Combination treatment improves response to immunotherapy for lung cancer
2024-09-25
(Press-News.org) Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 10:00hrs BST Wednesday 25 September 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
Combination treatment improves response to immunotherapy for lung cancer
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute, in collaboration with Revolution Medicines, have tested a combination of treatments in mice with lung cancer and shown that these allow immunotherapies to target non-responsive tumours.
Their findings show that targeting tumours in different ways simultaneously might increase response to treatments.
In research published today in Nature Communications, the scientists tested a combination of tool compounds in mice with lung cancer. These compounds were used to represent:
Targeted drugs which block a cancer-causing protein called KRAS G12C. These have been approved for use in lung cancer, but often fail to benefit patients in the long term because the tumours develop resistance to these medicines over time.
Immunotherapy drugs. These are designed to stimulate the immune system to fight the tumour, but only 20% of people with lung cancer respond, as tumours often block immune cells from entering.
The researchers combined a newly identified KRAS G12C inhibitor1, with a compound that blocks a protein called SHP2, which inhibits cancer cells and can also activate tumor immunity.
These two inhibitors were combined with an immune checkpoint inhibitor, which blocks proteins that help the cancer cells hide from the immune system.
In mice with functional immune systems, the triplet combination shrank the tumours and, in some mice, fully eradicated them. These mice were also more resistant to the lung cancer coming back after treatment.
The team believe that these targeted compounds provide a window of opportunity where the immune checkpoint inhibitor can kick into gear and allow the body’s natural defences to attack the tumour.
Even in mice with ‘immune cold’ tumours that are normally unresponsive to immunotherapy, the combination allowed tumours to become sensitised to the immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Given the success in studies with mice, an evaluation of the combination could be conducted in people with lung cancer to determine if it has a similar effect. Research will also be needed to understand and counteract potential side effects associated with combining treatments.
Julian Downward, Principal Group Leader of the Oncogene Biology Laboratory at the Crick, and co-senior author with Miriam Molina-Arcas, said: “Blocking genes like KRAS in lung cancer has led to some exciting new developments, but we still see problems with resistance. We’ve now been able to report partial or complete eradication of tumours in mice by combining KRAS and SHP2 inhibitors with immunotherapy. We also showed that this combination therapy allows ‘immune cold’ tumours to respond to the body’s own defences.”
Panos Anastasiou, PhD student in the Oncogene Biology Laboratory at the Crick, and first author, said: “Our work stresses the importance of targeting tumours from all angles, especially ones that don’t respond easily to treatment. It will be critical to see if the combination of inhibitors works in the same way in humans.”
Panos worked with the Experimental Histopathology, Bioinformatics and Biostatistics, Genomics, Scientific Computing, Flow Cytometry, Cell Services and Biological Resources teams at the Crick. The research was funded by a collaborative research agreement with Revolution Medicines, with additional funding from the European Union and the Wellcome Trust.
-ENDS-
For further information, contact: press@crick.ac.uk or +44 (0)20 3796 5252
Notes to Editors
The newly identified KRAS G12C inhibitor targets the active or ‘ON’ form of KRAS compared with the drugs currently approved for clinical use which target the inactive or ‘OFF’ form of KRAS G12C.
Reference: Anastasiou, P. et al. (2024). Combining RAS(ON) G12C-selective inhibitor with SHP2 inhibition sensitises lung tumours to immune checkpoint blockade. Nature Communications. 10.1038/s41467-024-52324-3.
The Francis Crick Institute is a biomedical discovery institute dedicated to understanding the fundamental biology underlying health and disease. Its work is helping to understand why disease develops and to translate discoveries into new ways to prevent, diagnose and treat illnesses such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, infections, and neurodegenerative diseases.
An independent organisation, its founding partners are the Medical Research Council (MRC), Cancer Research UK, Wellcome, UCL (University College London), Imperial College London and King’s College London.
The Crick was formed in 2015, and in 2016 it moved into a brand new state-of-the-art building in central London which brings together 1500 scientists and support staff working collaboratively across disciplines, making it the biggest biomedical research facility under a single roof in Europe.
http://crick.ac.uk/
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-25
Researchers led by Ryuhei Nakamura at the RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science (CSRS) in Japan and The Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) of Tokyo Institute of Technology have discovered inorganic nanostructures surrounding deep-ocean hydrothermal vents that are strikingly similar to molecules that make life as we know it possible. These nanostructures are self-organized and act as selective ion channels, which create energy that can be harnessed in the form of electricity. Published Sep. 25 in Nature Communications, the findings impact not only our understanding of how life began, but can also ...
