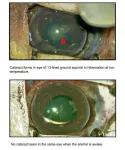
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their collaborators have identified a protein, known as RNF114, that reverses cataracts, a clouding of the eye’s lens that occurs commonly in people as they age. The study, which was conducted in the 13-lined ground squirrel and rats, may represent a possible surgery-free strategy for managing cataracts, a common cause of vision loss. The study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“Scientists have long searched for an alternative to cataract surgery, which is effective, but not without risk. Lack of access to cataract surgery is a barrier to care in some parts of the world, causing untreated cataracts to be a leading cause of blindness worldwide,” said Xingchao Shentu, M.D., a cataract surgeon and the co-lead investigator from Zhejiang University, China.
This new discovery was part of ongoing research at NIH’s National Eye Institute (NEI) involving a mammalian hibernator, the 13-lined ground squirrel. In these ground squirrels, the light-sensitive photoreceptor cells in the retina are mostly cones, which makes the ground squirrel helpful for studying cone-related properties, such as color vision. In addition, the squirrel’s ability to withstand months of cold and metabolic stress during hibernation make it model for vision scientists to study a range of eye diseases.
Researchers learned that during hibernation, the ground squirrel’s lenses became cloudy at around 4 degrees Celsius but quickly turned transparent after rewarming. By comparison, non-hibernators (rats in this study) developed cataracts at low temperatures, but they did not resolve with rewarming.
Cataract formation in hibernating animals exposed to low temperatures is likely a cellular response to cold stress and is one of many changes their bodies undergo as their tissues adapt to freezing temperatures and metabolic stress. Humans do not develop cataracts when exposed to low temperatures.
“Understanding the molecular drivers of this reversible cataract phenomenon might point us in a direction toward a potential treatment strategy,” said the study’s co-lead investigator, Wei Li, Ph.D., senior investigator in the NEI Retinal Neurophysiology Section.
The main job of the lens is to focus light onto the retina at the back of the eye. As we age, cataracts form when proteins in the lens start misfolding and forming clusters that block, scatter, and distort light as it passes through the lens. For reasons that are not clear, aging can disrupt protein homeostasis—a process that maintains the balance of newly made proteins and the turnover of old proteins.
To explore the ground squirrel’s reversible cataracts at the molecular level, the team developed a lab-based, lens-in-a-dish model using stem cells engineered from ground squirrel cells by the Li Lab at NEI. Using this platform, the researchers zeroed in on a part of an extensive network that maintains protein homeostasis in part by breaking down old proteins, known as the ubiquitin proteasome system.
Specifically, RNF114 was significantly elevated during rewarming in the ground squirrel, compared with the non-hibernating rat. RNF114 had previously been shown to help identify old proteins and facilitate their degradation.
To look further at RNF114’s effect, they again used a non-hibernator (rat) cataract model by incubating its lenses at 4 degrees Celsius. Normally, such cataracts would not resolve with rewarming. However, when the lenses were pretreated with RNF114, there was a rapid clearing of the cataract upon rewarming.
According to the scientific team, these findings are proof-of-principle that it is possible to induce cataract clearance in animals. In future studies, the process will need to be fine-tuned so scientists can stimulate specific protein degradation to see how to precisely regulate protein stability and turnover. This mechanism is also an important factor in many neurodegenerative diseases, they said.
The research was supported by the NEI Intramural Research Program and was conducted in collaboration with researchers at Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China.
For more information, visit the NEI website on cataracts.
Reference:
Yang H, Ping X, Zhou J, Ailifeire H, Wu J, Nicolas-Nada F, Miyagishima KJ, Bao J, Huang Y, Cui Y, Xing X, Wang S, Yao K, Li W, Shentu X. “Reversible cold-induced lens opacity in a hibernator reveals a molecular target for treating cataracts”. Published online Sept. 17, 2024 in JCI. doi: 10.1172/JCI169666
This press release describes a basic research finding. Basic research increases our understanding of human behavior and biology, which is foundational to advancing new and better ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat disease. Science is an unpredictable and incremental process— each research advance builds on past discoveries, often in unexpected ways. Most clinical advances would not be possible without the knowledge of fundamental basic research. To learn more about basic research, visit https://www.nih.gov/news-events/basic-research-digital-media-kit.
NEI leads the federal government’s efforts to eliminate vision loss and improve quality of life through vision research…driving innovation, fostering collaboration, expanding the vision workforce, and educating the public and key stakeholders. NEI supports basic and clinical science programs to develop sight-saving treatments and to broaden opportunities for people with vision impairment. For more information, visit https://www.nei.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit https://www.nih.gov/.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
END
NIH-led studies point to potential development of a cataract drug
Findings in animals suggest a surgery-free treatment for cataracts
2024-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Artificial intelligence grunt work can be outsourced using a new blockchain-based framework developed by Concordians
2024-09-18
Tomorrow’s workplace will be run on mind-boggling amounts of data. To make sense of it all, businesses, developers and individuals will need better artificial intelligence (AI) systems, better trained AI workers and more efficient number-crunching servers.
While big tech companies have the resources and expertise to meet these demands, they remain beyond the reach of most small and medium-sized enterprises and individuals. To respond to this need, a Concordia-led international team of researchers has developed a new framework to make complex AI tasks more accessible ...
