(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study highlights the wide variation of nonprofit hospitals’ tax benefit across states, its high concentration among a small number of hospitals, and the primary role played by state and local taxes. Policy efforts to strengthen nonprofit hospitals’ taxpayer accountability are likely to be more effective when pursued at the local level.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ge Bai, PhD, CPA, email gbai@jhu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.13413)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.13413?guestAccessKey=9e08842a-8f7c-4038-a5cc-c2e509bde2a6&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=092624
END
Estimation of tax benefit of nonprofit hospitals
JAMA
2024-09-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists discover gene responsible for rare, inherited eye disease
2024-09-26
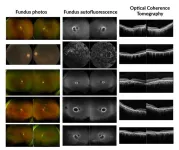
Scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their colleagues have identified a gene responsible for some inherited retinal diseases (IRDs), which are a group of disorders that damage the eye’s light-sensing retina and threatens vision. Though IRDs affect more than 2 million people worldwide, each individual disease is rare, complicating efforts to identify enough people to study and conduct clinical trials to develop treatment. The study’s findings published today in JAMA Ophthalmology.
In a small study of six unrelated participants, researchers linked the gene UBAP1L to different forms of ...
Scientists discover "pause button" in human development
2024-09-26
In some mammals, the timing of the normally continuous embryonic development can be altered to improve the chances of survival for both the embryo and the mother. This mechanism to temporarily slow development, called embryonic diapause, often happens at the blastocyst stage, just before the embryo implants in the uterus. During diapause, the embryo remains free-floating and pregnancy is extended. This dormant state can be maintained for weeks or months before development is resumed, when conditions are favorable. Although not all mammals use this reproductive ...
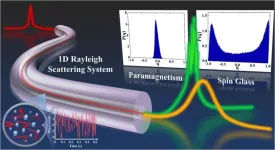
Replica symmetry breaking in 1D Rayleigh scattering system: Theory and validations
2024-09-26
In both the natural world and human society, there commonly exist complex systems such as climate systems, ecological systems, and network systems. Due to the involvement of numerous interacting elements, complex systems can stay in multiple different states, and their overall behavior generally exhibits randomness and high disorder. For example, due to the complex interactions between factors such as solar radiation, terrain, and ocean currents, the climate system can exhibit various states like sunny, cloudy, and rainy. The dynamic changes and mutual influences of these factors make the behavior of the climate highly uncertain and difficult to predict accurately. For instance, the formation ...
New research identifies strong link between childhood opportunities and educational attainment and earnings as a young adult
2024-09-26
Washington, September 26, 2024—The number of educational opportunities that children accrue at home, in early education and care, at school, in afterschool programs, and in their communities as they grow up are strongly linked to their educational attainment and earnings in early adulthood, according to new research. The results indicate that the large opportunity gaps between low- and high-income households from birth through the end of high school largely explain differences in educational and income achievement ...
Statement by NIH on research misconduct findings
2024-09-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE
Thursday, September 26, 2024 - 9 a.m. EDT
Contact:
NIH Office of Communications and Public Liaison
NIH News Media Branch
301-496-5787
Statement by NIH on Research Misconduct Findings
Following an investigation, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has made findings of research misconduct against Eliezer Masliah, M.D., due to falsification and/or fabrication involving re-use and relabel of figure panels representing different experimental results in two publications. NIH will notify the two journals of its findings so that appropriate action can be taken. NIH initiated its research misconduct review process ...
Pregnant women who sleep less than 7 hours a night may have children with developmental delays
2024-09-26
WASHINGTON—Pregnant women who do not get enough sleep may be at higher risk of having children with neurodevelopmental delays, according to new research published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Short sleep duration (SSD) is defined as sleeping less than seven hours per night. Pregnant woman may have trouble sleeping due to hormonal changes, pregnancy discomfort, frequent urination, and other factors.
It’s been reported that almost 40% of pregnant women have SSD. These women may have ...
ESO telescope captures the most detailed infrared map ever of our Milky Way
2024-09-26
Astronomers have published a gigantic infrared map of the Milky Way containing more than 1.5 billion objects ― the most detailed one ever made. Using the European Southern Observatory’s VISTA telescope, the team monitored the central regions of our Galaxy over more than 13 years. At 500 terabytes of data, this is the largest observational project ever carried out with an ESO telescope.
“We made so many discoveries, we have changed the view of our Galaxy forever,” says Dante Minniti, ...
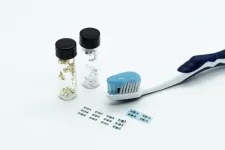
An edible toothpaste-based transistor
2024-09-26
Milan (Italy), 26 September 2024 - A toothpaste-based transistor is the latest innovation from the research team at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT-Italian Institute of Technology) in Milan, which pushes the boundaries of edible electronics. This innovative nano-device is expected to become a key component of future smart pills, designed to monitor health conditions from within the body and then safely dissolve after completing their function. The research findings have been published in the journal Advanced Science.
Several commercial toothpaste formulations contain crystals of copper phthalocyanine, a blue pigment that acts as a whitening ...
Increased antioxidants and phenolic compounds produced in salted red perilla leaves during Japanese apricot pickling
2024-09-26
The diverse biochemical composition of Japanese apricot fruits explains their broad spectrum of action on the human body. The high levels of key phenolic compounds and hydroxycinnamic acids contribute to various health benefits including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties.
A recent study published in Food Research International on July 19, 2024, led by Prof. Yukiharu Ogawa and Jutalak Suwannachot from Chiba University, quantitatively evaluated the changes in phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity during the production of Shiso-zuke Umeboshi (PP). The study also simulated the digestive process to characterize the release of these compounds and ...
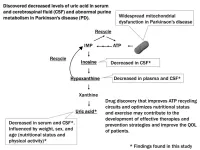
Unlocking the energy crisis in Parkinson’s: New findings offer hope for future treatment
2024-09-26
Parkinson’s disease (PD), the second most common neurodegenerative disorder globally, has long baffled scientists with its progressive nature and debilitating effects on motor function.
A recent study from the School of Medicine at Fujita Health University has brought new insights into the metabolic disruptions experienced by patients with PD. By analyzing the blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the patients, researchers have discovered critical impairments in purine metabolism and the recycling of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)—the molecule responsible for energy production in cells.
For years, scientists have noted the decreased levels ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
[Press-News.org] Estimation of tax benefit of nonprofit hospitalsJAMA