(Press-News.org) Scientists have pinpointed thousands of genetic changes in a gene that may increase a person’s risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer, paving the way for better risk assessment and more personalised care.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and their collaborators focused on the ‘cancer protection’ gene RAD51C, finding over 3,000 harmful genetic changes that could potentially disrupt its function and increase ovarian cancer risk six-fold and risk of aggressive subtypes of breast cancer four-fold. These findings were confirmed by analysing data from large-scale health databases.
The findings, published today (18 September) in Cell, are freely available so that they can be immediately used to help doctors and diagnostic laboratory scientists better assess cancer risk, especially for individuals with a family history of these cancers, reducing the uncertainty that often accompanies genetic testing.
The study also identified regions of the protein essential for its function, pointing to new roles in cancer development and potential therapeutic targets.
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK, with around 56,800 new cases every year. One in seven UK females will be diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime2. Ovarian cancer is the sixth most common cancer in females in the UK, with around 7,500 new cases every year3.
The RAD51C gene encodes a protein crucial for DNA repair. Variants in this gene that stop the protein from working are known to increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancers and rarely, if there are two harmful gene changes are present, may result in Fanconi Anaemia, a severe genetic disorder4. Women with a faulty RAD51C gene face a 15 to 30 per cent lifetime risk of developing breast cancer and a 10 to 15 per cent risk of developing ovarian cancer5.
While genetic testing is common for individuals with a strong family history of cancer, the health impacts of most RAD51C variants were previously unknown. This uncertainty over cancer risk often leaves patients and doctors struggling to determine appropriate medical care moving forward.
In this new study, researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and their collaborators set out to understand the effect of 9,188 unique changes in the RAD51C gene by artificially altering the genetic code of human cells grown in a dish, in a process known as ‘saturation genome editing’. They identified 3,094 of these variants that may disrupt the gene's function and increase cancer risk, with an accuracy above 99.9 per cent when compared to clinical data. Analysis of UK Biobank data and an ovarian cancer cohort of over 8,000 individuals further confirmed the link between these harmful RAD51C variants and cancer diagnoses.
By mapping the protein structure, the team also identified crucial surface areas of RAD51C essential for its DNA repair function. These regions may interact with other, yet-to-be-identified proteins or play a role in processes such as phosphorylation, offering valuable insights for drug development and potential new treatment targets.
The study also revealed the existence of ‘hypomorphic alleles’ – a type of variant that reduces the RAD51C gene's function without completely disabling it. These appear to be more common than previously thought and may significantly contribute to breast and ovarian cancer risk.
Rebeca Olvera-León, first author of the study at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, said: “This research demonstrates that genetic risk for breast and ovarian cancer isn't a simple yes-or-no scenario, but exists on a spectrum based on how genetic changes affect protein function. With a more comprehensive understanding of how RAD51C genetic variants contribute to cancer risk, this opens up new possibilities for more accurate risk prediction, prevention strategies, and potentially targeted therapies.”
Dr Andrew Waters, co-senior author of the study at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, said: “This work demonstrates the power of analysing genetic variants on a large scale within their genomic context. Not only can we understand how cancer-related DNA changes affect patients, helping with clinical decisions, but we can also explore how these variants impact the gene’s function at a detailed molecular level. This provides important insights into how proteins work and how genes evolve over time.”
Dr David Adams, co-senior author of the study at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, said: “The strong connection between harmful variants and cancer in large studies suggests that this approach to variant classification could be a valuable tool in personalised medicine and cancer prevention. We aim to extend this technique to many other genes, with the goal of covering the entire human genome in the next decade through the Atlas of Variant Effects.”
Professor Clare Turnbull, clinical lead of the study, Professor of Translational Cancer Genetics at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, and Consultant in Clinical Cancer Genetics at The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation, said: “These new data will be highly useful for diagnostic laboratories to better understand the RAD51C gene changes that we identify on clinical genetic testing in cancer patients and their family members. The assay data will help us to conclude which gene changes are harmful and which are innocent. This aids our decision making regarding which patients might benefit from offer of extra breast cancer screening and preventive surgery of the ovaries.”