2024-09-25
When thinking of animal camouflage, we typically imagine creatures remaining still, blending seamlessly into their surroundings. But remaining motionless isn’t always practical, and many animals are highly mobile, constantly moving through their environment to graze their food.
New research suggests that high-contrast patterns on animals’ bodies may serve a dual purpose: offering camouflage when stationary, then creating a ‘motion dazzle’ effect when moving, confusing potential predators into misjudging their location – and helping them avoid being ...
2024-09-25
New research published in Advanced Materials reports a novel nasal spray for preventing respiratory infections. The spray works by forming a protective coating on the nasal cavity, which captures airborne respiratory droplets and acts as a physical barrier against viruses and bacteria, while effectively neutralizing them.
In studies conducted on mice, the Pathogen Capture and Neutralizing Spray (PCANS) demonstrated up to 8 hours of nasal retention. In a severe Influenza A model, a single pre-exposure dose of PCANS resulted in a greater than 99.99% reduction ...
2024-09-25
In research published in Brain and Behavior, investigators found increased rates of menstrual irregularities in women living in areas affected by the 2023 earthquake in Turkey.
In the study, 309 women of reproductive age living in regions declared as disaster areas completed online forms 9 months after the earthquake. Responses revealed an increase of menstrual irregularities from 14.3% before the earthquake to 44.8% after the earthquake. Risk factors for menstrual irregularities included post-traumatic stress symptoms, chronic diseases, and smoking.
The findings reveal that reproductive health ...
2024-09-25
During missions into outer space, galactic cosmic radiation (GCR) will penetrate current spacecraft shielding and thus pose a significant risk to human health. Previous studies have shown that GCR can cause short-term cognitive deficits in male rodents. Now a study published in the Journal of Neurochemistry reveals that GCR exposure can also cause long-lasting learning deficits in female rodents.
The impact of GCR on cognition was lessened when mice were fed an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound called CDDO-EA.
Beyond ...
2024-09-25
Preventive health technologies—such as wrist-worn activity trackers or health and fitness apps—are popular tools for promoting wellbeing, but new research published in the Journal of Consumer Affairs reveals that consumer engagement with these technologies can be considered a double-edged sword.
The study, which involved 30 in-depth interviews with users, found that consumers engage with preventive health technologies based on a variety of health goals—for example, to lose weight, improve performance, monitor data of an enjoyable activity, or acquire a healthy routine.
These diverse goals led users ...
2024-09-25
Researchers from the Brigham detail how the spray they created may offer broad-spectrum protection from respiratory infections by COVID-19, influenza, everyday cold viruses, and pneumonia-causing bacteria
A new study details how a nasal spray formulated by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, may work to protect against viral and bacterial respiratory infections. Based on their preclinical studies, the researchers say the broad-spectrum nasal spray is long-lasting, safe, and, if validated in humans, could play a key role in reducing respiratory diseases ...
2024-09-25
Bacterial infections resulting in enteritis, sometimes extra-intestinal infections such as sepsis, continue to be a global health concern. A leading cause of diarrheal and extra-intestinal infectious mortality among children under 5 and elderly persons is infection with Campylobacter bacteria, against which there is no effective vaccine or medication. An Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has recently uncovered what could be an important step toward preventing, diagnosing, and treating a species of Campylobacter bacteria.
Researchers including Professor Shinji Yamasaki and Associate Professor Noritoshi Hatanaka of the Graduate School ...
2024-09-25
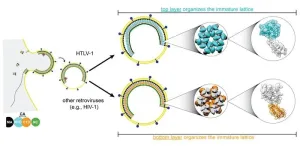
Martin Obr is on edge, anxiously waiting for his train to the airport. A storm called “Sabine” is brewing, shutting down all public transport. He catches his flight from Frankfurt to Vienna just in time.
Obr spent the last days in Germany meticulously analyzing what he calls the “perfect sample”. This sample helped him and Florian Schur from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) decode the structure of a virus called HTLV-1 (Human T-cell Leukemia Virus Type 1).
In collaboration with the University of Minnesota and Cornell University, ...
2024-09-25
Physics-informed virtual reality could be key to reducing the exposure of pedestrians and cyclists to harmful, non-exhaust vehicle emissions, according to a study published today (25 Sep) in the Royal Society Open Science journal.
The research lead by the University of Birmingham (supported by Rosetrees Trust and Research England QR Funding), targets the issue of major health risks and chronic diseases caused by exposure to unregulated particle pollutants from road, tyre and brake sources by providing easy, accessible guidance to the public, policy makers, and city planners, through immersive VR experiences.
Detailed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Combination treatment improves response to immunotherapy for lung cancer