(Press-News.org) AMHERST, Mass. – A new study by University of Massachusetts Amherst researchers demonstrates the effectiveness of homemade play putty at reading brain, heart, muscle and eye activity. Published in Device, the research outlines the conductive properties of this material, so-named “squishy circuits.”
“[Squishy circuits] are literally child’s play putty, that is also conductive” describes Dmitry Kireev, assistant professor of biomedical engineering and senior author on the paper.
The conductive squishy circuits – whether homemade or store-bought– are made of flour, water, salt, cream of tartar and vegetable oil. “Salt is what makes it conductive,” Kireev explains. As a child’s toy, this modeling clay is a maleable way to add lights to an art projectby connecting them to a power source as a way to teach kids about circuits. Now, Kireev and his team have demonstrated that the material has more potential.
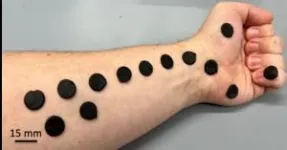
“We used the squishy circuits as an interface to measure electricity or measure bioelectrical potentials from a human body,” he says. They found that, compared to commercially available gel electrodes, these squishy circuits effectively captured various electrophysiology measurements: electroencephalogram (EEG) for brain activity, electrocardiogram (ECG) for heart recordings, electrooculogram (EOG) for tracking eye movement and electromyography (EMG) for muscle contraction.
“What makes one electrode material better than another in terms of the quality of the measurements is impedance,” he explains. Impedance is a measure that describes the quality of conductivity between two materials. “The lower the impedance between the electrode and the tissue, the better the conductivity in between and the better your ability to measure those bioelectrical potentials.”
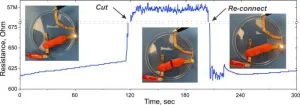
The study found that the impedance for the squishy circuit electrode was on par with one of the commercially available gel electrodes and twice as better as a second comparison electrode.
Kireev highlights several benefits to this material. First is cost: Even using pre-made putty, the cost per electrode was about 1cent. Typical electrodes cost on average between $0.25 and $1.
Also, the material is resilient: it can be formed and reformed, molded to the contours of the skin, combined with more putty to make it bigger, reused and easily reconnected if it comes apart. Other comparable state-of-the-art wearable bioelectronics have been made of carbon nanotubes, graphene, silver nanowires and organic polymers. While highly conductive, these materials can be expensive, difficult to handle or make, single use or fragile.
Kireev also highlights the availability of these materials. “It’s something you can do at home or in high school laboratories, for example, if needed,” he says. “You can democratize these applications [so it’s] more widespread.”
He gives credit to his research team of undergraduate students (some of whom have since graduated and are continuing with graduate studies at UMass): Alexandra Katsoulakis, Favour Nakyazze, Max Mchugh, Sean Morris, Monil Bhavsar and Om Tank.
END
Homemade ‘play-putty’ can read the body’s electric signals, find UMass researchers
The material could open a new field of flexible, cost-effective biometric sensors
2024-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Magnifying deep space through the “carousel lens”
2024-09-18
In a rare and extraordinary discovery, researchers have identified a unique configuration of galaxies that form the most exquisitely aligned gravitational lens found to date. The Carousel Lens is a massive cluster-scale gravitational lens system that will enable researchers to delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos, including dark matter and dark energy.
“This is an amazingly lucky ‘galactic line-up’ – a chance alignment of multiple galaxies across a line-of-sight spanning most of the observable universe,” said David Schlegel, a co-author of the study and a senior scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Physics Division. "Finding one such alignment is ...
Another new wasp species discovered by researchers Rice campus
2024-09-18
A newly identified wasp species, Chrysonotomyia susbelli, has been discovered in Houston, Texas, marking the 18th new species identified by Rice University’s Scott Egan and his research team since 2014. The discovery, the fourth wasp species found on the university grounds in seven years, reveals the hidden world of parasitoid wasps and the intricate ecosystems that thrive outside our doors.
The Chrysonotomyia susbelli is a parasitoid wasp, about 1 millimeter long, that emerges from galls, or tumorlike growths created by the gall wasp Neuroterus bussae found on southern live oak leaves. The galls serve as microhabitats within which larvae feed, develop and pupate. ...
