(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Sept. 20, 2024 – Within the cycling realm, “to Everest” involves riding up and down the same mountain until your ascents total the elevation of Mt. Everest — 8,848 meters.
After a new cycling “Everesting” record was set a few years ago, a debate ensued on social media about the strong tailwind the cyclist had on climbs — 5.5 meters per second (20 kilometers per hour or 12 miles per hour) — when he set the record. To what extent did the tailwind help him? Should limits be set on the allowed windspeed?
Martin Bier, a physics professor at East Carolina University in North Carolina, became intrigued by this debate and decided to explore the physics, and a little project ensued. In the American Journal of Physics, from AIP Publishing, he shares his finding that, ultimately, the wind turns out to be of negligible consequence.
First, a little background: From a physics perspective, cycling is easier to comprehend than running. “In running, the motion of the legs is repeatedly accelerated and decelerated, and the runner’s center of mass moves up and down,” said Bier. “Cycling uses ‘rolling,’ which is much smoother and faster, and more efficient — all of the work is purely against gravity and friction.”
But there’s something odd about air resistance. The force of air friction you fight goes up with the square of your speed. If air resistance is the main thing limiting your speed — which is true for a cyclist on flat ground or going downhill — then to double your speed, you need four times the force. Tripling your speed requires nine times as much force. But, on the other hand, when cycling uphill, your speed is much slower, so air resistance isn’t a big factor.
“When you’re riding up a hill and fighting gravity, doubling your power input means doubling your speed. In bike races, attacks occur on climbs because it’s where your extra effort gets you a bigger gap.”
On a solo Everesting effort, calculations are straightforward. A rider isn’t getting an aerodynamic draft from another rider ahead of them. The inputs are simply watts, gravity, and resistance.
“Naively, you may think that a strong tailwind can compensate for an uphill slope,” said Bier. “You then ride up the hill as if it’s a flat road, and on the way down the headwind and downward slope balance out and again give you the feel of a flat road. But it doesn’t work — the square I mentioned earlier wreaks havoc!”
His work shows the tailwind may help a little on the climb, but most of the work on the way up is the fight against gravity. The subsequent descent is fast and lasts a much shorter time, while the headwind there actually has a huge effect. And the speed on a descent is high — about 80 kph (49.7 mph).
“Air resistance goes with the square of the speed, which leads to the headwind on the descent and causes a big reduction in speed,” Bier said. “The wind boost on the ascent is canceled out.”
The obvious implication of Bier’s work is there’s no point in waiting for the ideal wind if you want to improve your Everesting time. “There are no easy tricks,” he said. “If you want to be a better Everester, you need to lose weight and generate more watts (exercise). This is what matters — there’s no way around it.”
###
The article “The physics of ‘Everesting’ on a bicycle” is authored by Martin Bier. It will appear in the American Journal of Physics on Sept. 20, 2024 (DOI: 10.1119/5.0131679). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1119/5.0131679.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
The American Journal of Physics is devoted to the instructional and cultural aspects of physics. The journal informs physics education globally with member subscriptions, institutional subscriptions, such as libraries and physics departments, and consortia agreements. It is geared to an advanced audience, primarily at the college level. Contents include novel approaches to laboratory and classroom instruction, insightful articles on topics in classical and modern physics, apparatus, and demonstration notes, historical or cultural topics, resource letters, research in physics education, and book reviews. See https://pubs.aip.org/aapt/ajp.
###
END
What role does a tailwind play in cycling’s ‘Everesting’?
Physics reveals a tailwind doesn’t help as much as you might think — it’s negligible.
2024-09-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Projections of extreme temperature–related deaths in the US
2024-09-20
About The Study: This cross-sectional study found that extreme temperature–related deaths in the contiguous U.S. were projected to increase substantially by mid–21st century, with certain populations, such as non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic adults, projected to disproportionately experience this increase. The results point to the need to mitigate the adverse outcome of extreme temperatures for population health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sameed Ahmed M. Khatana, MD, MPH, ...
Wearable device–based intervention for promoting patient physical activity after lung cancer surgery
2024-09-20
About The Study: In this nonrandomized clinical trial, integration of perioperative exercise interventions using wearable devices improved physical activity (especially moderate-to-vigorous physical activity) and dyspnea at 6 months after lung cancer surgery compared with usual care. This finding suggests a promising role for wearable devices in personalizing perioperative rehabilitation strategies.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Danbee Kang, PhD, (dbee.kang@gmail.com) and Hye Yun Park, MD, (hyeyunpark@skku.edu).
To access ...
Self-compassion is related to better mental health among Syrian refugees
2024-09-20
Displaced individuals experience high rates of emotional distress, depression and anxiety resulting from trauma and stress from displacement and loss. Their mental health may suffer further due to a lack of resources, language barriers, and discrimination during resettlement.