ENDS
Contact details:
Jelena Pupavac
Press Office
Wellcome Sanger Institute
Cambridge, CB10 1SA
Email: press.office@sanger.ac.uk
Notes to Editors:
C. Hu et al. (2024) ‘Functional and Clinical Characterization of Variants of Uncertain Significance Identifies a Hotspot for Inactivating Missense Variants in RAD51C’ Cancer Research. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-2319
https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/breast-cancer
https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/ovarian-cancer
Anaemia Fanconi anaemia is rare and occurs in 1 in 160,000 individuals worldwide, and can happen when a child inherits a faulty RAD51C variant from both parents. 17 other genes have been causally associated with the development of Anaemia Fanconi. https://www.genomicseducation.hee.nhs.uk/genotes/knowledge-hub/fanconi-anaemia/
https://www.facingourrisk.org/info/hereditary-cancer-and-genetic-testing/hereditary-cancer-genes-and-risk/genes-by-name/rad51c/cancer-risk#:~:text=Women%20with%20a%20RAD51C%20mutation%20have%20about%20a%2010%2D15,to%20together%20as%20ovarian%20cancer).
Publication:
R. Olvera-León et al. (2024) ‘High-resolution functional mapping of RAD51C by saturation genome editing.’ Cell. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.08.039
Funding:
This research was supported by Wellcome and Cancer Research UK. For full funding acknowledgements, please refer to the publication.
END
Breast and ovarian cancer newly linked to thousands of gene variants
New research identifies specific genetic changes that can increase a person’s risk of breast and ovarian cancers, to help guide clinical decision-making
2024-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Metal exposure can increase cardiovascular disease risk
2024-09-18
Metal exposure from environmental pollution is associated with increased calcium buildup in the coronary arteries at a level comparable to traditional risk factors like smoking and diabetes, according to a study published today in JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology. The findings support that metals in the body are associated with the progression of plaque buildup in the arteries and potentially provide a new strategy for managing and preventing atherosclerosis.
"Our findings highlight the importance ...
Penny for your thoughts? Master copper regulator discovery may offer Alzheimer’s clues
2024-09-18
New therapeutic opportunities often emerge from research on simple organisms. For instance, the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry awarded to Emmanuelle Charpentier, Ph.D., and Jennifer Doudna, Ph.D., for their CRISPR-based DNA editing discovery began with studies using bacteria just a decade prior. Today, CRISPR therapies are approved for several disorders, and more such treatments are in the offing.
Recognizing the translational potential of studies in simpler animal models, a team of scientists led by Randy D. Blakely, ...
Keck Hospital of USC named a 2024 top performer by Vizient, Inc.
2024-09-18
LOS ANGELES — Keck Hospital of USC has been named a top performer in the 2024 Bernard A. Birnbaum, MD, Quality Leadership award by Vizient, Inc., a leading health care performance improvement company.
The top performer designation acknowledges the hospital’s excellence in delivering high-quality care as measured by the annual Vizient Quality and Accountability Study.
Keck Hospital was among 14 top performers out of 115 comprehensive academic medical centers nationally and achieved a five-star ...
NSF and Simons Foundation launch 2 AI Institutes to help astronomers understand the cosmos
2024-09-18
Note: Embargoed until 8:00 a.m. ET on Sept. 18, 2024
From the early telescopes made hundreds of years ago by Galileo to the sophisticated astronomical observatories of today, people have built increasingly innovative tools to probe and measure the cosmos. Soon, researchers at two new institutes funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and the Simons Foundation will build a new breed of astronomical tools by harnessing the uniquely powerful abilities of artificial intelligence to assist and accelerate humanity's understanding of the universe.
