(Press-News.org) When millions of people went into lockdown during the pandemic, they went in search of new at-home hobbies to help cure their boredom. Among them was making sourdough bread. In addition to being sustainable for its use of natural ingredients and traditional methods which date back thousands of years to ancient Egypt, it also is valued for its nutritional benefits. For example, studies have shown that sourdough contains more vitamins, minerals and antioxidants compared to many other types of bread. For people with mild sensitivities to gluten, sourdough bread can be easier to digest since much of the gluten is broken down during the fermentation process. What’s more, many lactic acid bacteria species, which are foundational to sourdough, are considered probiotics, associated with improved gastrointestinal health.
A Flavor Profile Years in the Making
The process of making sourdough bread begins with a sourdough starter. These starters are created when microbes – communities of bacteria and yeast – stabilize in a flour and water mixture. Known as a microbiome, this community of wild yeast and bacteria is what makes sourdough bread rise and contributes to its taste and texture. Sourdough notably differs from most bread because it relies on this starter of wild microbes to help it rise instead of baker’s yeast packets.
Many sourdough starters are preserved over generations, with some samples dating back thousands of years. To maintain a sourdough starter, you extract a sample from a previous dough and mix it into new flour and water. With enough transfers of the sourdough starter, the microbial community will be composed of the yeast, lactic acid bacteria (LAB), and acetic acid bacteria (AAB) that are best adapted to the sourdough environment. What makes different sourdough starters unique are the varying strains of yeast and bacteria that produce the distinctive sour flavor.
Testing Genetic Diversity
Advances in sequencing technology have enabled researchers to rapidly profile microbial communities, such as the sourdough microbiome. At Syracuse University, members of biology professor Angela Oliverio’s lab have been studying acetic acid bacteria to determine how genetic diversity of AAB impacts sourdough communities.
While previous research has focused more on lactic acid bacteria and yeast, the ecology, genomic diversity, and functional contributions of AAB in sourdough remain largely unknown. Beryl Rappaport, a Ph.D. student in Oliverio’s group, recently led a paper published in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology, where she and other sourdough scientists, including Oliverio, Nimshika Senewiratne from the Oliverio lab, SU biology professor Sarah Lucas, and professor Ben Wolfe from Tufts University, sequenced 29 AAB genomes from a collection of over 500 sourdough starters and constructed synthetic starter communities in the lab to define the ways in which AAB shape emergent properties of sourdough. The team's work was supported by a National Science Foundation grant awarded to Oliverio earlier this year.
“While not as common in sourdough as lactic acid bacteria, acetic acid bacteria are better known for their dominant roles in other fermented foods like vinegar and kombucha,” says Rappaport. “For this study, we were interested in following up on previous findings which stated that when present in sourdough, AAB seems to have a strong impact on key properties including scent profile and metabolite production, which shape overall flavor formation.”
To assess the consequences of AAB on the emergent function of sourdough starter microbiomes, their team tested 10 strains of AAB, some distantly related and some very closely related. They set up manipulative experiments with these 10 strains, adding each one to a community of yeast and LAB. They kept a separate community of just yeast and LAB to serve as the control.
“Since we can manipulate what microbes and what concentrations of microbes go into these synthetic sourdough communities, we could see the direct effects of adding each strain of AAB to sourdough,” says Rappaport. “As we expected, every strain of AAB lowered the pH of the synthetic sourdough (associated with increasing sourness) since they release acetic acid and other acids as byproducts of their metabolic processes. Unexpectedly, however, AAB that were more closely related did not release more similar compounds. In fact, there was high variation in metabolites, many related to flavor formation, even between strains of the same species.”
According to Rappaport, strain diversity is often overlooked in microbial communities, in part because it is difficult to identify and manipulate levels of diversity due to the vastness of microorganisms within a given community. The human gut biome alone can have roughly 100 trillion bacteria living in it! By zooming into the diversity among closer relatives in the lab, researchers can start to understand key interactions in microbiomes.
A New Starter Source
When it comes to baking, she says their findings offer bread makers a new direction to shape sourdough flavor and texture.
“Since AAB reliably acidified the starters we worked with and released a large variety of flavor compounds, bakers who want their sourdough to be more sour or to create new flavors may try sourcing a starter with AAB or attempt to capture AAB themselves,” says Rappaport. “We hope that this study helps to shine a light on the diversity of microbes found in sourdough and their important functional roles.”
Their research could also have implications on the health benefits of sourdough bread.
