(Press-News.org)
Anyone who has ever pet a cat or shuffled their feet across the carpet knows that rubbing objects together generates static electricity. But an explanation for this phenomenon has eluded researchers for more than two millennia.
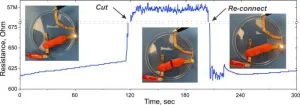
Now, Northwestern University scientists have finally uncovered the mechanics at play.
When an object slides, the front and back parts of that object experience different forces, researchers found. This difference in forces causes different electrical charges to build up on the front and back parts of the object. And the difference in electrical charges creates a current, leading to a light zap.
The study was published yesterday (Sept. 17) in the journal Nano Letters.
“For the first time, we are able to explain a mystery that nobody could before: why rubbing matters,” said Northwestern’s Laurence Marks, who led the study. “People have tried, but they could not explain experimental results without making assumptions that were not justified or justifiable. We now can, and the answer is surprisingly simple. Just having different deformations — and therefore different charges — at the front and back of something sliding leads to current.”
An expert in surface structures, Marks is a professor emeritus of materials science and engineering at Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering. Karl Olson, a Ph.D. student in Marks’ research group, is the paper’s first author.
Greek philosopher Thales of Miletus first reported friction-induced static electricity in 600 B.C. After rubbing amber with fur, he noticed the fur attracted dust.
“Since then, it has become clear that rubbing induces static charging in all insulators — not just fur,” Marks said. “However, this is more or less where the scientific consensus ended.”
Marks and his team started to unravel the mystery in 2019. In a study published in Physical Review Letters, they reported that rubbing two materials together bends tiny protrusions on the surfaces of those materials. Those bent, deformed protrusions give rise to voltages, the researchers found.
“In 2019, we had the seed of what was going on. However, like all seeds, it needed time to grow,” Marks said. “Now, it has blossomed. We developed a new model that calculates electrical current. The values for the current for a range of different cases were in good agreement with experimental results.”
A concept called “elastic shear” lies at the heart of the new model. Elastic shear can occur when a material resists a sliding force. If a person pushes a plate across a table, the plate will resist sliding. As soon as the person stops pushing it, the plate stops moving. This added friction — caused by the resistance to sliding — causes electrical charges to move.
“Sliding and shear are intimately connected,” Marks said.
Although static electricity can cause funny mishaps, like hair standing on end after going down a playground slide, it also can lead to serious problems. For example, sparks from static electricity cause industrial fires and even explosions. It also can hinder consistent dosing for powdered pharmaceuticals. With a better understanding of the mechanisms at play, researchers potentially could introduce new solutions to these issues.
“Static electricity affects life in both simple and profound ways,” Marks said. “Charging grains with static electricity has a major influence on how coffee beans are ground and taste. The Earth would probably not be a planet without a key step in the clumping of particles that form planets, which occurs because of the static electricity generated by colliding grains. It’s amazing how much of our lives are touched by static electricity and how much of the universe depends on it.”
The study, “What puts the ‘tribo’ in triboelectricity,” was supported by Northwestern Engineering.
END
UC San Diego Health has been honored as a top performer for Vizient’s 2024 Bernard A. Birnbaum, MD, Quality Leadership Performance Award, marking the sixth consecutive year the health system has achieved this prominent distinction. This award places UC San Diego Health among the top academic medical centers in the nation, highlighting its exceptional commitment to delivering high-quality, patient-centered care. This sustained excellence recognizes the region’s only academic medical center’s mission of advancing health care standards and outcomes at the highest level.
“Being named a Vizient top performer for the sixth year in a row underscores ...
As human population and development continue to expand, it’s more important than ever to set aside corridors of undeveloped land where wildlife can travel safely, helping to ensure their long-term survival. However, a recent study by the University of Maryland reveals that current methods of designing and evaluating wildlife corridors may not be adequate to ensure wildlife protection, and suggests that Best Management Practices should include analyzing corridors with a smarter and more thorough framework. University researchers tested different ...