Mental health challenges faced by children with cystic fibrosis are the focus of a major, multisite study led by UB
2024-09-18
BUFFALO, N.Y. — A University at Buffalo psychiatrist who has played a critical role in getting mental health screening and treatment integrated into routine care for adults and adolescents with cystic fibrosis (CF) has been awarded $3 million from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation to focus on the mental health of children with the disease.
Led by UB and launched this summer, the new study is an outgrowth of The International Depression Epidemiological Study (TIDES), which began in 2014 and was the largest study of mental health in adolescents and adults with CF. As a result of TIDES, ...
UC3M and Universia obtain an ENIA Chair in artificial intelligence in data economy
2024-09-18
The Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) is one of 22 institutions that have been selected by the Ministry for Digital Transformation and the Civil Service to create an ENIA Chair to further the development of artificial intelligence (AI)-based applications. The AImpulsa UC3M-Universia Chair, as it is called, will be the only one of its kind in Spain in the area of Data Economy and will collaborate with Universia-Banco Santander, through Santander Universities.
The ENIA Chairs' objectives, which depend on the Secretary of State for Digitalisation and Artificial Intelligence of the Ministry for Digital Transformation and ...
Why petting your cat leads to static electricity
2024-09-18
Anyone who has ever pet a cat or shuffled their feet across the carpet knows that rubbing objects together generates static electricity. But an explanation for this phenomenon has eluded researchers for more than two millennia.
Now, Northwestern University scientists have finally uncovered the mechanics at play.
When an object slides, the front and back parts of that object experience different forces, researchers found. This difference in forces causes different electrical charges to build up on the front and back parts of the object. And the difference in electrical charges creates a current, leading to a light zap.
The study was published yesterday (Sept. 17) in the journal ...
UC San Diego Health maintains top quality care status by Vizient
2024-09-18
UC San Diego Health has been honored as a top performer for Vizient’s 2024 Bernard A. Birnbaum, MD, Quality Leadership Performance Award, marking the sixth consecutive year the health system has achieved this prominent distinction. This award places UC San Diego Health among the top academic medical centers in the nation, highlighting its exceptional commitment to delivering high-quality, patient-centered care. This sustained excellence recognizes the region’s only academic medical center’s mission of advancing health care standards and outcomes at the highest level.
“Being named a Vizient top performer for the sixth year in a row underscores ...
If you build it, will they come? Wildlife corridors need smarter design
2024-09-18
As human population and development continue to expand, it’s more important than ever to set aside corridors of undeveloped land where wildlife can travel safely, helping to ensure their long-term survival. However, a recent study by the University of Maryland reveals that current methods of designing and evaluating wildlife corridors may not be adequate to ensure wildlife protection, and suggests that Best Management Practices should include analyzing corridors with a smarter and more thorough framework. University researchers tested different ...
Sea surface temperature record in the southwestern Pacific: Coral colony from Fiji reveals warmest temperatures in over 600 years
2024-09-18
The sea surface temperature in the Fijian archipelago in the southwestern Pacific is now at its maximum for more than 600 years. This is the result of an international research team's evaluation of a new coral record providing further evidence for unprecedented warming in the western Pacific Ocean. According to this, the year 2022 was the warmest year in the region since 1370. The scientists used the giant coral Diploastrea heliopora colony in Fiji to obtain the data for the new reconstruction. These unique and long-lived massive corals record long-term climatic and ...
Homemade ‘play-putty’ can read the body’s electric signals, find UMass researchers
2024-09-18
AMHERST, Mass. – A new study by University of Massachusetts Amherst researchers demonstrates the effectiveness of homemade play putty at reading brain, heart, muscle and eye activity. Published in Device, the research outlines the conductive properties of this material, so-named “squishy circuits.”
“[Squishy circuits] are literally child’s play putty, that is also conductive” describes Dmitry Kireev, assistant professor of biomedical engineering and senior author on the paper.
The conductive squishy ...
Magnifying deep space through the “carousel lens”
2024-09-18
In a rare and extraordinary discovery, researchers have identified a unique configuration of galaxies that form the most exquisitely aligned gravitational lens found to date. The Carousel Lens is a massive cluster-scale gravitational lens system that will enable researchers to delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos, including dark matter and dark energy.
“This is an amazingly lucky ‘galactic line-up’ – a chance alignment of multiple galaxies across a line-of-sight spanning most of the observable universe,” said David Schlegel, a co-author of the study and a senior scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Physics Division. "Finding one such alignment is ...
Another new wasp species discovered by researchers Rice campus
2024-09-18
A newly identified wasp species, Chrysonotomyia susbelli, has been discovered in Houston, Texas, marking the 18th new species identified by Rice University’s Scott Egan and his research team since 2014. The discovery, the fourth wasp species found on the university grounds in seven years, reveals the hidden world of parasitoid wasps and the intricate ecosystems that thrive outside our doors.
The Chrysonotomyia susbelli is a parasitoid wasp, about 1 millimeter long, that emerges from galls, or tumorlike growths created by the gall wasp Neuroterus bussae found on southern live oak leaves. The galls serve as microhabitats within which larvae feed, develop and pupate. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] NIH-led studies point to potential development of a cataract drugFindings in animals suggest a surgery-free treatment for cataracts