(Press-News.org) Drug overdose mortality has risen faster among adolescents than the general population in recent years, largely due to fentanyl, a potent opioid pain medication. A new study published in JAMA sheds light on trends in nonfatal opioid overdoses in youth – an area that was not as well characterized, but key to formulating prevention strategies to save lives.
Researchers from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and colleagues analyzed data using Emergency Medical Services (EMS) encounters from January 2018 to December 2022. They found that opioid overdoses in youth increased at pandemic onset and remained elevated compared to pre-pandemic levels. The majority (86 percent) occurred in young adults in the 18-24 age group. Adolescents aged 12-17, however, also emerged as high-risk, with significantly increasing trends both before and during the pandemic. Most of the opioid overdoses in youth (58 percent) happened at home.
“Since so many overdoses occur at home, a critical message for parents of youth, especially adolescents, is to keep naloxone, an over-the-counter medication that can reverse opioid overdoses, at home,” said lead author Jamie Lim, MD, a third-year fellow in Pediatric Emergency Medicine at Lurie Children’s. “Providers also need to screen youth for substance use and risk of opioid overdose, since it is clearly a growing concern among young people. Parents and patients need to be advised that fentanyl is now in a lot of street drugs too and can lead to accidental overdoses.”
Senior author and attending physician from Boston Children’s Hospital’s Division of Emergency Medicine, Michael Toce, MD, expands on the broader impact of the findings: “Evaluating prehospital data for opioid overdose among U.S. youth may provide crucial insights into the opioid epidemic outside of emergency department surveillance data. Although overdose rates have stabilized post-pandemic, it’s important to understand at-risk youth populations to develop better-targeted prevention strategies and inform future public health measures.”
Co-authors from Lurie Children’s include Sriram Ramgopal, MD, and Jennifer Hoffmann, MD, MS.
Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago is a nonprofit organization committed to providing access to exceptional care for every child. It is the only independent, research-driven children’s hospital in Illinois and one of less than 30 nationally. This is where the top doctors go to train, practice pediatric medicine, teach, advocate, research and stay up to date on the latest treatments. Exclusively focused on children, all Lurie Children’s resources are devoted to serving their needs. Research at Lurie Children’s is conducted through Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute, which is focused on improving child health, transforming pediatric medicine and ensuring healthier futures through the relentless pursuit of knowledge. Lurie Children’s is the pediatric training ground for Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. It is ranked as one of the nation’s top children’s hospitals by U.S. News & World Report. Emergency medicine-focused research at Lurie Children’s is conducted through the Grainger Research Program in Pediatric Emergency Medicine.
END
Nonfatal opioid overdoses in youth spiked during pandemic
Majority occurred at home, with significantly increasing trends among 12-17-year-olds
2024-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Characteristics and trends of prehospital encounters for opioid overdoses among US youth, 2018-2022
2024-09-18
About The Study: Prehospital encounters for youth opioid overdoses were increasing prior to the pandemic, increased with the onset, and then stabilized, remaining higher than pre-pandemic levels. Although overall patterns were largely driven by those ages 18 through 24, adolescents ages 12 through 17 were the only subgroup with an increasing number of encounters both before and during the pandemic.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jamie Lim, MD, email jlim@luriechildrens.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
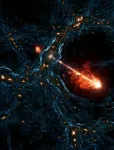
Gargantuan black hole jets are biggest seen yet
2024-09-18
** Caltech is hosting an embargoed media zoom about this result on Monday, September 16 at 10am Pacific/1pm Eastern. You can register here:
https://caltech.zoom.us/webinar/register/WN_gYEV5Tl1S0uZkZG1gDIEnQ#/registration
Astronomers have spotted the biggest pair of black hole jets ever seen, spanning 23 million light-years in total length. That's equivalent to lining up 140 Milky Way galaxies back to back.
"This pair is not just the size of a solar system, or a Milky Way; we are talking about 140 Milky Way diameters in total," says Martijn ...
