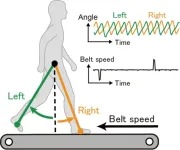
(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan – Walking is an activity that is often taken for granted. Most people usually think they can multitask by “walking and chewing gum” simultaneously with hardly any taxation of their mental effort. Indeed, each leg can move rhythmically independently of the other, controlled by its side of the spinal cord. However, the ability of the human brain to coordinate the gait so that a walker’s legs are half a stride out of phase with each other, called the “antiphase relationship,” is not so trivial when an obstacle or asymmetry occurs, such as a curve in the path. A better understanding of how a normal walking cadence is maintained may lead to enhanced rehabilitation techniques for patients who have experienced brain trauma or other neurological problems.
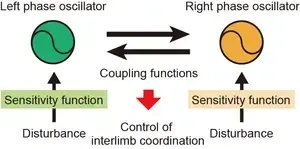
In a study recently published in Communications Biology, researchers from Osaka University captured kinematic data from healthy patients walking on a treadmill that was occasionally perturbed by a sudden change in speed. This led to a momentary loss of the antiphase relationship, but it was quickly restored as the subjects reoriented their walking movements. The data from this experiment was analyzed using a mathematical model of two coupled oscillators – similar to two pendulums connected by a spring – along with a Bayesian inference method. The approach allowed the researchers to calculate the most probable function that represents how the brain applied its control to coordinate the leg motions.
To simplify the problem further, phase reduction theory was applied, which assumes that the perturbed system is returning to a regular periodic solution, called the limit cycle. “Using Bayesian inference enabled us to infer the control of leg coordination in a quantitative way,” says lead author of the study, Takahiro Arai.
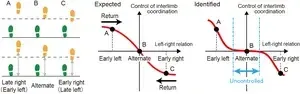
Surprisingly, the researchers found that the relative phase is not actively controlled by the brain until the deviation from correct the antiphase orientation exceeds a certain threshold. That is, the brain does not actively intervene to coordinate the relative position of the legs until they are a certain amount out of lockstep. They suggest that not requiring the constant application of control improves both energy efficiency and maneuverability.
“Based on our model, we see that the brain is neither overly controlling, which would limit our ability to negotiate obstacles and also consume a lot of brainpower, nor overly lax, which could lead to falling over when the legs become too uncoordinated,” says senior author, Shinya Aoi.
This research may be important to help improve the walking of elderly people, or individuals who have experienced the neurological effects of a stroke or Parkinson’s disease. It may also lead to the development of physical aids that help people walk more naturally.
###
The article, “Interlimb coordination is not strictly controlled during walking,” was published in Communications Biology at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-024-06843-w
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world. Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
END
Walking in lockstep
Researchers at Osaka University use experimental data and Bayesian inference to study the control of leg motion during walking, and find that intervention occurs only when discoordination exceeds a certain threshold, which may help improve rehab methods
2024-09-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New blood test could be an early warning for child diabetes
2024-09-20
A new type of blood test using lipids could make it easier to identify children at risk of complications around obesity including type two diabetes, liver and heart disease, say scientists.
A new study from King’s College London published in Nature Medicine reveals a new relationship between lipids and diseases impacting metabolism in children, which could serve as an early warning system for conditions like liver disease.
Using machines that test blood plasma in babies that already exist in hospitals, the researchers suggest this ...
Oceanic life found to be thriving thanks to Saharan dust blown from thousands of kilometers away
2024-09-20
Iron is a micronutrient indispensable for life, enabling processes such as respiration, photosynthesis, and DNA synthesis. Iron availability is often a limiting resource in today’s oceans, which means that increasing the flow of iron into them can increase the amount of carbon fixed by phytoplankton, with consequences for the global climate.
Iron ends up in oceans and terrestrial ecosystems through rivers, melting glaciers, hydrothermal activity, and especially wind. But not all its chemical forms are ‘bioreactive’, that is, available for organisms ...
Analysis sheds light on COVID-19-associated disease in Japan
2024-09-20
As society learns to live with COVID-19, research on the disease and its complications remains important. Thus, an Osaka Metropolitan University team has pored through data to understand the incidence in Japan of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA), a severe invasive fungal infection of the lungs.
