(Press-News.org) Amongst women who experience recurrent pregnancy loss, around 20% test positive for a specific antibody that targets the mother’s own body. A Kobe University-led research team now found a treatment that drastically increases these women’s chances of carrying to full-term without complications.
Recurrent pregnancy loss is a condition of women who have lost two or more pregnancies for non-obvious reasons. The Kobe University obstetrician TANIMURA Kenji and his team have previously found that in 20% of these women, they can detect a specific antibody in their blood that targets their own bodies. Tanimura explains: “There is no known treatment for this particular condition, but the antibodies have a similar target to those that play a role in a different condition that has an established treatment.” Therefore, he wanted to test whether that treatment also works in the cases with the newly discovered antibody.
Tanimura enlisted the help of obstetricians across five hospitals in Japan and over the course of two years analyzed the blood of consenting women suffering from recurrent pregnancy loss for the antibodies. If any of these women got pregnant during this time frame, their doctors would offer treatment options also containing those drugs that are effective against the chemically similar condition, specifically, low-dose aspirin or a drug called “heparin.” The research team then observed how many of the women who included these drugs in their treatment had full-term live births or pregnancy complications and compared that to the pregnancy outcomes in women who did not take either of the two drugs.
The Kobe University researchers now published their results in the journal Frontiers in Immunology. They report that women who received the treatment were much more likely to have live births (87% did) compared to the ones without treatment (of which only 50% had live births). In addition, amongst the live births, the treatment reduced the likelihood of complications from 50% to 6%. “The sample size was rather small (39 women received the treatment and 8 did not), but the results still clearly show that a treatment with low-dose aspirin or heparin is very effective in preventing pregnancy loss or complications also in women who have these newly discovered self-targeting antibodies,” summarizes Tanimura.
Many women who tested positive for the newly discovered self-targeting antibodies also tested positive for the previously known ones. However, the Kobe University-led team found that women who only had the newly discovered antibodies and who received the treatment were even more likely to have a live birth (93%) and, amongst these, none had pregnancy complications.
Looking ahead, Tanimura says: “The newly discovered self-targeting antibody has been demonstrated to be involved also in infertility and recurrent implantation failure, as well as a risk factor for arterial thrombosis in women with systemic rheumatic diseases. I therefore expect that studies about the effectivity of the treatment against a broader range of conditions might produce encouraging results.”
This research was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grants 24K12532, 20K09642, 23K08888, JP18H05279, 24K02691 and JP18K19450), the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (grants JP18gk0110018, JP21gk0110047, JP23fk0108682, JP22gn0110061, JP17fm0208004 and JP19ek0410053), the Japan Science and Technology Agency (grant JPMJMS2021), and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology Japan (grant JP190H04808). It was conducted in collaboration with researchers from the University of Toyama, the University of Yamanashi, the University of Tokyo, Okayama University, the Department of Public Health, Dokkyo Medical University and Osaka University.
Kobe University is a national university with roots dating back to the Kobe Commercial School founded in 1902. It is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive research universities with nearly 16,000 students and nearly 1,700 faculty in 10 faculties and schools and 15 graduate schools. Combining the social and natural sciences to cultivate leaders with an interdisciplinary perspective, Kobe University creates knowledge and fosters innovation to address society’s challenges.
END
Treatment for major cause of recurrent pregnancy loss
2024-09-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
In an era of climate change, clean water and reliable water storage for floods and droughts is a possibility!
2024-09-26
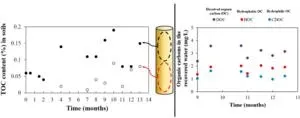
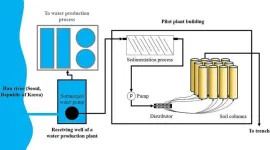
In recent years, the world has seen a recurrence of extreme floods and droughts due to climate change. In response to this, aquifer storage technology is being used for actual water supply in countries such as the United States, the Netherlands, and Australia. In South Korea, it rains intensively in the summer and extreme rainfall occurs, causing increasing difficulties in water supply in rural areas and island areas other than urban areas. In this situation, aquifer storage technology is attracting attention as a way to stably store and supply water.
Dr. Seongpil Jeong and Kyungjin Cho of the Center for Water Cycle Research at the Korea ...
