(Press-News.org) TUCSON, Ariz., Sept. 19, 2024 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) is thrilled to announce its Polycystic Kidney Disease Outcomes Consortium (PKDOC) has been awarded an Autosomal Dominant Tubulointerstitial Kidney Disease (ADTKD) focused Broad Agency Announcement (BAA) contract from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The overarching objective of the work supported by the BAA award is to leverage collaboration with the Wake Forest Rare Inherited Kidney Disease team and its ADTKD registry, to analyze clinical and laboratory data that will help evaluate prognosis in ADTKD and help set the stage for future clinical trials.
ADTKD only affects the kidney, resulting in slowly worsening kidney function and the need for dialysis or kidney transplant at an average age of 45 years. It is caused predominantly by genetic changes (mutations) in the UMOD and MUC1 genes. Because of the inheritance pattern (autosomal dominant), a child of an affected parent has a 50% chance of also being affected. Thus, many family members have kidney disease and will eventually need a kidney transplant or dialysis. Unlike many other kidney diseases, there is no blood or protein in the urine. While this condition was infrequently recognized in the past, identification of the genetic causes of this condition has resulted in increased detection. It is now estimated that ADTKD is the third most common form of inherited kidney disease and affects more than 25,000 individuals in the U.S.
Given its recent identification as a cause of kidney disease and its rarity, little is known about factors that affect progression of kidney disease in ADTKD. Understanding rates of progression is important for patients (to learn about prognosis) and important for the development of future clinical trials. C-Path will now play a major role in analyzing available clinical data about ADTKD and helping to better understand the factors associated with disease progression. The goal of this proposal is to identify endpoints for future clinical trials and benefit ADTKD drug development efforts and regulatory review of these medications by providing tools to increase the ability to analyze the effectiveness of medications as treatments for ADTKD.
“We are very grateful for the support we have received from FDA to pursue this important project,” said Sorin Fedeles, Ph.D., MBA, Executive Director of PKDOC. “This proposal represents our commitment to advancing the quantitative understanding of ADTKD progression through incorporation of relevant biomarkers into disease progression models, thus allowing a path forward for more efficient clinical trials and eventual drug approvals for this devastating disease. Our close collaboration with Wake Forest will allow us to accelerate progress towards future ADTKD treatments. In addition, this support will enhance our outreach efforts to leverage expertise across ADTKD stakeholders in order to collaborate and accelerate the development of life-changing therapies for the ADTKD community.”
“We are really delighted to work with C-Path on this important project. C-Path has made great strides in its work in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, and we are happy to be working with them on this new endeavor. It is really a great day for patients with ADTKD, and we are happy that the FDA has provided our patients with hope and funding as we move towards finding a treatment for ADTKD. We invite all patients who have or think they have ADTKD to contact us at kidney@wakehealth.edu and become part of this work,” said Anthony Bleyer, Ph.D., professor of kidney disease at Wake Forest School of Medicine and leader of the Rare Inherited Kidney Disease team.
About Critical Path Institute
Critical Path Institute (C-Path) is an independent, nonprofit established in 2005 as a public-private partnership, in response to the FDA’s Critical Path Initiative.C-Path’s mission is to lead collaborations that advance better treatments for people worldwide. Globally recognized as a pioneer in accelerating drug development, C-Path has established numerous international consortia, programs and initiatives that currently include more than 1,600 scientists and representatives from government and regulatory agencies, academia, patient organizations, disease foundations and pharmaceutical and biotech companies. With dedicated team members located throughout the world, C-Path’s global headquarters is in Tucson, Arizona and C-Path’s Europe subsidiary is headquartered in Amsterdam, Netherlands. For more information, visit c-path.org.
Critical Path Institute is supported by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and is 54% funded by the FDA/HHS, totaling $19,436,549, and 46% funded by non-government source(s), totaling $16,373,368. The contents are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement by, FDA/HHS or the U.S. Government.
About Wake Forest Rare Inherited Kidney Disease Team
The Wake Forest Rare Inherited Kidney Disease team helps families identify the genetic cause of inherited kidney disease. Its mission statement is “To help one patient, one family at a time.” The team has identified mutations in the UMOD, REN, MUC1, and APOA4 gene as causes of inherited kidney disease and has provided help to over 1,000 families. The team is interested in working with individuals with UMOD mutations or unknown causes of inherited kidney disease and can be contacted at kidney@wakehealth.edu.
Media Contacts:
Roxan Triolo Olivas
C-Path
520.954.1634
rolivas@c-path.org
Kissy Black
C-Path
615.310.1894
kblack@c-path.org
END
C-Path’s PKD outcomes consortium receives BAA Award for project to advance drug development tools for autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease
2024-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New insights into hot carrier solar cells: Increasing generation and extraction
2024-09-24
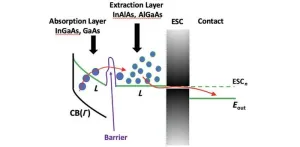
Hot carrier solar cells, a concept introduced several decades ago, have long been seen as a potential breakthrough in solar energy technology. These cells could surpass the Shockley–Queisser efficiency limit, which is a theoretical maximum efficiency for single-junction solar cells. Despite their promise, practical implementation has faced significant challenges, particularly in managing the rapid extraction of hot electrons across material interfaces.
