(Press-News.org) Seoul National University’s College of Engineering announced that a research team led by Prof. Yongtaek Hong from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, in collaboration with Prof. Byeongmoon Lee from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST), has developed a ‘printing-based selective metal film deposition technique’ that enables the facile and fast fabrication of high-performance soft electronic devices and circuits in various forms.
The results of this research were published on the 22nd of August in Nature Communications, a prestigious international scientific journal.
Metal thin films formed using vapor deposition have excellent electrical conductivity and surface quality, making them key components of electronic devices and circuits. However, patterning these metal thin films into desired shapes typically requires the use of rigid masks such as shadow masks or photomasks, which makes it difficult to modify patterns and limits the ability to carry out processes on surfaces of various forms.
To address this issue, the research team developed a 'printing-based selective metal thin film deposition technique.' This method utilizes polymer patterns to block the condensation of metal vapor, allowing the vapor deposition and patterning processes to be performed at the same time without the need for a separate mask. This approach enables the production of patterns with line widths ranging from micrometers (μm) to millimeters (mm) on a large scale.
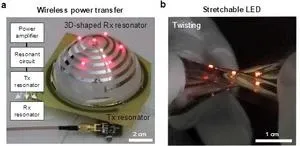
According to the research team, the polymer pattern’s excellent stretchability and mechanical durability allow metal thin film patterns to be easily formed on multi-curvature or elastic substrates, which were previously impossible with conventional methods. During the research, they demonstrated next-generation free-form electronic devices and circuits, including wireless power transmission, curvilinear OLEDs (Organic Light Emitting Diodes), and stretchable LED arrays, by using metal thin films in various shapes.
Prof. Yongtaek Hong highlighted the significance of the research, stating, “This study not only developed a technology for easily custom-fabricating high-performance metal thin film patterns based on vapor deposition, but also set the stage for maximizing the utility of metal thin films in the field of soft electronics by applying this technology to curved and stretchable systems.” He added, “In the future, this selective metal thin film deposition technology is expected to be directly applied to forming porous transparent structures in the top common electrode of OLED panels, a key element for under-display camera and under-display face recognition sensor technologies that require various form factors.”
Meanwhile, Dr. Sujin Jeong and Dr. Hyungsoo Yoon, co-first authors of the paper, are currently working at Samsung Display Research Center, focusing on the development of next-generation future displays, including stretchable displays. The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
□ Introduction to the SNU College of Engineering
Seoul National University (SNU) founded in 1946 is the first national university in South Korea. The College of Engineering at SNU has worked tirelessly to achieve its goal of ‘fostering leaders for global industry and society.’ In 12 departments, 323 internationally recognized full-time professors lead the development of cutting-edge technology in South Korea and serving as a driving force for international development.
END
SNU researchers develop ‘Selective Metal Films Deposition Technique’ enabling fabrication of soft electronics with various form factors
Increases applicability of highly conductive evaporated metal thin films in soft electronics including curvilinear OLEDs and stretchable LED arrays
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Extinct volcanoes a ‘rich’ source of rare earth elements
2024-09-24
A mysterious type of iron-rich magma entombed within extinct volcanoes is likely abundant with rare earth elements and could offer a new way to source these in-demand metals, according to new research from The Australian National University (ANU) and the University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Rare earth elements are found in smartphones, flat screen TVs, magnets, and even trains and missiles. They are also vital to the development of electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies such as wind turbines.
Dr Michael Anenburg from ANU said the iron-rich magma that solidified to form some extinct volcanoes is up to ...
PSU English professor to lift curtain on one of world’s most powerful supercomputers
2024-09-24
Supercomputers are the largest and most powerful computers in the world and yet few people know what they do or why they should care. That’s why an English professor at Portland State is helping to demystify one of the world’s fastest and largest supercomputers with a grant from the National Science Foundation.
Sarah Read, an associate professor and director of PSU’s Technical and Professional Writing program, is teaming up with Clemson University’s Jordan Frith to give the public a better understanding of Aurora, ...
UTSA Center for Public Opinion Research releases survey of Bexar County voter opinions ahead of November 5 election
2024-09-24
SAN ANTONIO, TEXAS — A scientific survey of registered voters in Bexar County says that two city charter amendments have low support among voters and there is no early leader in the 2025 San Antonio mayoral race. Additionally, voters have mixed opinions about new San Antonio Spurs and San Antonio Missions facilities according to the Bexar County Registered Voter Poll, which was conducted from September 11 to 16, 2024 by the UTSA Center for Public Opinion Research (CPOR).