A new study by University of California San Diego researchers reports that displaced Syrian refugees with higher reported self-compassion were less likely to report poor mental health outcomes. The study was published in PLOS ONE on September 19, 2024.
Sarah Alsamman, a student at UC San Diego School of Medicine, and Wael Al-Delaimy, M.D., Ph.D., professor of public health at the Herbert Wertheim School of Public ...
Microplastics found in coral skeletons
2024-09-20
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers from Japan and Thailand investigating microplastics in coral have found that all three parts of the coral anatomy—surface mucus, tissue, and skeleton—contain microplastics. The findings were made possible thanks to a new microplastic detection technique developed by the team and applied to coral for the first time.
These findings may also explain the ‘missing plastic problem’ that has puzzled scientists, where about 70% of the plastic litter that has entered the oceans cannot be found. The team hypothesizes ...
Stroke rates increasing in individuals living with SCD despite treatment guidelines
2024-09-20
(WASHINGTON, September 20, 2024) –The incidence of stroke continues to increase for adults and children living with sickle cell disease (SCD) despite the Stroke Prevention Trial in Sickle Cell Anemia (STOP) establishing standards of care like transfusions and tests to measure blood flow in the brain for those deemed high-risk, according to a study published today in Blood.
Individuals living with SCD, the most common inherited red blood cell disorder in the United States, are especially susceptible to cerebrovascular events (CVEs). This includes ischemic or hemorrhagic strokes, when a blood vessel leading to the brain is ...
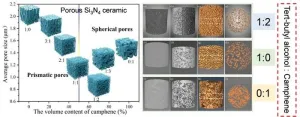
Synergistic promotion of dielectric and thermomechanical properties of porous Si3N4 ceramics by a dual-solvent template method
2024-09-20
Radomes and wave-transmitting antenna windows are critical structural components in aircraft, protecting radar antennas from external interference while ensuring reliable communication. Currently, the most widely used wave-transmitting materials are ceramics based on oxides and nitrides. Si3N4 ceramics, with their high melting point and superior mechanical properties, are considered promising candidates for hypersonic vehicle applications. However, the dielectric and thermal insulation properties of dense Si3N4 ceramics need improvement to meet the precise guidance and thermal protection demands of high-speed flight. By adjusting the microstructure, it is possible to enhance the ...
Korean research team proposes AI-powered approach to establishing a 'carbon-neutral energy city’
2024-09-20
A joint research team from the Renewable Energy System Laboratory and the Energy ICT Research Department at the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) has developed key technologies to realize "Urban Electrification" using artificial intelligence (AI).
Urban electrification aims to reduce the use of fossil fuels and introduce renewable energy sources, such as building-integrated solar technology, to transform urban energy systems. While this concept is relatively unfamiliar in the Republic of Korea, it is being promoted as a key strategy in the U.S. and Europe for achieving carbon neutrality and creating sustainable urban environments.
In ...
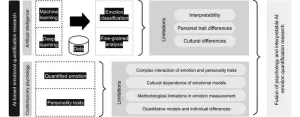
AI is learning to read your emotions, and here’s why that can be a good thing
2024-09-20
Using a fusion of traditional and novel technological methods, researchers are hoping to better quantify emotions to transform the face of the emotion quantification field
Human emotions are complex and are not always easily able to be boiled down to a recognizable pattern. Determining one’s emotional state can be difficult human-to-human, and the many nuances of existence as an emotional entity seem impossible to train a non-human entity to understand, identify and learn from. However, a considerable amount of work and research has been put into training artificial intelligence (AI) to observe, quantify and recognize various states of emotion in humans. ...
Antidepressant shows promise for treating brain tumors
2024-09-20
Key points:
Glioblastoma is an incurable and fatal type of brain cancer.
In a large-scale drug screening, the antidepressant, vortioxetine emerged as one of the most effective agents against these types of cancer cells.
Clinical trials are already in the planning phase at the University Hospital Zurich.
Glioblastoma is a particularly aggressive brain tumour that at present is incurable. Cancer doctors can extend patients’ life expectancy through operations, radiation, chemotherapy or surgical interventions. Nevertheless, half of patients die within twelve months of diagnosis.
Drugs that are effective against brain tumours are ...
European Green Deal: a double-edged sword for global emissions
2024-09-20
The European Union aims to be carbon-neutral by 2050 as part of the comprehensive Green Deal that was agreed upon four years ago. However, an analysis of the policy documents outlining the practical measures of the Green Deal shows that it will decrease carbon emissions in Europe, but also increase carbon emissions outside of the EU. This increase is more than double the amount of carbon emissions saved by the Green Deal. This analysis was published in Nature Sustainability on <DATE> by an international team of scientists led by Klaus Hubacek, Professor of Science, Technology and Society ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] What role does a tailwind play in cycling’s ‘Everesting’?Physics reveals a tailwind doesn’t help as much as you might think — it’s negligible.