(Press-News.org) The European Union aims to be carbon-neutral by 2050 as part of the comprehensive Green Deal that was agreed upon four years ago. However, an analysis of the policy documents outlining the practical measures of the Green Deal shows that it will decrease carbon emissions in Europe, but also increase carbon emissions outside of the EU. This increase is more than double the amount of carbon emissions saved by the Green Deal. This analysis was published in Nature Sustainability on <DATE> by an international team of scientists led by Klaus Hubacek, Professor of Science, Technology and Society at the University of Groningen.
The European Green Deal is a set of policies intended to fully decarbonize Europe by 2050, but it also includes measures for clean energy production and ecological restoration. Hubacek and colleagues from the United States and China carried out full supply chain analyses of the policy documents underlying the Green Deal. Their conclusion is that the Green Deal in its current form will lead to an increase in emissions in countries outside the EU by 244.8 percent compared to the Green Deal's carbon reduction goal in the land, land use change, and forestry sector within EU borders.
Skeptical
One example is the measure to increase biodiversity in Europe by planting three billion trees. ‘However, trees require a lot of land that cannot be used to produce food. That means that food must be produced elsewhere, and to do this, land must be converted into cropland. This increases the carbon dioxide emission and reduces biodiversity,’ says Hubacek. In this way, the EU would reduce carbon emissions within its borders, but ‘export’ them to the countries that would produce our food, for example Africa or South America.
Of course, the Green Deal does contain a paragraph forbidding the import of products (such as meat or animal feed) for which woodland is converted to farmland. Hubacek is sceptical: ‘Nothing stops these other countries from growing products for Europe on existing farmland and felling forests to produce for the local market. There are simply too many uncertainties in these types of regulations.’ The Green Deal also calls for an increase in organic farming, but this requires more farmland in Europe. Hubacek: ‘Again, there is very little information available on the impact on land use.’
No free lunch
However, the scientists did not just reveal the negative impacts of the Green Deal on the rest of the world. They also looked at different scenarios to see if overall carbon reductions could be enhanced. ‘We found one very effective way to do this.’ says Hubacek, ‘By adopting the more plant-based “planetary health diet”, it is possible to save an enormous amount of carbon emissions.’ Another measure is to phase out food-based biofuels within the EU, which would reduce the amount of farmland needed and thus save carbon emissions and prevent biodiversity loss. Also, the EU could assist developing regions to increase their agricultural efficiency, which would also reduce land use.
Although the Nature Sustainability article shows that the European Green Deal in its present form could result in a net loss for the global environment, the scientists conclude that it can be remedied. ‘By adopting the planetary health diet, which is relatively simple’, says Hubacek. However, there is one more thing that needs to change, he stresses: ‘The programme is driven by techno-optimism, but our analysis underlines that there is no free lunch. I very much doubt that “Green Growth” is possible, as everything you produce requires an input of resources. So we really need to consume less.’ There is a strong sense of urgency now that global warming seems set to surpass the 1.5 degrees from the 1995 Paris Agreement, and many other planetary boundaries are also being overstepped. Hubacek: ‘It is time to implement measures that work.’
Reference: Honglin Zhong et al, Global spillover effects of the European Green Deal and plausible mitigation options. Nature Sustainability, 20 September 2024
END
European Green Deal: a double-edged sword for global emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions will fall in the EU, but rise even more elsewhere
2024-09-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Walking in lockstep
2024-09-20
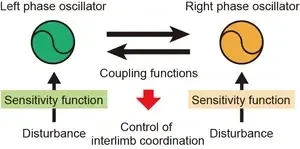
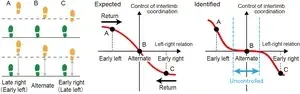
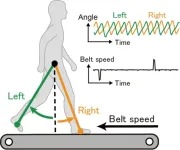
Osaka, Japan – Walking is an activity that is often taken for granted. Most people usually think they can multitask by “walking and chewing gum” simultaneously with hardly any taxation of their mental effort. Indeed, each leg can move rhythmically independently of the other, controlled by its side of the spinal cord. However, the ability of the human brain to coordinate the gait so that a walker’s legs are half a stride out of phase with each other, called the “antiphase relationship,” is not so trivial when an obstacle or asymmetry occurs, such as a curve in the path. A better understanding of how a normal walking cadence is maintained ...
New blood test could be an early warning for child diabetes
2024-09-20
A new type of blood test using lipids could make it easier to identify children at risk of complications around obesity including type two diabetes, liver and heart disease, say scientists.
A new study from King’s College London published in Nature Medicine reveals a new relationship between lipids and diseases impacting metabolism in children, which could serve as an early warning system for conditions like liver disease.