Recent research has focused on using satellite valleys in the conduction band to temporarily store hot electrons before collection. However, ...
Clinical trial results show low-intensity therapy can achieve positive outcomes for certain pediatric leukemia subtypes
2024-09-24
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – Sept. 24, 2024) – Clinical trial results from St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital demonstrate benefits to using genomics and early treatment response to guide risk classification of children with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). Traditionally, the intensity of a patient’s chemotherapy regime is guided by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) risk classification, which is largely determined by clinical characteristics such as age and white blood cell count at presentation. Through the flagship St. Jude ...
How emotion boosts memory for context
2024-09-24
Researchers at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology demonstrated that emotion enhances memory for contextual details, challenging the view that emotion impairs the ability to remember such information.
The report was led by doctoral student Paul Bogdan, currently a postdoc at Duke University, and Florin and Sanda Dolcos, professors of psychology and neuroscience at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.
Their research appears in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: ...
Specially designed video games may benefit mental health of children and teenagers
2024-09-24
In a review of previous studies, a Johns Hopkins Children’s Center team concludes that some video games created as mental health interventions can be helpful – if modest – tools in improving the mental well-being of children and teens with anxiety, depression and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
A report on the review of studies from peer-reviewed journals between 2011 and March 20, 2024, was published Sept. 23, 2024, in JAMA Pediatrics.
An estimated 20% of children and teenagers between the ages of three and 17 in the U.S. have a mental, emotional, developmental or behavioral ...
President Obama 2012 reelection linked to significantly better mental health in Black men — but only those with a college education
2024-09-24
Following Barack Obama’s reelection as U.S. president in 2012, the mental health of college-educated Black men improved significantly, while those who didn’t attend college reported worse mental health, according to new research from Rice University sociologists.
“Four More Years! Or So What? The Mental Health Significance of Barack Obama’s 2012 Presidential Re-Election among Black Adults” will appear in an upcoming edition of Du Bois Review: Social Science Research on Race.
Lead researcher Tony Brown, distinguished professor of sociology at Rice, said he and his co-authors were interested in following up ...
Finding the sweet spot: Machine learning reveals factors for successful crowdfunding
2024-09-24
Toronto -- Modern crowdfunding has grown from relatively modest beginnings in the late 1990s to a multi-billion-dollar financing market for all kinds of early-stage innovations. The platform Kickstarter alone went from $276 million pledged in 2012 to $7.8 billion in 2024. There are even professional project designers to help craft that winning proposal.
With stakes like those, getting the pitch right is everything.
Enter machine learning to assist. Researchers from the University of Toronto’s Rotman School of Management put four different types of this artificial intelligence application to the test, including Deep Learning. Machine learning proved not only superior ...
University of Houston unveils guideline to enhance treatment access for opioid use disorder in community pharmacies
2024-09-24
Pharmacists now have more guidance in combatting the opioid crisis and providing treatment to patients thanks to new national guidelines developed at the University of Houston College of Pharmacy. The Pharmacy Access to Resources and Medication for Opioid Use Disorder Guideline, released today, addresses critical barriers in the treatment of Opioid Use Disorder across the nation’s community pharmacies.
With approximately 2.7 million individuals in the U.S. affected by OUD, the need for effective management strategies has never been more urgent. The PhARM-OUD Guideline marks a significant advancement as ...
Atmospheric methane increase during pandemic due primarily to wetland flooding
2024-09-24
A new analysis of satellite data finds that the record surge in atmospheric methane emissions from 2020 to 2022 was driven by increased inundation and water storage in wetlands, combined with a slight decrease in atmospheric hydroxide (OH). The results have implications for efforts to decrease atmospheric methane and mitigate its impact on climate change.
“From 2010 to 2019, we saw regular increases – with slight accelerations – in atmospheric methane concentrations, but the increases that occurred from ...
Violence, harassment from students is overwhelmingly ‘part of the job’ for Saskatchewan education sector workers
2024-09-24
Saskatchewan education sector workers are experiencing disturbing levels of workplace violence and harassment, says a new report spotlighting a situation that has reached “a breaking point,” according to its authors.
Testimonies catalogued by University of Ottawa researchers found Saskatchewan schools are far from offering a safe and violence-free environment as workplace violence becomes increasingly normalized.
“I’ve been punched in the face, had push pins held to my eyeballs, and scissors held to my throat,” the report quotes one ...
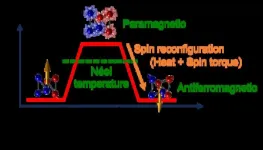
Thermal effects in spintronics systematically assessed for first time
2024-09-24
Spintronics – devices that use microscopic magnetism in conjunction with electric current – could lead to computing technology as fast as conventional electronics but much more energy efficient. As such devices are developed and studied, an important unresolved question is how device operation is affected by heating.
A new experimental technique, reported by researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign in the journal APL Materials, directly measures heating in spintronic devices, allowing direct comparison to other effects. The researchers say that this technique can be used to select spintronic materials whose magnetic behavior is minimally impacted by heating, ...