(Press-News.org) In research published in Brain and Behavior, investigators found increased rates of menstrual irregularities in women living in areas affected by the 2023 earthquake in Turkey.
In the study, 309 women of reproductive age living in regions declared as disaster areas completed online forms 9 months after the earthquake. Responses revealed an increase of menstrual irregularities from 14.3% before the earthquake to 44.8% after the earthquake. Risk factors for menstrual irregularities included post-traumatic stress symptoms, chronic diseases, and smoking.
The findings reveal that reproductive health can be significantly affected in the aftermath of natural disasters, and they highlight the importance of addressing mental health in post-disaster interventions to mitigate these effects.
“Traumatic events like earthquakes can disrupt not only physical but also hormonal and psychological balances, which can directly affect women's reproductive health,” said corresponding author Sibel Kiyak, RN, PhD, of Necmettin Erbakan University.
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/brb3.7003
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
Brain and Behavior is an open access journal that publishes research relating to every area of neurology, neuroscience, psychology and psychiatry. We publish interdisciplinary research reports - all enhancing the understanding of the brain and behavior. Brain and Behavior is part of Wiley’s Forward Series which are inclusive open access journals increasing discoverability.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Do natural disasters jeopardize women’s reproductive health?
2024-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Can cosmic radiation in outer space affect astronauts’ long-term cognition?
2024-09-25
During missions into outer space, galactic cosmic radiation (GCR) will penetrate current spacecraft shielding and thus pose a significant risk to human health. Previous studies have shown that GCR can cause short-term cognitive deficits in male rodents. Now a study published in the Journal of Neurochemistry reveals that GCR exposure can also cause long-lasting learning deficits in female rodents.
The impact of GCR on cognition was lessened when mice were fed an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound called CDDO-EA.
Beyond ...
Do preventive health technologies promote or harm consumers’ wellbeing?
2024-09-25
Preventive health technologies—such as wrist-worn activity trackers or health and fitness apps—are popular tools for promoting wellbeing, but new research published in the Journal of Consumer Affairs reveals that consumer engagement with these technologies can be considered a double-edged sword.
The study, which involved 30 in-depth interviews with users, found that consumers engage with preventive health technologies based on a variety of health goals—for example, to lose weight, improve performance, monitor data of an enjoyable activity, or acquire a healthy routine.
These diverse goals led users ...
Preclinical studies suggest a drug-free nasal spray could ward off respiratory infections
2024-09-25
Researchers from the Brigham detail how the spray they created may offer broad-spectrum protection from respiratory infections by COVID-19, influenza, everyday cold viruses, and pneumonia-causing bacteria
A new study details how a nasal spray formulated by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, may work to protect against viral and bacterial respiratory infections. Based on their preclinical studies, the researchers say the broad-spectrum nasal spray is long-lasting, safe, and, if validated in humans, could play a key role in reducing respiratory diseases ...
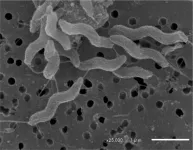
Campylobacter jejuni-specific antibody gives hope to vaccine development
2024-09-25
Bacterial infections resulting in enteritis, sometimes extra-intestinal infections such as sepsis, continue to be a global health concern. A leading cause of diarrheal and extra-intestinal infectious mortality among children under 5 and elderly persons is infection with Campylobacter bacteria, against which there is no effective vaccine or medication. An Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has recently uncovered what could be an important step toward preventing, diagnosing, and treating a species of Campylobacter bacteria.
Researchers including Professor Shinji Yamasaki and Associate Professor Noritoshi Hatanaka of the Graduate School ...
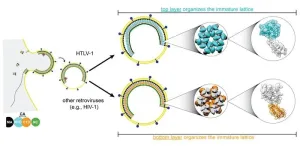
A viral close-up of HTLV-1
2024-09-25
Martin Obr is on edge, anxiously waiting for his train to the airport. A storm called “Sabine” is brewing, shutting down all public transport. He catches his flight from Frankfurt to Vienna just in time.
Obr spent the last days in Germany meticulously analyzing what he calls the “perfect sample”. This sample helped him and Florian Schur from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) decode the structure of a virus called HTLV-1 (Human T-cell Leukemia Virus Type 1).
In collaboration with the University of Minnesota and Cornell University, ...
Virtual reality can help pedestrians and cyclists swerve harmful pollutants – study
2024-09-25
Physics-informed virtual reality could be key to reducing the exposure of pedestrians and cyclists to harmful, non-exhaust vehicle emissions, according to a study published today (25 Sep) in the Royal Society Open Science journal.
The research lead by the University of Birmingham (supported by Rosetrees Trust and Research England QR Funding), targets the issue of major health risks and chronic diseases caused by exposure to unregulated particle pollutants from road, tyre and brake sources by providing easy, accessible guidance to the public, policy makers, and city planners, through immersive VR experiences.
Detailed ...
Neuroscience luminary Hermona Soreq sheds light on the roles of RNA regulators in neurodegenerative diseases
2024-09-25
In a compelling Genomic Press Interview published in Brain Medicine on September 25, 2024, Professor Hermona Soreq of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem in Israel unveils the profound implications of her groundbreaking research on the cholinergic system and small RNA regulators in brain-body communication.
Prof. Soreq, holder of the Endowed Slesinger Professorship of Molecular Neuroscience, has dedicated her career to unraveling the complexities of the parasympathetic nervous system, with a particular focus on acetylcholine's role in stress responses and neurodegenerative diseases. Her work has revolutionized our understanding of how the brain ...
Ancient reef-builders dodged extinction — at least temporarily
2024-09-25
Will modern coral reefs go extinct? The answer is uncertain, but some of their ancient counterparts managed to dodge a bullet — for a while, at least.
Scientists from Osaka Metropolitan University have discovered that ancient reef-building organisms called stromatoporoids survived the Late Devonian mass extinction event and continued to thrive as major reef-builders long after their presumed extinction. These findings shed light on how life on Earth has responded to past environmental changes, offering ...
Citizen scientists help discover microplastics along the entire German coastline
2024-09-25
The global production of plastics and the resulting plastic waste has increased to such an extent that plastics have become ubiquitous in our environment. Plastics of various sizes are also found along the German North Sea and Baltic coasts. Previous studies of microplastic pollution on German beaches have often been limited to a few locations. In the citizen science project “Microplastic Detectives”, researchers from the Alfred Wegener Institute, together with citizens, have now collected samples from beaches along the entire German coast to be analyzed for microplastics. The resulting dataset is the first to be large enough to ...
Rising waters, waning forests: How scientists are using tree rings to study how rising sea levels affect coastal forests
2024-09-25
Sunlight filters through the canopy of pines, holly, sweet gum, and red maple while bird calls echo in the distance. These coastal forests may seem like others in the Mid-Atlantic, but a hidden challenge looms. Standing tall next to their salt marsh neighbors, where the wind carries the sharp scent of sulfidic seawater, these trees are more than just part of the landscape—they are living monuments to a rapidly changing environment. As sea levels rise, the future of these forests is uncertain. While the adjacent salt marshes can adapt to encroaching waters, the trees, vulnerable to the increasing frequency ...