog organization, and was awarded five stars, the highest rating possible, on the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) quality star rating report.
###
Keck Hospital is part of Keck Medicine of USC. For more information about Keck Medicine, please visit news.KeckMedicine.org.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-18
Note: Embargoed until 8:00 a.m. ET on Sept. 18, 2024
From the early telescopes made hundreds of years ago by Galileo to the sophisticated astronomical observatories of today, people have built increasingly innovative tools to probe and measure the cosmos. Soon, researchers at two new institutes funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and the Simons Foundation will build a new breed of astronomical tools by harnessing the uniquely powerful abilities of artificial intelligence to assist and accelerate humanity's understanding of the universe.
The new National Artificial Intelligence ...
2024-09-18
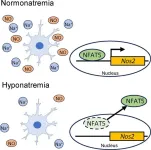
Low serum sodium concentrations in blood are called hyponatremia, a prevalent clinical electrolyte disorder. In contrast to acute hyponatremia, chronic hyponatremia has been previously considered asymptomatic because the brain can successfully adapt to hyponatremia. If not treated, chronic hyponatremia can lead to complications such as fractures, falls, memory impairment, and other mental issues. Treating the chronic condition is, however, quite tricky as it has been observed that overly rapid correction of hyponatremia ...
2024-09-18
EMBARGOED by Alzheimer’s & Dementia until 7 a.m., ET, Sept. 18, 2024
Contact: Gina DiGravio, Boston University, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
Contact: Andrea Zeek, IU School of Medicine, 317-671-3114, anzeek@iu.edu
(Boston)— The failure to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease, the most common form of dementia in the elderly, at an early stage of molecular pathology is considered a major reason why treatments fail in clinical trials. Previous research to molecularly diagnose Alzheimer’s disease yielded "A/T/N" central biomarkers based on the measurements of proteins, β-amyloid (“A”) and tau (“T”), ...
2024-09-18
About The Study: In this study, a higher burden of comorbidity was associated with worse clinical outcomes in people with multiple sclerosis (MS), although comorbidity could potentially be a partial mediator of other negative prognostic factors. The findings suggest a substantial adverse association of the comorbidities investigated with MS disease activity and that prevention and management of comorbidities should be a pressing concern in clinical practice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Amber Salter, PhD, email amber.salter@utsouthwestern.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
2024-09-18
London, United Kingdom, 18 September 2024 – UK Research and Innovation (UKRI), the UK’s largest public funder of research, has confirmed funding for a new phase of the DARE UK (Data and Analytics Research Environments UK) programme with up to £18.2 million made available over 2.5 years.
Starting this month, Phase 2 of the DARE UK programme will bring together Trusted Research Environments (TREs) across the UK to test and build new capabilities for a connected national network of secure data ...
2024-09-18
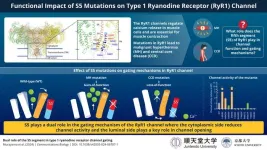
The type 1 ryanodine receptor (RyR1) is an important calcium release channel in skeletal muscles essential for muscle contraction. It mediates calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a calcium-storing organelle in muscle cells, a process vital for muscle function. Mutations in the RyR1 gene can affect the channel's function in extremely contrasting ways leading to severe muscle diseases such as malignant hyperthermia (MH) and central core disease (CCD). MH is an inherited disease that causes high fever and muscle contractures in response to inhalational anesthetics in patients with gain-of-function RyR1 variants. CCD is one ...
2024-09-18
Millions of birds migrate every year to escape winter, but spending time in a warmer climate does not save them energy, according to research by the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior (MPI-AB). Using miniaturized loggers implanted in wild blackbirds, scientists recorded detailed measurements of heart rate and body temperature from birds every 30 minutes from fall to the following spring—the first time the physiology of free flying birds has been quantified continuously at this scale over the entire wintering period. The data offer unprecedented insights into the true energetic costs of migrant and resident strategies and reveal a previously unknown mechanism used by migrants to ...
2024-09-18
Amyloid-beta and tau proteins have long been associated with Alzheimer’s disease. The pathological buildup of these proteins leads to cognitive decline in people with the disease. How it does that, though, remains poorly understood.
A new study from the labs of Sylvain Baillet at The Neuro and Sylvia Villeneuve at the Douglas Research Centre provides important insight into how these proteins impact brain activity and possibly contribute to cognitive decline.
The team led by Jonathan Gallego Rudolf, a Ph.D. candidate in Baillet and Villeneuve’s ...
2024-09-18
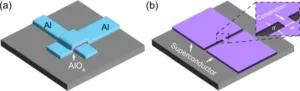
UPTON, N.Y. — Scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have shown that a type of qubit whose architecture is more amenable to mass production can perform comparably to qubits currently dominating the field. With a series of mathematical analyses, the scientists have provided a roadmap for simpler qubit fabrication that enables robust and reliable manufacturing of these quantum computer building blocks.
This research was conducted as part of the Co-design Center for ...
2024-09-18
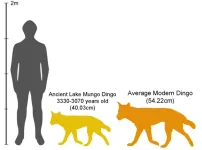
New archaeological research by the University of Sydney has discovered for the first time clear links between fossils of the iconic Australian dingo, and dogs from East Asia and New Guinea.
The remarkable findings suggest that the dingo came from East Asia via Melanesia, and challenges previous claims that it derived from pariah dogs of India or Thailand.
Previous studies used traditional morphometric analysis – which looks at the size and shape of the animal using callipers – ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Keck Hospital of USC named a 2024 top performer by Vizient, Inc.
Hospital receives a 5-star rating, the highest possible, for excellence in delivering high-quality care