Effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on renal and pulmonary function in hepatic decompensation with and without hepatorenal and hepatopulmonary syndromes
2024-09-25
(Press-News.org)
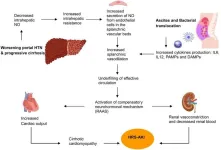
Cirrhosis is one of the leading causes of mortality from non-communicable diseases, with complications arising as liver function deteriorates. HRS and HPS represent the most severe outcomes of cirrhosis, associated with systemic vasodilation driven by elevated levels of vasodilators like nitric oxide (NO). These complications significantly impair renal and pulmonary functions, leading to high mortality rates. TIPS, by shunting blood from the portal to systemic circulation, can potentially improve renal function by increasing systemic blood volume. However, the diversion of NO through TIPS could exacerbate systemic hypotension, posing a risk to renal function.
TIPS Procedure
The TIPS procedure involves the creation of a shunt between the portal vein and a hepatic vein, effectively reducing portal hypertension. This minimally invasive procedure has shown efficacy in treating complications of cirrhosis such as variceal bleeding and refractory ascites. However, it carries risks, including hepatic encephalopathy, particularly in patients with pre-existing conditions that could worsen post-procedure outcomes.
Effects of TIPS on Renal Function
TIPS generally improves renal function in patients with portal hypertension, regardless of HRS presence. Studies have demonstrated that TIPS can increase glomerular filtration rates (GFR) and reduce serum creatinine levels, particularly in patients with refractory ascites. However, the data is insufficient to recommend TIPS specifically for HRS, as the procedure's benefits may be limited by the extent of liver damage in these patients.
Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS)
HRS is characterized by severe renal impairment in patients with advanced cirrhosis, with a poor prognosis even with current treatments like vasoconstrictors and albumin. The pathophysiology of HRS involves systemic inflammation, increased portal pressure, and circulatory dysfunction. Although TIPS has shown some potential in improving renal function in HRS, the evidence is limited and primarily based on small studies.
Effects of TIPS on Pulmonary Function
TIPS has shown inconsistent effects on pulmonary function, particularly in patients with HPS. While some studies report transient improvements in gas exchange, these effects are not sustained, and TIPS does not appear to significantly affect pulmonary gas exchange in patients without HPS. The potential for TIPS to exacerbate pulmonary hypertension due to the diversion of NO-rich blood is a concern, but the available data does not support a persistent decline in pulmonary function post-TIPS.
Hepatopulmonary Syndrome (HPS)
HPS involves hypoxemia due to pulmonary vasodilation in cirrhotic patients, leading to significant morbidity. The pathophysiology is linked to increased levels of vasodilators and angiogenic factors. Although liver transplantation remains the definitive treatment for HPS, the role of TIPS is less clear. Studies suggest that while TIPS may temporarily improve oxygenation, these benefits are not long-lasting.
Conclusions
TIPS is a valuable intervention for managing complications of cirrhosis, particularly in improving renal function in patients with portal hypertension. However, its role in treating HRS and HPS is less definitive. The procedure's effects on renal and pulmonary functions, especially in the context of these syndromes, require further investigation through large, randomized controlled trials to establish its safety and efficacy. While TIPS does not seem to impair renal or pulmonary function persistently, its benefits in HRS and HPS are not robust enough to recommend its use specifically for these conditions. Future research should focus on understanding the mechanisms behind the varied responses to TIPS in HRS and HPS and exploring its potential role as a therapeutic option in these critically ill patients.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2310-8819/JCTH-2024-00188
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
The Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology (JCTH) is owned by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University and published by XIA & HE Publishing Inc. JCTH publishes high quality, peer reviewed studies in the translational and clinical human health sciences of liver diseases. JCTH has established high standards for publication of original research, which are characterized by a study’s novelty, quality, and ethical conduct in the scientific process as well as in the communication of the research findings. Each issue includes articles by leading authorities on topics in hepatology that are germane to the most current challenges in the field. Special features include reports on the latest advances in drug development and technology that are relevant to liver diseases. Regular features of JCTH also include editorials, correspondences and invited commentaries on rapidly progressing areas in hepatology. All articles published by JCTH, both solicited and unsolicited, must pass our rigorous peer review process.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-25
A landmark study led by UCLA Health has begun to unravel one of the fundamental mysteries in neuroscience – how the human brain encodes and makes sense of the flow of time and experiences.
The study, published in the journal Nature, directly recorded the activity of individual neurons in humans and found specific types of brain cells fired in a way that mostly mirrored the order and structure of a person’s experience. They found the brain retains these unique firing patterns after the experience is concluded and can rapidly replay them while at rest. Furthermore, the brain is also able to utilize these learned patterns to ready itself for future stimuli following that experience. ...