Few studies have been conducted on CAPA in Japan, but reports from overseas put the incidence between 3.8% and 35%.
Using Japanese administrative claims data, Graduate School of Medicine Lecturer Waki Imoto, graduate student Mr. Yasutaka Ihara, Professor Ayumi Shintani, ...
Cooler heads prevail: New research reveals best way to prevent dogs from overheating
2024-09-20
FOR MORE INFORMATION
Michael San Filippo
Senior Media Relations Manager
American Veterinary Medical Association
Cell/Text: 847-732-6194
msanfilippo@avma.org
Cooler heads prevail: New research reveals best way to prevent dogs from overheating
(SCHAUMBURG, Illinois) September 19, 2024— As temperatures continue to soar across the country, a simple yet innovative technique could be the key to keeping dogs safe from heat-related illnesses.
New research published in the Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association (JAVMA) reveals that teaching dogs ...
UC Riverside medical school develops new curriculum to address substance use crisis
2024-09-20
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Nearly 6,000 opioid-related overdose deaths occurred in California in 2021, many due to fentanyl, a synthetic opioid. To address the crisis, a team of researchers in the School of Medicine, or SOM, at the University of California, Riverside, plans to develop and implement a curriculum that offers education on substance use disorders to medical students early and throughout their education.
To facilitate the development of the curriculum, the team has been awarded a grant of $900,000 from the Substance Abuse ...
Food fussiness a largely genetic trait from toddlerhood to adolescence
2024-09-19
Fussy eating is mainly influenced by genes and is a stable trait lasting from toddlerhood to early adolescence, finds a new study led by researchers from UCL (University College London), King’s College London and the University of Leeds.
The study, published in the Journal of Child Psychology & Psychiatry and funded by the UK mental health charity MQ Mental Health Research, compared survey results of parents with identical or non-identical twins in England and Wales from the ages of 16 months to 13 years.
The ...
Celebrating a century of scholarship: Isis examines the HSS at 100
2024-09-19
Isis: A Journal of the History of Science Society is widely recognized as a leading voice in the history of science. George Sarton founded the journal in 1912, and two years later the History of Science Society (HSS) was formed to advance the journal’s mission and centralize the nascent discipline. The September 2024 issue of Isis pays tribute to the centennial anniversary of the HSS with a collection of articles that delve into the rich history of the society and its publications.
In their introduction to the issue, editors Alexandra Hui and Matthew Lavine write that the issue can be seen as “a love letter of sorts: to the Isis readership, ...
Key biomarkers identified for predicting disability progression in multiple sclerosis
2024-09-19
A pioneering study presented today at ECTRIMS 2024 has identified critical biomarkers that can predict disability worsening in multiple sclerosis (MS). The breakthrough research has the potential to transform treatment strategies for millions of MS patients worldwide, paving the way for more personalised and effective treatment plans.1
In this multicentre observational study, conducted across 13 hospitals in Spain and Italy, Dr. Enric Monreal and his team found that elevated serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) levels—a protein indicating nerve cell damage—at the onset of MS can predict both relapse-associated worsening (RAW) and progression independent ...
Study: AI could lead to inconsistent outcomes in home surveillance
2024-09-19
CAMBRIDGE, MA — A new study from researchers at MIT and Penn State University reveals that if large language models were to be used in home surveillance, they could recommend calling the police even when surveillance videos show no criminal activity.
In addition, the models the researchers studied were inconsistent in which videos they flagged for police intervention. For instance, a model might flag one video that shows a vehicle break-in but not flag another video that shows a similar activity. Models often disagreed with one another over whether to call the police ...
Study: Networks of Beliefs theory integrates internal & external dynamics
2024-09-19
The beliefs we hold develop from a complex dance between our internal and external lives. Our personal-level cognition and our relationships with others work in concert to shape our views of the world and influence how likely we are to update those views when we encounter new information. In the past, these two levels of belief have been studied largely in isolation: psychologists have modeled the individual-level cognitive processes while researchers in fields from computational social science to statistical physics have offered insights ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] Walking in lockstepResearchers at Osaka University use experimental data and Bayesian inference to study the control of leg motion during walking, and find that intervention occurs only when discoordination exceeds a certain threshold, which may help improve rehab methods