(Press-News.org) Virginia Tech researchers have learned how bacteria manipulate molecules to infect the host organism.
Daniel Capelluto and his research team have discovered the mechanism by which the bacterial pathogen Shigella flexneri, the causative agent of dysentery, manipulates molecular activity to assure its survival against its host’s natural defenses. Their findings were recently published in Structure, a Cell Press journal that supports open access.
“This infection strategy may be employed by other bacteria, making this research a potential foundation for understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying various bacterial infections,” said Capelluto, associate professor of biological sciences.
By understanding the specific manner in which a typical bacterium progresses, researchers can more precisely target preventive measures that will interrupt that process.
To survive, bacteria infect a host by replicating themselves, infecting cells, and then exiting those infected cells. A typical example of this process is seen in Shigella flexneri, a bacterium transmitted through contaminated water or food and that targets the intestinal lining.
According to Capelluto, dysentery is prevalent in low- and middle-income countries, especially among children under 5 years old, and is responsible for 160,000 deaths worldwide each year.
“Pathogens such as bacteria infect cells and they change the metabolism or the behavior of the cell they are infecting to prepare for their invasion,” said Capelluto, an affiliate with the Fralin Life Sciences Institute. “The bacteria release a bunch of different proteins, and those proteins begin to mess up the host to make sure the bacteria can survive under the hostile environment.”
Bacterial proteins disrupt the homeostasis, or balance, of the metabolism in the host, which causes an acidic environment and produces a large amount of lipids that is usually present in traces in the host cell.
In a healthy organism, certain proteins, TOM1 and TOLLIP, serve the function of delivering no longer needed membrane proteins for degradation. However, when disrupted by a bacterial infection and under acidic conditions, TOM1 and possibly TOLLIP are intracellularly sequestered by binding to the bacterially produced lipid, promoting the survival of the infected cell so the bacterium can progress its infection cycle.
“Using high resolution biochemical and biophysical tools, we identified the lipid binding site in TOM1 and show evidence that this mechanism prevents TOM1 from its normal function,” Capelluto said.
Locating the site where the critical binding occurs is fundamental to understanding this bacterial infection pathway, and it has the potential to provide insight to unravel other bacterial infection pathways.
Going forward, Capelluto aims to continue this research on another level.
“It would be nice to do some sort of studies at the cellular level, and that’s what we plan to do next,” Capelluto said.
Capelluto’s Virginia Tech research team included the following members:
Wen Xiong '20, Ph.D. in biological sciences
Tiffany G. Roach '24, Ph.D. in biological sciences
Nicolas Ball current Ph.D. student in biochemistry
Marija Corluka, Ph.D. student in the molecular and cellular biology graduate program
Josephine Beyer '23 in nanomedicine
Anne M. Brown, associate professor of biochemistry END
Research team discovers molecular mechanism for a bacterial infection
With funding from the National Science Foundation, a Virginia Tech research team has identified a path that allows bacterial infection
2024-09-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
What role does a tailwind play in cycling’s ‘Everesting’?
2024-09-20
WASHINGTON, Sept. 20, 2024 – Within the cycling realm, “to Everest” involves riding up and down the same mountain until your ascents total the elevation of Mt. Everest — 8,848 meters.
After a new cycling “Everesting” record was set a few years ago, a debate ensued on social media about the strong tailwind the cyclist had on climbs — 5.5 meters per second (20 kilometers per hour or 12 miles per hour) — when he set the record. To what extent did the tailwind help him? Should limits be set on the allowed ...
Projections of extreme temperature–related deaths in the US
2024-09-20
About The Study: This cross-sectional study found that extreme temperature–related deaths in the contiguous U.S. were projected to increase substantially by mid–21st century, with certain populations, such as non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic adults, projected to disproportionately experience this increase. The results point to the need to mitigate the adverse outcome of extreme temperatures for population health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sameed Ahmed M. Khatana, MD, MPH, ...
Wearable device–based intervention for promoting patient physical activity after lung cancer surgery
2024-09-20
About The Study: In this nonrandomized clinical trial, integration of perioperative exercise interventions using wearable devices improved physical activity (especially moderate-to-vigorous physical activity) and dyspnea at 6 months after lung cancer surgery compared with usual care. This finding suggests a promising role for wearable devices in personalizing perioperative rehabilitation strategies.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Danbee Kang, PhD, (dbee.kang@gmail.com) and Hye Yun Park, MD, (hyeyunpark@skku.edu).
To access ...