2024-09-25
TAMPA, Fla. (Sept. 23, 2024) – The ocean’s twilight zone is deep, dark, and — according to new research — iron deficient.
No sunlight reaches this region 200 to 1,000 meters below the sea surface, where levels of iron, a key micronutrient, are so low that the growth of bacteria is restricted. To compensate, these bacteria produce molecules called siderophores, which help the bacteria scavenge trace amounts of iron from the surrounding seawater.
The paper detailing these unexpected findings from the Pacific Ocean will publish on Wednesday, Sept. 25, at 11 a.m. ET (4 p.m. London Time) in Nature, and will be viewable at that time at this link. The ...
2024-09-25
These fossils, belonging to the mammal-precursor species Brasilodon quadrangularis and Riograndia guaibensis, offer critical insights into the development of the mammalian jaw and middle ear, revealing evolutionary experiments that occurred millions of years earlier than previously thought.
Mammals stand out among vertebrates for their distinct jaw structure and the presence of three middle ear bones. This transition from earlier vertebrates, which had a single middle ear bone, has long fascinated scientists. The new study explores how mammal ancestors, known as cynodonts, evolved these features ...
2024-09-25
People with Down’s syndrome face a higher risk of developing Leukemia. Now researchers from the University of Copenhagen and Stanford University explain why, by identifying specific changes in blood cells of people with Down’s syndrome.
In the world, one out of 700 children are born with Down’s syndrome. A syndrome, where the child has an extra copy of chromosome 21, resulting in 47 chromosomes instead of 46. This typically results in characteristic physical features and some level of learning disability.
But newborns with Downs syndrome also tend to have an elevated number of red blood ...
2024-09-25
About The Study: Treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations were commonly detected, especially in individuals who were immunosuppressed in this cohort study of 156 participants. However, these mutations were generally present at low frequencies and were transient in nature, suggesting a low risk for the spread of nirmatrelvir resistance in the community with the current variants and drug usage patterns.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jonathan Z. Li, MD, MMsc, email jli@bwh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
2024-09-25
About The Study: In this study, semaglutide was associated with reduced opioid overdose risk in patients with comorbid type 2 diabetes and opioid use disorder, suggesting its potential therapeutic value for preventing overdoses. The results need validation from other data resources and study populations. Further research is warranted to investigate the underlying mechanisms and randomized clinical trials are necessary to corroborate the clinical effects on opioid use disorder.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Rong Xu, PhD, (rxx@case.edu) ...
2024-09-25
Food fermentation is the oldest production practice using microorganisms in human history. Milk fermentation, for example, can be traced back to 6000–4000 BC in India, and Mediterranean populations produced and consumed cheese as early as 7000 before present (BP).
Despite the long history of human consumption of fermented products, though, little has been known about the history of the use of fermentative microorganisms and the history of related cultural transmission. In particular, the evolutionary trajectories, especially functional adaptation, of these ...
2024-09-25
Adults with opioid use disorder who receive a higher daily dose of the opioid addiction treatment medication buprenorphine may have a lower risk of subsequent emergency department visits or use of inpatient services related to behavioral health (such as for mental health and substance use disorders) than adults receiving the recommended dose, according to an analysis funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). These findings suggest that higher buprenorphine doses could be more effective in managing opioid use disorder, which may be particularly relevant for improving treatment for those who use fentanyl, a major ...
2024-09-25
With the climate pattern known as El Niño in full force from mid-2023 to mid-2024, global temperatures broke records for 12 months in a row. As one of the strongest El Niño events on record, it was likely the main culprit of unprecedented heat, floods and droughts worldwide.
In a new study published Sep. 25 in the journal Nature, a University of Colorado Boulder climate scientist and collaborators reveal that the planet could see more frequent extreme El Niño events by 2050 if greenhouse gas emissions continue to increase.
“It’s ...
2024-09-25
Imagine being one cartwheel away from changing your appearance. One flip, and your brunette locks are platinum blond. That’s not too far from what happens in some prokaryotes, or single-cell organisms, such as bacteria, that undergo something called inversions.
A study led by scientists at Stanford Medicine has shown that inversions, which cause a physical flip of a segment of DNA and change an organism’s genetic identity, can occur within a single gene, challenging a central dogma of biology — that one gene can code ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on renal and pulmonary function in hepatic decompensation with and without hepatorenal and hepatopulmonary syndromes