Risk of buprenorphine triggering sudden opioid withdrawal is low
2024-09-26
Buprenorphine, an evidence-based treatment for opioid use disorder, is currently underprescribed because of concerns that it can cause ‘precipitated withdrawal’, in which the first dose causes sudden, intense pain and anxiety that resolves within a few hours. A new review of the best available evidence has found that the rate of buprenorphine-precipitated withdrawal in adults with opioid use disorder is low and should not be a barrier to use. The review is published in the scientific journal Addiction.
Lead author Dr Caroline Gregory, of the University of Ottawa, explains: “There is a lot of speculation ...
FAIR Health releases interactive tool tracking opioid abuse and dependence state by state
2024-09-26
NEW YORK, NY—September 26, 2024—Today FAIR Health released the Opioid Tracker, a free, interactive tool tracking opioid abuse and dependence state by state. A brief released simultaneously offers a user’s guide to the Opioid Tracker.
Available on FAIR Health’s website fairhealth.org, the Opioid Tracker includes a heat map representing the percentage of patients with opioid abuse and dependence diagnoses compared to all patients receiving medical services in 2023 for each state. Clicking on a state displays an infographic for ...
Duke-NUS discovery advances quest for treatment for age- and cancer-related muscle degeneration
2024-09-26
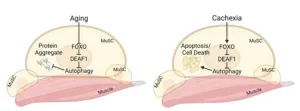
With the global population ageing rapidly, sarcopenia, a condition that affects millions of older adults and severely diminishes their quality of life, is emerging as an urgent public health issue. Now, a new discovery by scientists at Duke-NUS Medical School could lead to improved treatments for the condition.
In the study, published in the journal Autophagy, the scientists found that the levels of a certain type of protein, called DEAF1 (Deformed epidermal autoregulatory factor-1), need to be maintained within optimal levels ...
Women with premature ovarian insufficiency are at greater risk of severe autoimmune diseases
2024-09-26
Severe autoimmune conditions such Type I diabetes, Addison’s disease, lupus and inflammatory bowel disease, are between two to three times more common in women who have been diagnosed with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) compared to the general population.
The research, published today (Thursday) in Human Reproduction, one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals, is the largest to investigate the link between autoimmune conditions and POI, has followed nearly 20,000 women for ...
Remote video consultations linked to reduced depression and anxiety
2024-09-25
Remote video consultations between patients and mental health specialists show a small but significant improvement on symptoms of depression and anxiety, finds a trial published by The BMJ today.
Although the effect size is small, the researchers say the effect is still meaningful given the high levels of these disorders in the community.
Globally, depression and anxiety disorders are among the top leading causes of years lived with disability, but most people with depression and anxiety ...
Questions over safety and effectiveness of new Alzheimer’s drug
2024-09-25
The safety and effectiveness of donanemab - an Alzheimer’s drug recently approved by the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA) - is called into question in an investigation published by The BMJ today.
Journalists Jeanne Lenzer and Shannon Brownlee explore concerns not only about its effectiveness and the number of deaths among patients taking the drug, but also about financial ties to drug makers among the “independent” advisory panellists who recommended approval.
Donanemab, developed by Eli Lilly, is the latest in a new class ...
Additional GP funding has been squeezed this year, finds BMJ investigation
2024-09-25
Budgetary decisions by commissioners across England are affecting GPs’ ability to offer their patients what most people regard as essential services and forcing some practices to close, an investigation by The BMJ has found.
This year, eight in 10 Integrated Care Boards (ICBs) - responsible for planning health services for their local population - either reduced or froze discretionary funding for general practices as a proportion of their overall budget for services such as taking blood, wound care, ...
AI could predict breast cancer risk via ‘zombie cells’
2024-09-25
Women worldwide could see better treatment with new AI technology which enables better detection of damaged cells and more precisely predict the risk of getting breast cancer, shows new research from the University of Copenhagen.
Breast cancer is one of the most common types of cancer. In 2022, the disease caused 670,000 deaths worldwide. Now, a new study from the University of Copenhagen shows that AI can help women with improved treatment by scanning for irregular-looking cells to give better risk assessment.
The study, published in The Lancet Digital Health, found that the AI technology was far better at predicting risk of cancer ...
Breakthrough research identifies new targets for wound healing
2024-09-25
(Thursday, 26 September 2024) Novel research, presented today at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress 2024, has identified key molecular targets that could significantly enhance the healing of both acute and chronic wounds.1
These findings represent a crucial advancement in wound care, paving the way for more effective treatment options and improved patient outcomes.
Globally, acute and chronic wounds affect nearly one billion people.2 In particular, chronic wounds pose a substantial economic burden on healthcare systems and severely impact ...