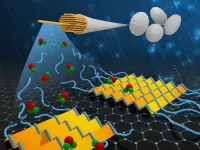
(Press-News.org) Stuttgart – Scientists at the Max-Planck-Institute for Intelligent Systems (MPI-IS) have developed hexagon-shaped robotic components, called modules, that can be snapped together LEGO-style into high-speed robots that can be rearranged for different capabilities. The team of researchers from the Robotic Materials Department at MPI-IS, led by Christoph Keplinger, integrated artificial muscles into hexagonal exoskeletons that are embedded with magnets, allowing for quick mechanical and electrical connections. The team’s work, “Hexagonal electrohydraulic modules for rapidly reconfigurable high-speed robots” will be published in Science Robotics on September 18, 2024.
Six lightweight rigid plates made from glass fiber serve as the exoskeleton of each HEXEL module. The inner joints of the hexagons are driven by hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic (HASEL) artificial muscles. Applying a high voltage to the module causes the muscle to activate, rotating the joints of the hexagon and changing its shape from long and narrow to wide and flat.
“Combining soft and rigid components in this way enables high strokes and high speeds. By connecting several modules, we can create new robot geometries and repurpose them for changing needs”, says Ellen Rumley, a visiting researcher from the University of Colorado Boulder. She and Zachary Yoder, who are both Ph.D. students working in the Robotic Materials Department, are co-first authors of the publication.
In a video, the team shows the many behaviors that can be created with HEXEL modules. A group of modules crawls through a narrow gap, while a single module actuates so fast that it can leap into the air. Multiple modules are connected into larger structures that produce different motions depending on how the modules are attached. For instance, the team combined several modules into a robot which rapidly rolls.
“In general, it makes a lot of sense to develop robots with reconfigurable capabilities. It’s a sustainable design option – instead of buying five different robots for five different purposes, we can build many different robots by using the same components. Robots made from reconfigurable modules could be rearranged on demand to provide more versatility than specialized systems, which could be beneficial in resource-limited environments'', Yoder concludes.
Reference:
Zachary Yoder†, Ellen H. Rumley†, Ingemar Schmidt, Philipp Rothemund, Christoph Keplinger*, Hexagonal electrohydraulic modules for rapidly reconfigurable high-speed robots. Sci. Robot. (2024). DOI:10.1126/scirobotics.adl3546
†Equal contribution
*Corresponding author
END
Hexagonal electrohydraulic modules shape-shift into versatile robots
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart combined soft artificial muscles with a rigid, magnetic exoskeleton to create building blocks for fast-moving reconfigurable robots
2024-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Flexible circuits made with silk and graphene on the horizon
2024-09-18
RICHLAND, Wash.—After thousands of years as a highly valuable commodity, silk continues to surprise. Now it may help usher in a whole new direction for microelectronics and computing.
While silk protein has been deployed in designer electronics, its use is currently limited in part because silk fibers are a messy tangle of spaghetti-like strands.
Now, a research team led by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory has tamed the tangle. They report in the journal ...
Scott Emr and Wesley Sundquist awarded 2024 Horwitz Prize for discovering the ESCRT pathway
2024-09-18
NEW YORK, NY (September 18, 2024)—Columbia University will award the 2024 Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize to Scott Emr and Wesley Sundquist for discovering the ESCRT (Endosomal Sorting Complexes Required for Transport) pathway and revealing how it works.
ESCRT (pronounced “escort”) complexes deform the cell membrane and bend parts of it away from the cytoplasm, the space that houses all material inside a cell. This unique process plays an essential role in keeping cells healthy by packaging and sorting molecules, removing waste, and regulating important functions such as cell division, neuron remodeling, ...
Versatile knee exo for safer lifting
2024-09-18
Images
A set of knee exoskeletons, built with commercially available knee braces and drone motors at the University of Michigan, has been shown to help counteract fatigue in lifting and carrying tasks. They helped users maintain better lifting posture even when tired, a key factor in defending against on-the-job injuries, the researchers say.
"Rather than directly bracing the back and giving up on proper lifting form, we strengthen the legs to maintain it," said Robert Gregg, U-M professor of robotics and corresponding author of the study in Science Robotics. "This differs from what's more commonly done in industry."