Using machines that test blood plasma in babies that already exist in hospitals, the researchers suggest this ...
Oceanic life found to be thriving thanks to Saharan dust blown from thousands of kilometers away
2024-09-20
Iron is a micronutrient indispensable for life, enabling processes such as respiration, photosynthesis, and DNA synthesis. Iron availability is often a limiting resource in today’s oceans, which means that increasing the flow of iron into them can increase the amount of carbon fixed by phytoplankton, with consequences for the global climate.
Iron ends up in oceans and terrestrial ecosystems through rivers, melting glaciers, hydrothermal activity, and especially wind. But not all its chemical forms are ‘bioreactive’, that is, available for organisms ...
Analysis sheds light on COVID-19-associated disease in Japan
2024-09-20
As society learns to live with COVID-19, research on the disease and its complications remains important. Thus, an Osaka Metropolitan University team has pored through data to understand the incidence in Japan of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA), a severe invasive fungal infection of the lungs.
Few studies have been conducted on CAPA in Japan, but reports from overseas put the incidence between 3.8% and 35%.
Using Japanese administrative claims data, Graduate School of Medicine Lecturer Waki Imoto, graduate student Mr. Yasutaka Ihara, Professor Ayumi Shintani, ...
Cooler heads prevail: New research reveals best way to prevent dogs from overheating
2024-09-20
FOR MORE INFORMATION
Michael San Filippo
Senior Media Relations Manager
American Veterinary Medical Association
Cell/Text: 847-732-6194
msanfilippo@avma.org
Cooler heads prevail: New research reveals best way to prevent dogs from overheating
(SCHAUMBURG, Illinois) September 19, 2024— As temperatures continue to soar across the country, a simple yet innovative technique could be the key to keeping dogs safe from heat-related illnesses.
New research published in the Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association (JAVMA) reveals that teaching dogs ...
UC Riverside medical school develops new curriculum to address substance use crisis
2024-09-20
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Nearly 6,000 opioid-related overdose deaths occurred in California in 2021, many due to fentanyl, a synthetic opioid. To address the crisis, a team of researchers in the School of Medicine, or SOM, at the University of California, Riverside, plans to develop and implement a curriculum that offers education on substance use disorders to medical students early and throughout their education.
To facilitate the development of the curriculum, the team has been awarded a grant of $900,000 from the Substance Abuse ...
Food fussiness a largely genetic trait from toddlerhood to adolescence
2024-09-19
Fussy eating is mainly influenced by genes and is a stable trait lasting from toddlerhood to early adolescence, finds a new study led by researchers from UCL (University College London), King’s College London and the University of Leeds.
The study, published in the Journal of Child Psychology & Psychiatry and funded by the UK mental health charity MQ Mental Health Research, compared survey results of parents with identical or non-identical twins in England and Wales from the ages of 16 months to 13 years.
The ...
Celebrating a century of scholarship: Isis examines the HSS at 100
2024-09-19
Isis: A Journal of the History of Science Society is widely recognized as a leading voice in the history of science. George Sarton founded the journal in 1912, and two years later the History of Science Society (HSS) was formed to advance the journal’s mission and centralize the nascent discipline. The September 2024 issue of Isis pays tribute to the centennial anniversary of the HSS with a collection of articles that delve into the rich history of the society and its publications.
In their introduction to the issue, editors Alexandra Hui and Matthew Lavine write that the issue can be seen as “a love letter of sorts: to the Isis readership, ...
Key biomarkers identified for predicting disability progression in multiple sclerosis
2024-09-19
A pioneering study presented today at ECTRIMS 2024 has identified critical biomarkers that can predict disability worsening in multiple sclerosis (MS). The breakthrough research has the potential to transform treatment strategies for millions of MS patients worldwide, paving the way for more personalised and effective treatment plans.1
In this multicentre observational study, conducted across 13 hospitals in Spain and Italy, Dr. Enric Monreal and his team found that elevated serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) levels—a protein indicating nerve cell damage—at the onset of MS can predict both relapse-associated worsening (RAW) and progression independent ...
Study: AI could lead to inconsistent outcomes in home surveillance
2024-09-19
CAMBRIDGE, MA — A new study from researchers at MIT and Penn State University reveals that if large language models were to be used in home surveillance, they could recommend calling the police even when surveillance videos show no criminal activity.
In addition, the models the researchers studied were inconsistent in which videos they flagged for police intervention. For instance, a model might flag one video that shows a vehicle break-in but not flag another video that shows a similar activity. Models often disagreed with one another over whether to call the police ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] European Green Deal: a double-edged sword for global emissionsGreenhouse gas emissions will fall in the EU, but rise even more elsewhere