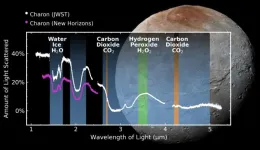
(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — October 1, 2024 — A Southwest Research Institute-led team has detected carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide for the first time on the frozen surface of Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, using observations from the James Webb Space Telescope. These discoveries add to Charon’s known chemical inventory, previously identified by ground- and space-based observations, that includes water ice, ammonia-bearing species and the organic materials responsible for Charon’s gray and red coloration.
“Charon is the only midsized Kuiper Belt object, in the range of 300 to 1,000 miles in diameter, that has been geologically mapped, thanks to the SwRI-led New Horizons mission, which flew by the Pluto system in 2015,” said SwRI’s Dr. Silvia Protopapa, lead author of a new Nature Communications paper and co-investigator of the New Horizons mission. “Unlike many of the larger objects in the Kuiper Belt, the surface of Charon is not obscured by highly volatile ices such as methane and therefore provides valuable insights into how processes like sunlight exposure and cratering affect these distant bodies.”
The Webb telescope is an ideal platform for detailed exploration of Charon and other icy bodies in the region beyond the orbit of Neptune. In 2022 and 2023, the team used Webb’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph to obtain four observations of the Pluto-Charon system. Different viewing geometries provided full coverage of Charon’s northern hemisphere.
“The advanced observational capabilities of Webb enabled our team to explore the light scattered from Charon’s surface at longer wavelengths than what was previously possible, expanding our understanding of the complexity of this fascinating object,” said Dr. Ian Wong, a staff scientist at the Space Telescope Science Institute and co-author of the paper.
The extended wavelength coverage of Charon’s Webb measurements reveals signatures of carbon dioxide. The team compared the spectroscopic observations with laboratory measurements and detailed spectral models of the surface, concluding that carbon dioxide is present primarily as a surface veneer on a water ice-rich subsurface.
“Our preferred interpretation is that the upper layer of carbon dioxide originates from the interior and has been exposed to the surface through cratering events. Carbon dioxide is known to be present in regions of the protoplanetary disk from which the Pluto system formed,” Protopapa said.
The presence of hydrogen peroxide on the surface of Charon clearly indicates that the water ice-rich surface is altered by solar ultraviolet light and energetic particles from the solar wind and galactic cosmic rays. Hydrogen peroxide forms from oxygen and hydrogen atoms originating from the breakup of water ice due to incoming ions, electrons or photons.
“Laboratory experiments conducted at SwRI’s CLASSE (Center for Laboratory Astrophysics and Space Science Experiments) facility were instrumental in demonstrating that hydrogen peroxide can form even in mixtures of carbon dioxide and water ice under conditions analogous to those at Charon,” said SwRI’s Dr. Ujjwal Raut, leader of CLASSE lab and second author of the paper.
The team’s research showcases the Webb telescope’s unparalleled capability to uncover complex surface signatures shaped by impacts and irradiation processes.
“The new insights were made possible by the synergy between Webb observations, spectral modeling and laboratory experiments and are possibly applicable to other similar midsized objects beyond Neptune,” said Protopapa.
To access the Nature Communications paper, “Detection of carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide on the stratified surface of Charon with JWST,” see https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-51826-4.
See also the ‘Behind the Paper’ post from lead author Dr. Silvia Protopapa on the Springer Nature Research Communities webpage.
The data used in this work were acquired with the JWST/NIRSpec instrument through Program 1191 (PI: J. Stansberry).
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/planetary-science.
END
SwRI-led team discovers carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide on Pluto’s moon Charon
Charon’s surface preserves materials from both formation and evolutionary processes
2024-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
More clarity on hereditary colorectal cancer
2024-10-01
The genetic confirmation of a suspected diagnosis of "hereditary colorectal cancer" is of great importance for the medical care of affected families. However, many of the variants identified in the known genes cannot yet be reliably classified in terms of their causal role in tumor formation. Under the leadership of the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn, an international team of researchers has reassessed the medical relevance of a significant number of unclear variants and thus significantly ...
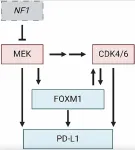
FOXM1 and PD-L1 in CDK4/6-MEK resistance in nerve tumors
2024-10-01
“We suggest that future therapeutic strategies targeting the oncogenic network of CDK4/6, MEK, PD-L1, and FOXM1 represent exciting future treatment options for MPNST patients.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 1, 2024 – A new mini review was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on September 30, 2024, entitled, “Linking FOXM1 and PD-L1 to CDK4/6-MEK targeted therapy resistance in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors.”
As highlighted in the abstract of this paper, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs) are aggressive, Ras-driven sarcomas characterized ...
