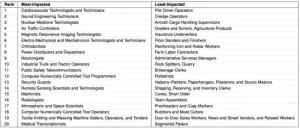
(Press-News.org) Artificial intelligence (AI) may reshape many industries, but the impact of the nascent technology on various jobs remains unclear. Daniele Quercia and colleagues used machine learning to investigate itself, by identifying patents for AI technologies that may impact various occupational tasks. The model used a dataset of 17,879 task descriptions from O*NET, a US government-run occupations database, as well as 24,758 AI patents filed with the United States Patent and Trademark Office between 2015 and 2022 and measured semantic similarity between occupation task descriptions and patent descriptions. The analysis was not merely an exercise in word matching but compared entire task descriptions to entire patents. For each task, the most similar patent was identified and if the patent was more than 90% similar to the task, that task was considered impacted by AI. Each occupation was then given an AI Impact (AII) score by dividing the number of its tasks impacted by AI patents by the total number of tasks for that occupation. Using this method, the team identified the most impacted occupations, which include orthodontists, security guards, and air traffic controllers. The team also identified the least impacted occupations, which include pile driver operators, dredge operators, and graders of agricultural products. According to the authors, occupations including repetitive tasks were not always those most impacted by AI—jobs that include tasks in a specific sequence that produce a machine-readable output were most likely to be impacted. The team found that research often overestimates how much AI will take away jobs because sectors potentially impacted by AI, like healthcare and transportation, currently need more workers, not fewer and because AI is likely to augment rather than replace many jobs. For example, AI can analyze medical images like X-rays to help doctors find issues but cannot replace doctors. According to the authors, tech developers should focus on creating tools that support rather than replace people, and leaders should promote the use of AI with an emphasis on training and education so everyone can benefit.
See a visualization of the data at https://social-dynamics.net/aii/.
END
The impact of AI on specific jobs
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Diagnosing respiratory infections with breath
2024-09-24
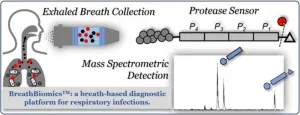
A proof-of-concept study promises the speedy diagnosis of lower respiratory tract infections through analysis of human breath. Lower respiratory tract infections, such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and bronchiolitis, are currently diagnosed by culturing bacteria from respiratory specimens, but the procedure is invasive, laborious, and time intensive. Molecular sequencing techniques cannot differentiate between clinical infection and mere colonization, in which bacteria are benignly present in the respiratory tract. Dapeng Chen and colleagues have designed a medical device that measures the protease activity ...
Well-being as student success
2024-09-24
In a Perspective, Holly C. White and colleagues argue that student well-being should be a goal of pedagogy, along with traditional metrics such as GPA and student retention. Despite evidence linking certain academic experiences with well-being outcomes, few students report having had such experiences. Well-being is defined as a sense of belonging, agency, purpose, identity, civic engagement, and financial well-being. The authors summarize data-backed teaching practices that support elements of student well-being, including supportive mentorships and experiential or authentic learning opportunities. Six exceptional initiatives are described, which can act as models ...
Spinning artificial spider silk into next-generation medical materials
2024-09-24
It’s almost time to dust off the Halloween decorations and adorn the house with all manner of spooky things, including the classic polyester spider webs. Scientists reporting in ACS Nano have made their own version of fake spider silk, but this one consists of proteins and heals wounds instead of haunting hallways. The artificial silk is strong enough to be woven into bandages that helped treat joint injuries and skin lesions in mice.
Spider silk is one of the strongest materials on Earth, technically stronger than steel for a material of ...
Low-temperature conversion of ammonia to hydrogen via electric field-aided surface protonics
2024-09-24
Hydrogen gas, owing to its high energy density and carbon-free nature, is gaining much attention as the energy source for a green and sustainable future. Despite being the most abundant element in the universe, hydrogen is mostly found in a bound state as chemical compounds such as ammonia, metal hydrides, and other hydrogenated compounds.
Among all the hydrogen carriers, ammonia stands out as a promising candidate owing to its wide availability, high hydrogen content with hydrogen making up 17.6% of its mass, and ease of liquefaction as well as transportation. A major drawback that hinders its exploitation as an ...
Challenges in availing reproductive health services experienced by migrant Nepalese men and women in Japan
2024-09-24
Despite a substantial Nepalese community in Japan many Nepalese women face significant challenges in accessing essential sexual and reproductive health services (SRHSs) due to language barriers and differences in healthcare laws and services between Nepal and Japan. In Nepal, women have free access to a wide range of contraceptive and abortion services, while Japan places more restrictions on certain contraceptives and does not provide free abortion services. These limited options make women more reliant on their male partner to use contraceptives for birth control. These challenges in accessing contraceptives, especially female-oriented contraceptives, lead them to acquire contraceptives ...
A risky business: Why do some Parkinson’s disease treatments affect decision making?
2024-09-24
Parkinson’s disease (PD), also known simply as Parkinson’s, is a disorder of the nervous system that affects millions of people worldwide. The nerve cell damage associated with Parkinson’s can cause tremors, slowed movements, problems with balance, and many other symptoms which worsen gradually over time. Although there is no cure, there are medications available that can treat PD symptoms. Some of these medications, however, have previously unexplained side effects – including impaired decision-making that leads to potentially harmful behaviors such as pathological gambling, binge eating and compulsive shopping.
Now, in ...
New species of flatworm invading the United States
2024-09-24
A new species of flatworm has been discovered and has already invaded several states in the southern United States. The particularity of the new species is that it looks a lot like Obama nungara, a species that has invaded much of Europe. The new species has been named Amaga pseudobama in reference to this resemblance.
An international team reports the discovery of a new species of flatworm. The team includes researchers from National Museum of Natural History in Paris, France, Drexel University and North Carolina State ...
First observation of ultra-rare process that could uncover new physics
2024-09-24
Scientists at CERN have discovered an ultra-rare particle decay process, opening a new path to find physics beyond our understanding of how the building blocks of matter interact.
Today the NA62 collaboration presented at a CERN EP seminar the first experimental observation of the ultra-rare decay of the charged kaon into a charged pion and a neutrino-antineutrino pair (K+ → π p+νν).
This is an ultra-rare occurrence - the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics, which explains how particles ...
New indoor vertical farming research could help future-proof food demand for a changing planet
2024-09-24
To make sure everyone eats well in our crowded world, we need to innovate. Vertical farming systems, which grow plants intensively in an indoor setting, could be part of the answer – but to use them on a large scale we need to overcome key problems, especially the management of the energy-intensive, expensive light the plants need to grow. Now scientists show how manipulating light according to the needs of specific crops could make them grow stronger and healthier while minimizing energy use.
“The biggest benefit of vertical farming systems is that healthy food can be grown ...
Common brain network detected among veterans with traumatic brain injury could protect against PTSD
2024-09-24
A Brigham led study suggests using neurostimulation therapies on a specific brain circuit could treat post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Brigham researchers analyzed 193 patients from the Vietnam Head Injury Study with penetrating traumatic brain injury to determine if the location of shrapnel damage to their brains influenced risk of developing PTSD.
Damage to areas connected to the amygdala was associated with a lower chance of developing PTSD.
The study suggests lesions that could protect against PTSD map to a specific brain circuit connected to the amygdala and the medial prefrontal ...