The sea surface temperature in the Fijian archipelago in the southwestern Pacific is now at its maximum for more than 600 years. This is the result of an international research team's evaluation of a new coral record providing further evidence for unprecedented warming in the western Pacific Ocean. According to this, the year 2022 was the warmest year in the region since 1370. The scientists used the giant coral Diploastrea heliopora colony in Fiji to obtain the data for the new reconstruction. These unique and long-lived massive corals record long-term climatic and ...
AMHERST, Mass. – A new study by University of Massachusetts Amherst researchers demonstrates the effectiveness of homemade play putty at reading brain, heart, muscle and eye activity. Published in Device, the research outlines the conductive properties of this material, so-named “squishy circuits.”
“[Squishy circuits] are literally child’s play putty, that is also conductive” describes Dmitry Kireev, assistant professor of biomedical engineering and senior author on the paper.
The conductive squishy ...
In a rare and extraordinary discovery, researchers have identified a unique configuration of galaxies that form the most exquisitely aligned gravitational lens found to date. The Carousel Lens is a massive cluster-scale gravitational lens system that will enable researchers to delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos, including dark matter and dark energy.
“This is an amazingly lucky ‘galactic line-up’ – a chance alignment of multiple galaxies across a line-of-sight spanning most of the observable universe,” said David Schlegel, a co-author of the study and a senior scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Physics Division. "Finding one such alignment is ...
A newly identified wasp species, Chrysonotomyia susbelli, has been discovered in Houston, Texas, marking the 18th new species identified by Rice University’s Scott Egan and his research team since 2014. The discovery, the fourth wasp species found on the university grounds in seven years, reveals the hidden world of parasitoid wasps and the intricate ecosystems that thrive outside our doors.
The Chrysonotomyia susbelli is a parasitoid wasp, about 1 millimeter long, that emerges from galls, or tumorlike growths created by the gall wasp Neuroterus bussae found on southern live oak leaves. The galls serve as microhabitats within which larvae feed, develop and pupate. ...
Researchers have achieved a groundbreaking advancement in plant biotechnology by using a magnetofected pollen gene delivery system to genetically transform cucumbers. This cutting-edge method uses DNA-coated magnetic nanoparticles to introduce foreign genes into pollen, producing genetically modified seeds without the need for traditional tissue culture or regeneration steps. This technique significantly streamlines and accelerates crop genetic modification, opening up new avenues to boost agricultural productivity and resilience.
Genetic modification in horticultural crops, particularly within the Cucurbitaceae family, is often hindered by complex tissue culture requirements and ...
Some of the greatest discoveries don’t come merely from observations but from thinking. Einstein developed theories about relativity through thought experiments, and Galileo derived insights about gravity through mental simulations. A review published September 18 in the journal Trends in Cognitive Sciences shows that this process of thinking is not exclusive to humans. Artificial intelligence, too, is capable of self-correction and arriving at new conclusions through “learning by thinking.”
“There are some recent demonstrations of what looks like learning by thinking in AI, ...
In an opinion article publishing September 18 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Molecular Medicine, physician-scientists argue that with most placentas discarded after birth, placental pathology is underutilized clinically, should be a routine part of obstetric and neonatal care, and also deserves more research attention.
“Placentas should not be considered a waste tissue,” says senior author Mana Parast, MD, PhD, professor of pathology at University of California San Diego School of Medicine. ...
Drug overdose mortality has risen faster among adolescents than the general population in recent years, largely due to fentanyl, a potent opioid pain medication. A new study published in JAMA sheds light on trends in nonfatal opioid overdoses in youth – an area that was not as well characterized, but key to formulating prevention strategies to save lives.
Researchers from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and colleagues analyzed data using Emergency Medical Services (EMS) encounters from January 2018 to December 2022. They found that opioid overdoses in youth increased at pandemic onset and remained elevated compared to pre-pandemic levels. The majority ...