McMaster University researchers identify new therapeutic approach to preventing cancer from spreading to the brain
2024-10-01
Researchers at McMaster University have identified a new therapeutic approach to preventing cancer from spreading to the brain.
In a new study, published recently in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, researchers Sheila Singh and Jakob Magolan discovered a critical vulnerability in metastatic brain cancer, which they say can be exploited with new drugs to prevent spread.
Singh, a professor in McMaster’s Department of Surgery and director of the Centre for Discovery in Cancer Research, says brain metastases are becoming increasingly prevalent and are extremely fatal, with 90 per cent of patients dying within one ...
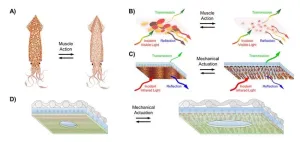
Squid-inspired fabric for temperature-controlled clothing
2024-10-01
WASHINGTON, October 1, 2024 – Too warm with a jacket on but too cold without it? Athletic apparel brands boast temperature-controlling fabrics that adapt to every climate with lightweight but warm products. Yet, consider a fabric that you can adjust to fit your specific temperature needs.
Inspired by the dynamic color-changing properties of squid skin, researchers from the University of California, Irvine developed a method to manufacture a heat-adjusting material that is breathable and washable and can be integrated into flexible fabric. They published their ...
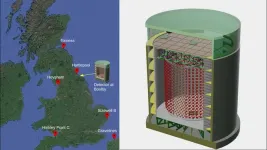
Using antimatter to detect nuclear radiation
2024-10-01
WASHINGTON, Oct. 1, 2024 – Nuclear fission reactors act as a key power source for many parts of the world and worldwide power capacity is expected to nearly double by 2050. One issue, however, is the difficulty of discerning whether a nuclear reactor is being used to also create material for nuclear weapons. Capturing and analyzing antimatter particles has shown promise for monitoring what specific reactor operations are occurring, even from hundreds of miles away.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Sheffield and the University of Hawaii developed ...
Modeling the minutia of motor manipulation with AI
2024-10-01
In neuroscience and biomedical engineering, accurately modeling the complex movements of the human hand has long been a significant challenge. Current models often struggle to capture the intricate interplay between the brain's motor commands and the physical actions of muscles and tendons. This gap not only hinders scientific progress but also limits the development of effective neuroprosthetics aimed at restoring hand function for those with limb loss or paralysis.
EPFL professor Alexander Mathis and his team have developed an AI-driven approach that ...
Survival gap eliminated for Black cord blood recipients with blood cancers, study finds
2024-10-01
Patients who receive umbilical cord blood transplants for blood cancers now live equally long regardless of their race, new research from UVA Cancer Center shows.
The findings, from UVA Health’s Karen Ballen, MD, and collaborators, suggests that a previously identified survival gap for Black recipients has closed and that overall survival for all recipients has increased.
The retrospective analysis looked at more than 2,600 adults and children with blood cancers who received cord blood between 2007 and 2017 ...
Nominate a stroke hero today: 2025 Stroke Hero Awards open for submissions
2024-10-01
DALLAS, Oct. 1, 2024 – Strokes can strike at any age, challenging survivors to overcome physical, emotional and cognitive changes. Nominations are open now for the 2025 Stroke Hero Awards from the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association, which is celebrating a century of lifesaving impact this year. The awards recognize stroke survivors, caregivers, advocates and experts making a difference in the stroke community.
Every 40 seconds someone in the U.S. has a stroke[1], according to the American Heart Association’s 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistical Update. Nearly 1 in 4 stroke survivors face the ...
Seven years on, INSEAD study reveals #MeToo's unexpected impact
2024-10-01
Seven years after actor Alyssa Milano’s tweet launched the #MeToo movement into the global consciousness, attitudes towards sexual harassment and assault have shifted in many countries. A new study shows that the movement’s impact doesn’t stop there.
INSEAD professors Frédéric Godart and David Dubois, alongside Clément Bellet of Erasmus University Rotterdam, found that #MeToo triggered far-reaching changes in consumer behaviour. Sales of stereotypically feminine shoes like high heels dropped significantly weeks after the #MeToo movement swept the media ...
Addressing the geriatric healthcare workforce shortage
2024-10-01
INDIANAPOLIS – The pandemic has highlighted the acute shortage of nurses and nursing assistants needed to care for the growing number of older adults in long-term care facilities. Yet getting nursing students excited, engaged and feeling competent to take on the challenges of caring for nursing home patients has proved elusive.
To address this critical workforce gap, researchers from Regenstrief Institute and the Indiana University School of Medicine have developed and tested an innovative curriculum for nursing students, exposing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] SwRI-led team discovers carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide on Pluto’s moon CharonCharon’s surface preserves materials from both formation and evolutionary processes