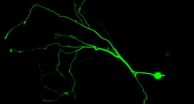
NIH-funded study uses new technology to peek deep into the brain
Time-lapse technique can show cellular changes related to problems like addiction and brain tumors
2011-01-19
(Press-News.org) Changes within deep regions of the brain can now be visualized at the cellular level, based on research on mice, which was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Published Sunday in Nature Medicine, the study used a groundbreaking technique to explore cellular-level changes over a period of weeks within deep brain regions, providing a level of detail not possible with previously available methods. The study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), the National Cancer Institute, and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Researchers at Stanford University used time-lapse fluorescence microendoscopy, a technique that uses miniature probes to directly visualize specific cells over a period of time, to explore structural changes that occur in neurons as a result of tumor formation and increased stimulation in the mouse brain. This could lead to greater information on how the brain adapts to changing situations, including repeated drug exposure.
"Continued drug use leads to changes in neuronal circuits that are evident well after a person stops taking an addictive substance," said Dr. Nora D. Volkow, director of NIDA. "This study demonstrates an innovative technique that allows for a glimpse of these cellular changes within the brain regions implicated in drug reward, providing an important tool in our understanding and treatment of addiction."
Investigators focused on two brain regions within the study, the hippocampus and striatum. The striatum, a brain region important for motor function and habit formation, is also a major target for abused drugs. Some researchers believe that a shift in activity within the striatum is at least partly responsible for the progression from voluntary drug-taking to addiction. This new technique could allow a better understanding of how these processes occur at the cellular level, leading to insights into mechanisms underlying addictive behaviors.
"The results should now allow neuroscientists to track longitudinally in the living brain the effects of drugs of abuse at the levels of neural circuitry, the individual neuron, and neuronal dendrites," said Dr. Mark Schnitzer, corresponding author for the article. "For example, our imaging methods work well in the dorsal striatum, which we have followed with microscopic resolution over weeks in the live brain. This should permit researchers interested in the reward system to address a range of issues that were previously out of reach."
INFORMATION:
The study can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm.2292.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse is a component of the National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIDA supports most of the world's research on the health aspects of drug abuse and addiction. The Institute carries out a large variety of programs to inform policy and improve practice. Fact sheets on the health effects of drugs of abuse and information on NIDA research and other activities can be found on the NIDA home page at www.drugabuse.gov. To order publications in English or Spanish, call NIDA's new DrugPubs research dissemination center at 1-877-NIDA-NIH or 240-645-0228 (TDD) or fax or email requests to 240-645-0227 or drugpubs@nida.nih.gov. Online ordering is available at http://drugpubs.drugabuse.gov. NIDA's new media guide can be found at http://drugabuse.gov/mediaguide/.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) — The Nation's Medical Research Agency — includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. It is the primary Federal agency for conducting and supporting basic, clinical and translational medical research, and it investigates the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-01-19
The first letter of our childhood surname determines much about our consumer behavior as grownups, according to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research.
Why are some people more likely than others to wait in line overnight to buy a just-released book or to queue up for the new iPad? "The tendency to act quickly to acquire items such as those above is related to the first letter of one's childhood surname," write authors Kurt A. Carlson (Georgetown University) and Jacqueline M. Conard (Belmont University).
The authors studied how quickly adults responded to opportunities ...
2011-01-19
When we don't feel confident about our government, we choose indirect ways of showing support, like buying U.S. based products, according to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research.
"Today, we can barely watch television for any length of time without hearing about verbal attacks on the government, or a given religion or education system," write authors Keisha M. Cutright (Duke University), Eugenia C. Wu (Cornell University), Jillian C. Banfield (University of Waterloo), Aaron C. Kay (Duke University), and Gavan J. Fitzsimons (Duke University).
The results ...
2011-01-19
At least one in five horses used for leisure are overweight or obese. It's a condition which can lead to laminitis and equine metabolic syndrome.
The pilot study, carried out by The University of Nottingham's School of Veterinary Medicine and Science, showed that rates of obesity among horses are likely to be just as high as they are among people. The results are published online on Monday 17 January 2011 in the journal Veterinary Record.
The study, by third year veterinary student Helen Stephenson from Lydney in Gloucestershire, assessed the prevalence of obesity among ...
2011-01-19
Over the last few years, researchers have used a type of brain scanning, known as functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI, to help them map changes in blood flow in the brain and to correlate this with thoughts and behavior. A new way to analyze fMRI data, which could improve is reported in the International Journal of Computational Biology and Drug Design.
Scientists have known since the 1890s that changes in blood flow and blood oxygenation in the brain (hemodynamics) are correlated with activity in brain cells, neurons. When a neuron is active it needs more energy ...
2011-01-19
Adding physical distance between people during negotiations may lead to more mutually beneficial outcomes, according to new research from The University of Texas at Austin.
Psychologist Marlone Henderson examined how negotiations that don't take place in person may be affected by distance. He compared distant negotiators (several thousand feet away) with those who are nearby (a few feet away) in three separate studies. While much work has examined the consequences of different forms of non-face-to-face communication, previous research has not examined the effects of ...
2011-01-19
(Boston) – Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have for the first time shown that reduced vitamin D absorption in patients with quiescent Crohn's disease (CD) may be the cause for their increased risk for vitamin D deficiency. The findings, which currently appear on-line in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, also showed that the only way to determine absorption efficiency is to perform a vitamin D bioavailability test.
Vitamin D is ingested in the diet as well as synthesized in the skin from UVB
irradiation from the sun. People living in areas that ...
2011-01-19
Scientists at The University of Nottingham have brought cancer cells back under normal control — by reactivating their cancer suppressor genes. The discovery could form a powerful new technology platform for the treatment of cancer of the breast and other cancers.
Breast cancer is diagnosed in about 1.4 million women throughout the world every year, with half a million dying from the disease. A common cause of cancer is when cells are altered or mutated and the body's tumour suppressor genes are switched off.
Research, published today in the Journal Molecular Cancer, ...
2011-01-19
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Jan. 18, 2011 – A study from researchers in Germany showed that magnetic maneuvering of a modified capsule endoscope in the stomach of healthy volunteers under clinical conditions is safe, well-tolerated, and technically feasible. Maneuverability of the capsule within the stomach was excellent and visualization of the gastric mucosa, the inner lining of the stomach, was satisfactory in the majority of subjects. Apart from a single experiment performed with a supervising flexible gastroscope, this was the first study to use the system in the stomach of ...
2011-01-19
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill have discovered a molecule that can make brain cells resistant to programmed cell death or apoptosis.
This molecule, a tiny strand of nucleotides called microRNA-29 or miR-29, has already been shown to be in short supply in certain neurodegenerative illnesses such as Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's disease. Thus, the discovery could herald a new treatment to prompt brain cells to survive in the wake of neurodegeneration or acute injury like stroke.
"There is the real possibility ...
2011-01-19
A new study in the Journal of Consumer Research shows that women are better than men at figuring out unusual products when they're among competing items.
"A lot of times when we look at how consumers respond to innovative change in a product's physical form, we fail to consider that the context where they see the product plays a major role in how they evaluate and interpret it," write authors Theodore J. Noseworthy, June Cotte, and Seung Hwan (Mark) Lee (all University of Western Ontario).
The researchers examined consumer reactions to innovative products, like a car ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NIH-funded study uses new technology to peek deep into the brain
Time-lapse technique can show cellular changes related to problems like addiction and brain tumors