COVID-19 linked to increased risk of acute kidney disorders: New study reveals time-varying effects
2024-09-30
(Press-News.org)
Researchers from West China Hospital, Sichuan University, have conducted a study revealing a significant association between COVID-19 and acute kidney disorders (AKD), including acute kidney injury (AKI), that varies over time. The study, led by Dr. Li Chunyang and Dr. Zeng Xiaoxi from the West China Biomedical Big Data Center, was recently published in the journal Health Data Science.
COVID-19, known for its impact on the respiratory system, also affects other organs, including the kidneys. The study aimed to investigate the time-dependent effects of COVID-19 on acute kidney disorders. Using data from the UK Biobank, the researchers conducted a matched cohort study and a Mendelian randomization analysis to explore both the association and potential causality between COVID-19 and AKD.
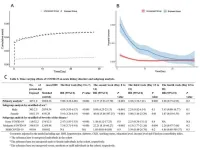
"Our research highlights the time-varying risk of acute kidney disorders in COVID-19 patients, particularly in the first three weeks following infection," said Dr. Li Chunyang, a research associate at the West China Biomedical Big Data Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University. "We observed that the hazard effects peak in the second week post-infection and decline by the fourth week."
The study involved 10,121 COVID-19 patients matched with 29,004 unexposed historical controls based on age, sex, deprivation index, and hospitalization status. A conditional and time-varying Cox proportional hazard regression model was used to assess the association between COVID-19 and AKD within four weeks of infection. The results indicated that the risk of AKD peaked during the second week after infection (hazard ratio, 12.77; 95% confidence interval, 5.93–27.70) and decreased by the fourth week (hazard ratio, 2.28; 95% confidence interval, 0.75–6.93).
The study also found that only patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 showed a significant risk of acute worsening of renal function. This risk was not observed in patients with mild COVID-19. A one-sample Mendelian randomization analysis further demonstrated a potential "short-term" causal effect of COVID-19 on AKD risk, primarily confined to the first week after infection.
The findings suggest that healthcare providers should closely monitor kidney function in COVID-19 patients, particularly those with moderate to severe cases, during the critical first few weeks after infection. The study provides important insights into the temporal nature of COVID-19's impact on kidney health, which may guide clinical management and follow-up strategies.
Looking ahead, the research team plans to further explore the time-varying impact of COVID-19 on the risk of incident acute kidney disorders in East Asian populations. Additionally, they aim to investigate the underlying molecular mechanisms that may link COVID-19 to subsequent acute kidney disorders to establish more definitive causal pathways.
"The molecular mechanisms behind the association between COVID-19 and kidney damage remain unclear," added Dr. Zeng Xiaoxi, an associate professor in the Nephrology Department at West China Hospital. "Our future research will focus on elucidating these mechanisms and verifying causality, which could pave the way for targeted interventions."
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-30
A new hand-held scanner developed by UCL researchers can generate highly detailed 3D photoacoustic images in just seconds, paving the way for their use in a clinical setting for the first time and offering the potential for earlier disease diagnosis.
In the study, published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, the team show their technology can deliver photoacoustic tomography (PAT) imaging scans to doctors in real time, providing them with accurate and intricate images of blood vessels, helping inform patient care.
Photoacoustic ...
2024-09-30
Kunming, China - A team of researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences has uncovered compelling evidence of a genetic link between bipolar disorder type I (BD-I) and epilepsy, potentially revolutionizing our understanding of these complex neuropsychiatric conditions. The study, published in Genomic Psychiatry on September 30, 2024, reveals shared genetic variants and a causal relationship between the two disorders, opening new avenues for research and treatment.
Led by Dr. Ming Li from the Kunming ...
2024-09-30
Lead researcher Dr Sarah Nason, from Bangor University’s School of History, Law and Social Sciences explained: “Debt, benefits, special educational needs, healthcare issues, these are everyday problems that many of us face, and it’s only natural to turn to people you know and trust for help and advice. However, we found that having to talk to more people or support services was an indicator that the problem was more complex and difficult to resolve.”
The team studied four distinct areas across England and Wales: Bryngwran, a village on Anglesey in North Wales; Deeplish, a district of Rochdale in Greater ...
2024-09-30
Aging societies and population decline have been on the rise globally, but in Japan, the situation has exasperated tenfold. A staggering 36.21 million people, or 28.9% of the populace, are 65 and over. Further, 74.6% of Japan’s 1,747 cities are categorized as shrinking, with urban policies struggling to keep up with the decline. However, the factors that correlate with population changes in cities of varying sizes have not been clarified.
Dr. Haruka Kato, a junior associate professor at Osaka Metropolitan University, ...
2024-09-30
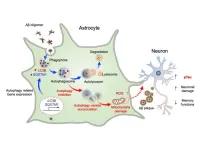
A research team led by Dr. Hoon Ryu from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Sang-Rok Oh) Brain Disease Research Group, in collaboration with Director Justin C. Lee of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, President Do-Young Noh) and Professor Junghee Lee from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, has uncovered a new mechanism involving astrocytes for treating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and proposed a novel therapeutic target. In this study, the researchers revealed that autophagy pathway ...
2024-09-30
Media contacts:
Lisa Robinson, lrobinson@aap.org
Alex Hulvalchick, ahulvalchick@aap.org
American Academy of Pediatrics Announces its First Clinical Practice Guideline for Opioid Prescriptions
Pediatricians should prescribe opioids for pain when necessary, with recommended precautions in place to increase safety, according to a clinical practice guideline released during the AAP 2024 National Conference & Exhibition
ORLANDO, Fla.--The American Academy of Pediatrics has published its first clinical ...
2024-09-30
Drivers of electric vehicles (EVs) are more likely to be involved in at-fault road traffic accidents than drivers of petrol and diesel cars, research by Lero, the Research Ireland Centre for Software, at University of Limerick and Universitat de Barcelona, reveals.
In the analysis of insurance claims and data from onboard sensors, due to be published in the November issue of the journal Accident Analysis & Prevention, the Lero researchers reveal a number of key findings:
Electric and hybrid drivers exhibit different behaviours ...
2024-09-30
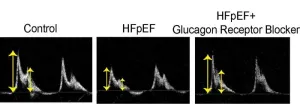
Duke-NUS scientists and their collaborators have discovered a potential new treatment for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), a type of heart disease that is notoriously difficult to treat. The team discovered that the diseased heart cells had high levels of glucagon activity, a pancreatic hormone that raises blood sugar (glucose) levels. Armed with this novel insight, the scientists demonstrated that a drug that blocks the hormone’s activity, can significantly improve heart ...
2024-09-29
WASHINGTON, September 29, 2024 — A substantial number of patients with brain metastases who experience cognitive side effects following radiation therapy may fully regain cognitive function, according to a pooled analysis of three large, phase III clinical trials. Recovery was more likely for people treated with conformal, or highly targeted, radiation techniques, compared to standard whole-brain treatment. The findings will be presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) ...
2024-09-29
WASHINGTON, September 29, 2024 — A radiopharmaceutical therapy that has successfully extended progression-free survival for patients with neuroendocrine tumors shows early promise for delivering similar benefits to patients with difficult-to-treat meningioma, a type of brain tumor. Findings of the nonrandomized phase II study will be presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting.
“We’ve found a therapy with a meaningful signal for effectiveness and safety for people with refractory meningioma, a condition with no ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] COVID-19 linked to increased risk of acute kidney disorders: New study reveals time-varying effects