Self-compassion is related to better mental health among Syrian refugees
2024-09-20
Displaced individuals experience high rates of emotional distress, depression and anxiety resulting from trauma and stress from displacement and loss. Their mental health may suffer further due to a lack of resources, language barriers, and discrimination during resettlement.
A new study by University of California San Diego researchers reports that displaced Syrian refugees with higher reported self-compassion were less likely to report poor mental health outcomes. The study was published in PLOS ONE on September 19, 2024.
Sarah Alsamman, a student at UC San Diego School of Medicine, and Wael Al-Delaimy, M.D., Ph.D., professor of public health at the Herbert Wertheim School of Public ...
Microplastics found in coral skeletons
2024-09-20
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers from Japan and Thailand investigating microplastics in coral have found that all three parts of the coral anatomy—surface mucus, tissue, and skeleton—contain microplastics. The findings were made possible thanks to a new microplastic detection technique developed by the team and applied to coral for the first time.
These findings may also explain the ‘missing plastic problem’ that has puzzled scientists, where about 70% of the plastic litter that has entered the oceans cannot be found. The team hypothesizes ...
Stroke rates increasing in individuals living with SCD despite treatment guidelines
2024-09-20
(WASHINGTON, September 20, 2024) –The incidence of stroke continues to increase for adults and children living with sickle cell disease (SCD) despite the Stroke Prevention Trial in Sickle Cell Anemia (STOP) establishing standards of care like transfusions and tests to measure blood flow in the brain for those deemed high-risk, according to a study published today in Blood.
Individuals living with SCD, the most common inherited red blood cell disorder in the United States, are especially susceptible to cerebrovascular events (CVEs). This includes ischemic or hemorrhagic strokes, when a blood vessel leading to the brain is ...
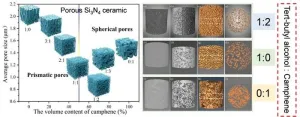
Synergistic promotion of dielectric and thermomechanical properties of porous Si3N4 ceramics by a dual-solvent template method
2024-09-20
Radomes and wave-transmitting antenna windows are critical structural components in aircraft, protecting radar antennas from external interference while ensuring reliable communication. Currently, the most widely used wave-transmitting materials are ceramics based on oxides and nitrides. Si3N4 ceramics, with their high melting point and superior mechanical properties, are considered promising candidates for hypersonic vehicle applications. However, the dielectric and thermal insulation properties of dense Si3N4 ceramics need improvement to meet the precise guidance and thermal protection demands of high-speed flight. By adjusting the microstructure, it is possible to enhance the ...
Korean research team proposes AI-powered approach to establishing a 'carbon-neutral energy city’
2024-09-20
A joint research team from the Renewable Energy System Laboratory and the Energy ICT Research Department at the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) has developed key technologies to realize "Urban Electrification" using artificial intelligence (AI).
Urban electrification aims to reduce the use of fossil fuels and introduce renewable energy sources, such as building-integrated solar technology, to transform urban energy systems. While this concept is relatively unfamiliar in the Republic of Korea, it is being promoted as a key strategy in the U.S. and Europe for achieving carbon neutrality and creating sustainable urban environments.
In ...
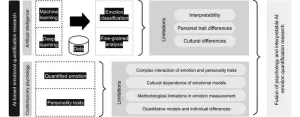
AI is learning to read your emotions, and here’s why that can be a good thing
2024-09-20
Using a fusion of traditional and novel technological methods, researchers are hoping to better quantify emotions to transform the face of the emotion quantification field
Human emotions are complex and are not always easily able to be boiled down to a recognizable pattern. Determining one’s emotional state can be difficult human-to-human, and the many nuances of existence as an emotional entity seem impossible to train a non-human entity to understand, identify and learn from. However, a considerable amount of work and research has been put into training artificial intelligence (AI) to observe, quantify and recognize various states of emotion in humans. ...
Antidepressant shows promise for treating brain tumors
2024-09-20
Key points:
Glioblastoma is an incurable and fatal type of brain cancer.
In a large-scale drug screening, the antidepressant, vortioxetine emerged as one of the most effective agents against these types of cancer cells.
Clinical trials are already in the planning phase at the University Hospital Zurich.
Glioblastoma is a particularly aggressive brain tumour that at present is incurable. Cancer doctors can extend patients’ life expectancy through operations, radiation, chemotherapy or surgical interventions. Nevertheless, half of patients die within twelve months of diagnosis.
Drugs that are effective against brain tumours are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Research team discovers molecular mechanism for a bacterial infectionWith funding from the National Science Foundation, a Virginia Tech research team has identified a path that allows bacterial infection