Already ...
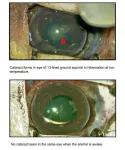
NIH-led studies point to potential development of a cataract drug
2024-09-18
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their collaborators have identified a protein, known as RNF114, that reverses cataracts, a clouding of the eye’s lens that occurs commonly in people as they age. The study, which was conducted in the 13-lined ground squirrel and rats, may represent a possible surgery-free strategy for managing cataracts, a common cause of vision loss. The study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“Scientists have long searched for an alternative to cataract surgery, which is effective, but not without risk. Lack of access to cataract surgery is a barrier to care in some ...
Artificial intelligence grunt work can be outsourced using a new blockchain-based framework developed by Concordians
2024-09-18
Tomorrow’s workplace will be run on mind-boggling amounts of data. To make sense of it all, businesses, developers and individuals will need better artificial intelligence (AI) systems, better trained AI workers and more efficient number-crunching servers.
While big tech companies have the resources and expertise to meet these demands, they remain beyond the reach of most small and medium-sized enterprises and individuals. To respond to this need, a Concordia-led international team of researchers has developed a new framework to make complex AI tasks more accessible ...
Mental health challenges faced by children with cystic fibrosis are the focus of a major, multisite study led by UB
2024-09-18
BUFFALO, N.Y. — A University at Buffalo psychiatrist who has played a critical role in getting mental health screening and treatment integrated into routine care for adults and adolescents with cystic fibrosis (CF) has been awarded $3 million from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation to focus on the mental health of children with the disease.
Led by UB and launched this summer, the new study is an outgrowth of The International Depression Epidemiological Study (TIDES), which began in 2014 and was the largest study of mental health in adolescents and adults with CF. As a result of TIDES, ...
UC3M and Universia obtain an ENIA Chair in artificial intelligence in data economy
2024-09-18
The Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) is one of 22 institutions that have been selected by the Ministry for Digital Transformation and the Civil Service to create an ENIA Chair to further the development of artificial intelligence (AI)-based applications. The AImpulsa UC3M-Universia Chair, as it is called, will be the only one of its kind in Spain in the area of Data Economy and will collaborate with Universia-Banco Santander, through Santander Universities.
The ENIA Chairs' objectives, which depend on the Secretary of State for Digitalisation and Artificial Intelligence of the Ministry for Digital Transformation and ...
Why petting your cat leads to static electricity
2024-09-18
Anyone who has ever pet a cat or shuffled their feet across the carpet knows that rubbing objects together generates static electricity. But an explanation for this phenomenon has eluded researchers for more than two millennia.
Now, Northwestern University scientists have finally uncovered the mechanics at play.
When an object slides, the front and back parts of that object experience different forces, researchers found. This difference in forces causes different electrical charges to build up on the front and back parts of the object. And the difference in electrical charges creates a current, leading to a light zap.
The study was published yesterday (Sept. 17) in the journal ...
UC San Diego Health maintains top quality care status by Vizient
2024-09-18
UC San Diego Health has been honored as a top performer for Vizient’s 2024 Bernard A. Birnbaum, MD, Quality Leadership Performance Award, marking the sixth consecutive year the health system has achieved this prominent distinction. This award places UC San Diego Health among the top academic medical centers in the nation, highlighting its exceptional commitment to delivering high-quality, patient-centered care. This sustained excellence recognizes the region’s only academic medical center’s mission of advancing health care standards and outcomes at the highest level.
“Being named a Vizient top performer for the sixth year in a row underscores ...
If you build it, will they come? Wildlife corridors need smarter design
2024-09-18
As human population and development continue to expand, it’s more important than ever to set aside corridors of undeveloped land where wildlife can travel safely, helping to ensure their long-term survival. However, a recent study by the University of Maryland reveals that current methods of designing and evaluating wildlife corridors may not be adequate to ensure wildlife protection, and suggests that Best Management Practices should include analyzing corridors with a smarter and more thorough framework. University researchers tested different ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Hexagonal electrohydraulic modules shape-shift into versatile robotsResearchers at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart combined soft artificial muscles with a rigid, magnetic exoskeleton to create building blocks for fast-moving reconfigurable robots