(Press-News.org) Metastatic cancer can be a devastating diagnosis. The cancer is spreading. It may travel to multiple organs in the body. This could mean more pain and ultimately, death.
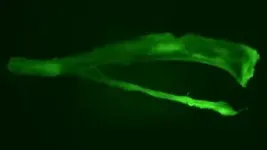
Unfortunately, just how cancer spreads remains unclear. But now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Adam Siepel and colleagues have a way to better understand that process. New technology developed at Weill Cornell Medicine barcodes cells to track the highways by which prostate cancer spreads throughout the body.
The resulting roadmap shows that most cancer cells actually stay put within the tumor. However, it also reveals that a small number of aggressive cells seed cancer’s rare migrations from the prostate to the bones, liver, lungs, and lymph nodes.
The discovery was made in collaboration with Dawid Nowak’s laboratory at Weill Cornell Medicine. It involved using a new mouse model called Evolution in Cancer Prostate (EvoCaP) along with an analysis pipeline known as Evolutionary Lineage Tracing in R (EvoTraceR). This allowed scientists to use short sequences of DNA that act as genetic barcodes to trace the movement of individual cancer cells.
The new technology offers a big step up from previous methods, says Siepel. In the past, researchers might have used a combination of imaging techniques and whole-genome sequencing. But that meant more time and money. Plus, it didn’t necessarily ensure more accurate readings. On the other hand, Siepel says, “This barcoding lets us read off the precise tracing information about how the cancer has spread from its origin to the tissues to which it’s metastasized.”
The readout provides researchers with a clearer picture of how cancer spreads. And that newfound clarity could set the stage for further advances. CSHL postdoc Armin Scheben explains: “We’ve laid the fundamental molecular biology foundation for a whole lot of other questions to be answered. This is the beginning phase of a much larger project where our colleagues are expanding this work to other types of cancer, and we start looking at therapeutic interventions for metastasis.”
If they’re successful, it could lead to new, more targeted therapeutics. There’s a long road ahead, but one day, mapping cancer’s spread could mean stopping it in its tracks.
END
How does cancer spread? Follow the map
2024-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Shrinking AR displays into eyeglasses to expand their use
2024-09-25
Augmented reality (AR) takes digital images and superimposes them onto real-world views. But AR is more than a new way to play video games; it could transform surgery and self-driving cars. To make the technology easier to integrate into common personal devices, researchers report in ACS Photonics how to combine two optical technologies into a single, high-resolution AR display. In an eyeglasses prototype, the researchers enhanced image quality with a computer algorithm that removed distortions.
AR systems, like those in bulky goggles and automobile head-up displays, require portable optical components. But shrinking the typical four-lens AR system to the size of eyeglasses or smaller ...
High academic award for economic geographer Ron Boschma
2024-09-25
Professor Ron Boschma is the first Dutch person to receive the Prix Vautrin Lud, the highest academic award within the field of geography. The award will be presented in Saint-Dié-des-Vosges, France on 6 October. Prior to the award ceremony, Prof. Boschma will give an invited lecture at the Sorbonne University in Paris on 4 October. Boschma was nominated for the award in recognition of his scientific contributions to the field of economic geography, especially for laying the foundations of evolutionary economic geography and his research into regional diversification and innovation policy. The European Union’s regional policy is based in part on his ...
Study reveals mallards' flight responses ineffective in preventing vehicle collisions
2024-09-25
Research Highlights Risk to Both Humans and Wildlife, Suggests Need for New Collision Mitigation Strategies
A recent article published in PeerJ Life & Environment has uncovered insights into how mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) respond to approaching vehicles, revealing that these common waterbirds are poorly equipped to avoid collisions, particularly at high speeds. The research, which used both simulated and real-world vehicle approaches, highlights the urgent need for improved methods to reduce bird-vehicle collisions—events that are not only financially costly but also dangerous to both humans and wildlife.
The study focused ...
Home- vs office-based narrowband UV-B phototherapy for patients with psoriasis
2024-09-25
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial, home-based phototherapy was as effective as office-based phototherapy for plaque or guttate psoriasis in everyday clinical practice and had less burden to patients.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Joel M. Gelfand, MD, email joel.gelfand@pennmedicine.upenn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.3897)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Major boost in carbon capture and storage essential to reach 2°C climate target
2024-09-25
Large expansion of carbon capture and storage is necessary to fulfill the Paris Climate Agreement. Yet a new study led by Chalmers University of Technology, in Sweden and University of Bergen, in Norway, shows that without major efforts, the technology will not expand fast enough to meet the 2°C target and even with major efforts it is unlikely to expand fast enough for the 1.5°C target.
The idea behind carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology is to capture carbon dioxide then store it deep underground. Some applications of CCS, such ...
‘Invisible forest’ of algae thrives as ocean warms
2024-09-25
An “invisible forest” of phytoplankton is thriving in part of our warming ocean, new research shows.
Phytoplankton are tiny drifting organisms that do about half of the planet’s “primary production” (forming living cells by photosynthesis).
The new study, by the University of Exeter, examined phytoplankton at the ocean surface and the “subsurface” – a distinct layer of water beneath – to see how climate variability is affecting them.
Published in the journal Nature Climate Change, the findings show these two communities are reacting differently.
Over the last decade, the total “biomass” (living material) of subsurface ...
How do rare genetic variants affect health? AI provides more accurate predictions
2024-09-25
Whether we are predisposed to particular diseases depends to a large extent on the countless variants in our genome. However, particularly in the case of genetic variants that only rarely occur in the population, the influence on the presentation of certain pathological traits has so far been difficult to determine. Researchers from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the Technical University of Munich have introduced an algorithm based on deep learning that can predict the effects of rare genetic variants. The method allows persons with high risk of disease to be distinguished more precisely and facilitates the identification ...
Replacing hype about artificial intelligence with accurate measurements of success
2024-09-25
The hype surrounding machine learning, a form of artificial intelligence, can make it seem like it is only a matter of time before such techniques are used to solve all scientific problems. While impressive claims are often made, those claims do not always hold up under scrutiny. Machine learning may be useful for solving some problems but falls short for others.
In a new paper in Nature Machine Intelligence, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) and Princeton University performed a systematic review of research comparing machine learning to traditional methods for solving ...
Researchers harness AI to repurpose existing drugs for treatment of rare diseases
2024-09-25
There are more than 7,000 rare and undiagnosed diseases globally.
Although each condition occurs in a small number of individuals, collectively these diseases exert a staggering human and economic toll because they affect some 300 million people worldwide.
Yet, with a mere 5 to 7 percent of these conditions having an FDA-approved drug, they remain largely untreated or undertreated.
Developing new medicines represents a daunting challenge, but a new artificial intelligence tool can propel the discovery of new therapies from existing medicines, offering hope for patients with rare and neglected conditions and for the clinicians who treat them.
The AI model, called TxGNN, is the first one ...
Combination treatment improves response to immunotherapy for lung cancer
2024-09-25
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 10:00hrs BST Wednesday 25 September 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
Combination treatment improves response to immunotherapy for lung cancer
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute, in collaboration with Revolution Medicines, have tested a combination of treatments in mice with lung cancer and shown that these allow immunotherapies to target non-responsive tumours.
Their findings show that targeting tumours in ...