An update on the survival of the first 50 face transplants worldwide
2024-09-18
About The Study: In this study, the overall survival of the face transplants is encouraging. These data suggest that the acceptable long-term survival of face transplants makes them a reconstructive option for extensive facial defects.
Quote from corresponding author Pauliina Homsy, MD, PhD:
“A total of 50 face transplants have been performed since 2005. Activity has been concentrated with only 18 centers in 11 countries giving this treatment. Our study demonstrates an overall 5- and 10-year survival of face transplants ...
Social determinants of health and insurance claim denials for preventive care
2024-09-18
About The Study: In this cohort study of 1.5 million patients seeking preventive care, denials of insurance claims for preventive care were disproportionately more common among at-risk patient populations. This administrative burden potentially perpetuates inequitable access to high-value health care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Alex Hoagland, PhD, email alexander.hoagland@utoronto.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.33316)
Editor’s ...
Patient self-guided interventions to reduce sedative use and improve sleep
2024-09-18
About The Study: The results of this randomized clinical trial showed that transitioning insomnia care for older adults away from long-term sedative use and toward cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia can be achieved using a mailed, direct-to-patient approach.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, David M. Gardner, PharmD, MSc CH&E, email david.gardner@dal.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.2731)
Editor’s ...
Brigham researchers use machine learning to improve cardiovascular risk assessment
2024-09-18
Risk calculators are used to evaluate disease risk for millions of patients, making their accuracy crucial. But when national models are adapted for local populations, they often deteriorate, losing accuracy and interpretability. Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, used advanced machine learning to increase the accuracy of a national cardiovascular risk calculator while preserving its interpretability and original risk associations. Their results showed higher accuracy overall in an electronic health records cohort ...
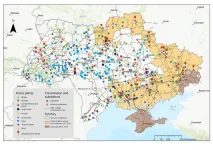
How Ukraine can rebuild its energy system
2024-09-18
One of the main targets of Russia’s ongoing attacks on Ukraine is the energy infrastructure. The extent of the destruction is enormous. “One year after the start of the war in February 2022, 76 percent of thermal power plants had been destroyed; now the figure is 95 percent,” says Ukrainian scientist Iryna Doronina. “And all the large hydroelectric power plants have also failed.” The breaching of the Kakhovka dam proved to be particularly devastating. The huge outflow of water – the reservoir ...
Research points a way to modulate scarring in spinal cord injury
2024-09-18
Media Contact: laura.kurtzman@ucsf.edu, (415) 502-6397
Subscribe to UCSF News
After a spinal cord injury, nearby cells quickly rush to action, forming protective scar tissue around the damaged area to stabilize and protect it. But over time, too much scarring can prevent nerves from regenerating, impeding the healing process and leading to permanent nerve damage, loss of sensation or paralysis.
Now, UC San Francisco researchers have discovered how a rarely studied cell type controls the formation of scar tissue in spinal cord injuries. Activating ...
Breast and ovarian cancer newly linked to thousands of gene variants
2024-09-18
Scientists have pinpointed thousands of genetic changes in a gene that may increase a person’s risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer, paving the way for better risk assessment and more personalised care.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and their collaborators focused on the ‘cancer protection’ gene RAD51C, finding over 3,000 harmful genetic changes that could potentially disrupt its function and increase ovarian cancer risk six-fold and risk of aggressive subtypes of breast ...
Metal exposure can increase cardiovascular disease risk
2024-09-18
Metal exposure from environmental pollution is associated with increased calcium buildup in the coronary arteries at a level comparable to traditional risk factors like smoking and diabetes, according to a study published today in JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology. The findings support that metals in the body are associated with the progression of plaque buildup in the arteries and potentially provide a new strategy for managing and preventing atherosclerosis.
"Our findings highlight the importance ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
[Press-News.org] Nonfatal opioid overdoses in youth spiked during pandemicMajority occurred at home, with significantly increasing trends among 12-17-year-olds