The new National Artificial Intelligence ...
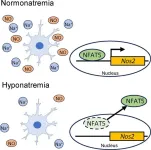
Exploring the effect of low sodium concentrations on brain microglial cells
2024-09-18
Low serum sodium concentrations in blood are called hyponatremia, a prevalent clinical electrolyte disorder. In contrast to acute hyponatremia, chronic hyponatremia has been previously considered asymptomatic because the brain can successfully adapt to hyponatremia. If not treated, chronic hyponatremia can lead to complications such as fractures, falls, memory impairment, and other mental issues. Treating the chronic condition is, however, quite tricky as it has been observed that overly rapid correction of hyponatremia ...
New Alzheimer’s studies reveal disease biology, risk for progression, and the potential for a novel blood test
2024-09-18
EMBARGOED by Alzheimer’s & Dementia until 7 a.m., ET, Sept. 18, 2024
Contact: Gina DiGravio, Boston University, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
Contact: Andrea Zeek, IU School of Medicine, 317-671-3114, anzeek@iu.edu
(Boston)— The failure to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease, the most common form of dementia in the elderly, at an early stage of molecular pathology is considered a major reason why treatments fail in clinical trials. Previous research to molecularly diagnose Alzheimer’s disease yielded "A/T/N" central biomarkers based on the measurements of proteins, β-amyloid (“A”) and tau (“T”), ...
Comorbidity and disease activity in multiple sclerosis
2024-09-18
About The Study: In this study, a higher burden of comorbidity was associated with worse clinical outcomes in people with multiple sclerosis (MS), although comorbidity could potentially be a partial mediator of other negative prognostic factors. The findings suggest a substantial adverse association of the comorbidities investigated with MS disease activity and that prevention and management of comorbidities should be a pressing concern in clinical practice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Amber Salter, PhD, email amber.salter@utsouthwestern.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
£18 million for DARE UK to support secure research on sensitive data
2024-09-18
London, United Kingdom, 18 September 2024 – UK Research and Innovation (UKRI), the UK’s largest public funder of research, has confirmed funding for a new phase of the DARE UK (Data and Analytics Research Environments UK) programme with up to £18.2 million made available over 2.5 years.
Starting this month, Phase 2 of the DARE UK programme will bring together Trusted Research Environments (TREs) across the UK to test and build new capabilities for a connected national network of secure data ...
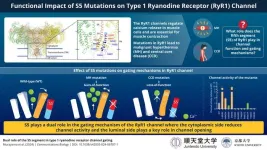
New study unveils the impact of mutations in the calcium release channel on muscle diseases
2024-09-18
The type 1 ryanodine receptor (RyR1) is an important calcium release channel in skeletal muscles essential for muscle contraction. It mediates calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a calcium-storing organelle in muscle cells, a process vital for muscle function. Mutations in the RyR1 gene can affect the channel's function in extremely contrasting ways leading to severe muscle diseases such as malignant hyperthermia (MH) and central core disease (CCD). MH is an inherited disease that causes high fever and muscle contractures in response to inhalational anesthetics in patients with gain-of-function RyR1 variants. CCD is one ...
Scientists quantify energetic costs of the migratory lifestyle in a free flying songbird
2024-09-18
Millions of birds migrate every year to escape winter, but spending time in a warmer climate does not save them energy, according to research by the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior (MPI-AB). Using miniaturized loggers implanted in wild blackbirds, scientists recorded detailed measurements of heart rate and body temperature from birds every 30 minutes from fall to the following spring—the first time the physiology of free flying birds has been quantified continuously at this scale over the entire wintering period. The data offer unprecedented insights into the true energetic costs of migrant and resident strategies and reveal a previously unknown mechanism used by migrants to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Breast and ovarian cancer newly linked to thousands of gene variantsNew research identifies specific genetic changes that can increase a person’s risk of breast and ovarian cancers, to help guide clinical decision-making