Greenhouse gains: cucumbers get a genetic upgrade through innovative pollen tech
2024-09-18
Researchers have achieved a groundbreaking advancement in plant biotechnology by using a magnetofected pollen gene delivery system to genetically transform cucumbers. This cutting-edge method uses DNA-coated magnetic nanoparticles to introduce foreign genes into pollen, producing genetically modified seeds without the need for traditional tissue culture or regeneration steps. This technique significantly streamlines and accelerates crop genetic modification, opening up new avenues to boost agricultural productivity and resilience.
Genetic modification in horticultural crops, particularly within the Cucurbitaceae family, is often hindered by complex tissue culture requirements and ...
Like humans, artificial minds can learn by thinking
2024-09-18
Some of the greatest discoveries don’t come merely from observations but from thinking. Einstein developed theories about relativity through thought experiments, and Galileo derived insights about gravity through mental simulations. A review published September 18 in the journal Trends in Cognitive Sciences shows that this process of thinking is not exclusive to humans. Artificial intelligence, too, is capable of self-correction and arriving at new conclusions through “learning by thinking.”
“There are some recent demonstrations of what looks like learning by thinking in AI, ...
Discarding the placenta after birth leads to loss of valuable information, pathologists say
2024-09-18
In an opinion article publishing September 18 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Molecular Medicine, physician-scientists argue that with most placentas discarded after birth, placental pathology is underutilized clinically, should be a routine part of obstetric and neonatal care, and also deserves more research attention.
“Placentas should not be considered a waste tissue,” says senior author Mana Parast, MD, PhD, professor of pathology at University of California San Diego School of Medicine. ...
Nonfatal opioid overdoses in youth spiked during pandemic
2024-09-18
Drug overdose mortality has risen faster among adolescents than the general population in recent years, largely due to fentanyl, a potent opioid pain medication. A new study published in JAMA sheds light on trends in nonfatal opioid overdoses in youth – an area that was not as well characterized, but key to formulating prevention strategies to save lives.
Researchers from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and colleagues analyzed data using Emergency Medical Services (EMS) encounters from January 2018 to December 2022. They found that opioid overdoses in youth increased at pandemic onset and remained elevated compared to pre-pandemic levels. The majority ...
Characteristics and trends of prehospital encounters for opioid overdoses among US youth, 2018-2022
2024-09-18
About The Study: Prehospital encounters for youth opioid overdoses were increasing prior to the pandemic, increased with the onset, and then stabilized, remaining higher than pre-pandemic levels. Although overall patterns were largely driven by those ages 18 through 24, adolescents ages 12 through 17 were the only subgroup with an increasing number of encounters both before and during the pandemic.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jamie Lim, MD, email jlim@luriechildrens.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
Gargantuan black hole jets are biggest seen yet
2024-09-18
** Caltech is hosting an embargoed media zoom about this result on Monday, September 16 at 10am Pacific/1pm Eastern. You can register here:
https://caltech.zoom.us/webinar/register/WN_gYEV5Tl1S0uZkZG1gDIEnQ#/registration
Astronomers have spotted the biggest pair of black hole jets ever seen, spanning 23 million light-years in total length. That's equivalent to lining up 140 Milky Way galaxies back to back.
"This pair is not just the size of a solar system, or a Milky Way; we are talking about 140 Milky Way diameters in total," says Martijn ...
An update on the survival of the first 50 face transplants worldwide
2024-09-18
About The Study: In this study, the overall survival of the face transplants is encouraging. These data suggest that the acceptable long-term survival of face transplants makes them a reconstructive option for extensive facial defects.
Quote from corresponding author Pauliina Homsy, MD, PhD:
“A total of 50 face transplants have been performed since 2005. Activity has been concentrated with only 18 centers in 11 countries giving this treatment. Our study demonstrates an overall 5- and 10-year survival of face transplants ...
Social determinants of health and insurance claim denials for preventive care
2024-09-18
About The Study: In this cohort study of 1.5 million patients seeking preventive care, denials of insurance claims for preventive care were disproportionately more common among at-risk patient populations. This administrative burden potentially perpetuates inequitable access to high-value health care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Alex Hoagland, PhD, email alexander.hoagland@utoronto.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.33316)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
[Press-News.org] Homemade ‘play-putty’ can read the body’s electric signals, find UMass researchersThe material could open a new field of flexible, cost-effective biometric sensors