Established in Fall 2023, CPOR is a full-scale, academic public opinion research center that produces and facilitates basic and applied opinion research broadening shared understanding ...
Emily Carter wins prestigious Marsha I. Lester Award from American Chemical Society
2024-09-24
Emily Carter, senior strategic advisor and associate laboratory director for applied materials and sustainability sciences at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), has won the 2024 Marsha I. Lester Award for Exemplary Impact in Physical Chemistry.
Awarded each year by the American Chemical Society (ACS) at its annual fall meeting, the award recognizes an “exemplary impact in physical chemistry research.” Nominees for the award must be members of the ACS’s physical chemistry ...
New report from the University of Phoenix Career Institute® and the Center on Rural Innovation reveals keys to retaining rural America’s future generation
2024-09-24
Today, the University of Phoenix Career Institute® and the Center on Rural Innovation (CORI), a nonprofit seeking to advance economic prosperity in rural communities, released the G.R.O.W. ™ Generating Rural Opportunities in the Workforce™ report, providing a comprehensive look at the barriers Americans living in rural communities face in their day-to-day lives, and the impact these barriers have on career development and advancement opportunities.
The findings of this study underscore the ways in which recent workforce transformation ...
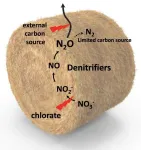
Greenhouse gas emissions from silage fed to livestock
2024-09-24
Changes in silage production could help cut greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture. Agriculture is the largest source of nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions in the United States. N2O is the third most impactful greenhouse gas, yet one potential source—silage—has not been thoroughly studied. Silage, which is moist, harvested plant material used to feed livestock during the winter, is preserved through fermentation. During this process, anaerobic bacteria produce lactic acid, which prevents the plants from spoiling. Jeongdae Im and colleagues suggest that silage could be a significant ...
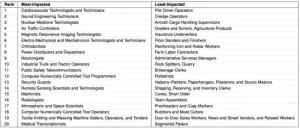
The impact of AI on specific jobs
2024-09-24
Artificial intelligence (AI) may reshape many industries, but the impact of the nascent technology on various jobs remains unclear. Daniele Quercia and colleagues used machine learning to investigate itself, by identifying patents for AI technologies that may impact various occupational tasks. The model used a dataset of 17,879 task descriptions from O*NET, a US government-run occupations database, as well as 24,758 AI patents filed with the United States Patent and Trademark Office between 2015 and 2022 and measured semantic similarity between occupation task descriptions and patent descriptions. The analysis was not merely an exercise ...
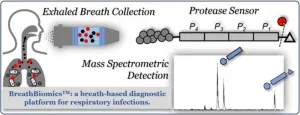
Diagnosing respiratory infections with breath
2024-09-24
A proof-of-concept study promises the speedy diagnosis of lower respiratory tract infections through analysis of human breath. Lower respiratory tract infections, such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and bronchiolitis, are currently diagnosed by culturing bacteria from respiratory specimens, but the procedure is invasive, laborious, and time intensive. Molecular sequencing techniques cannot differentiate between clinical infection and mere colonization, in which bacteria are benignly present in the respiratory tract. Dapeng Chen and colleagues have designed a medical device that measures the protease activity ...
Well-being as student success
2024-09-24
In a Perspective, Holly C. White and colleagues argue that student well-being should be a goal of pedagogy, along with traditional metrics such as GPA and student retention. Despite evidence linking certain academic experiences with well-being outcomes, few students report having had such experiences. Well-being is defined as a sense of belonging, agency, purpose, identity, civic engagement, and financial well-being. The authors summarize data-backed teaching practices that support elements of student well-being, including supportive mentorships and experiential or authentic learning opportunities. Six exceptional initiatives are described, which can act as models ...
Spinning artificial spider silk into next-generation medical materials
2024-09-24
It’s almost time to dust off the Halloween decorations and adorn the house with all manner of spooky things, including the classic polyester spider webs. Scientists reporting in ACS Nano have made their own version of fake spider silk, but this one consists of proteins and heals wounds instead of haunting hallways. The artificial silk is strong enough to be woven into bandages that helped treat joint injuries and skin lesions in mice.
Spider silk is one of the strongest materials on Earth, technically stronger than steel for a material of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
[Press-News.org] SNU researchers develop ‘Selective Metal Films Deposition Technique’ enabling fabrication of soft electronics with various form factorsIncreases applicability of highly conductive evaporated metal thin films in soft electronics including curvilinear OLEDs and stretchable LED arrays