During the fermentation process, AAB generates acetic acid, which significantly aids in breaking down gluten and complex carbohydrates, enhancing the digestibility of sourdough. By examining the genetic diversity of AAB and its influence on acetic acid production, researchers can develop strains that optimize this process.
The Broader Impact
The team uses sourdough primarily for its use as a model system because the sourdough microbiome is relatively simple to culture and use for repeated experiments in the lab. But their results stretch far beyond baking.
“Our findings will be relevant to people interested in more complex microbial communities, like the human gut or soil,” says Rappaport. This is because the sourdough system can be used to ask questions about ecology and evolution which would be more difficult to ask with more complex systems.
When it comes to the human gut, microbial communities can help build resilience to infections and improve efficiency in breaking down complex carbohydrates, fiber, proteins and fats. In the case of soil, microbes help to break down organic matter and maintain overall soil ecosystem stability. There are many unknowns, however, about how multiple levels of genetic diversity impact these processes.
By recognizing how strain diversity can have community-wide consequences on a microbiome, the team’s insights could have wide-ranging benefits for human health, wellness and environmental sustainability.
END
A tool to enhance the taste and texture of sourdough and study the complexity of microbiomes
Syracuse University researchers explore how acetic acid bacteria shapes emergent properties of sourdough, with implications across complex microbial systems
2024-10-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Structure of a eukaryotic CRISPR-Cas homolog, Fanzor2, shows its promise for gene editing
2024-10-01
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – October 1, 2024) A revolution in biomedicine is currently underway, driven by the application of genome engineering tools such as the prokaryotic CRISPR-Cas9. New genome editing systems continue to be identified in different organisms, adding to the potential toolbox for various therapeutic applications. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital studied the evolutionary journey of Fanzors, eukaryotic genome-editing proteins. Using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), the researchers provided insights into the structural divergence ...
St. Jude names M. Madan Babu, PhD, senior vice president and chief data scientist
2024-10-01
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital today announced M. Madan Babu, PhD, FRS, as the institution’s first Chief Data Scientist, Senior Vice President for Data Science, and leader of the newly formed Office of Data Science. This $195 million research enterprise will have 115 new positions.
In his new role, Babu will bring new, advanced computing technologies and data science approaches to biomedical research. His team will also facilitate the integration of biological and biomedical ...
It all adds up: Study finds forever chemicals are more toxic as mixtures
2024-10-01
BUFFALO, N.Y. — A first-of-its-kind study has measured the toxicity of several types of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), better known as “forever chemicals,” when mixed together in the environment and in the human body.
The good news: Most of the tested chemicals’ individual cytotoxicity and neurotoxicity levels were relatively low.
The bad news: the chemicals acted together to make the entire mixture toxic.
“Though they are structurally similar, not all forever chemicals are ...
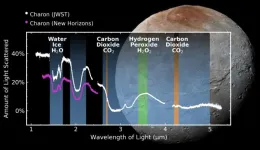
SwRI-led team discovers carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide on Pluto’s moon Charon
2024-10-01
SAN ANTONIO — October 1, 2024 — A Southwest Research Institute-led team has detected carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide for the first time on the frozen surface of Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, using observations from the James Webb Space Telescope. These discoveries add to Charon’s known chemical inventory, previously identified by ground- and space-based observations, that includes water ice, ammonia-bearing species and the organic materials responsible for Charon’s gray and red coloration.
“Charon is the only midsized Kuiper Belt object, in the range of 300 to 1,000 miles in diameter, that has been geologically mapped, thanks ...
More clarity on hereditary colorectal cancer
2024-10-01
The genetic confirmation of a suspected diagnosis of "hereditary colorectal cancer" is of great importance for the medical care of affected families. However, many of the variants identified in the known genes cannot yet be reliably classified in terms of their causal role in tumor formation. Under the leadership of the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn, an international team of researchers has reassessed the medical relevance of a significant number of unclear variants and thus significantly ...
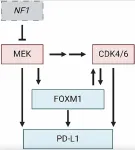
FOXM1 and PD-L1 in CDK4/6-MEK resistance in nerve tumors
2024-10-01
“We suggest that future therapeutic strategies targeting the oncogenic network of CDK4/6, MEK, PD-L1, and FOXM1 represent exciting future treatment options for MPNST patients.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 1, 2024 – A new mini review was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on September 30, 2024, entitled, “Linking FOXM1 and PD-L1 to CDK4/6-MEK targeted therapy resistance in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors.”
As highlighted in the abstract of this paper, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs) are aggressive, Ras-driven sarcomas characterized ...
McMaster University researchers identify new therapeutic approach to preventing cancer from spreading to the brain
2024-10-01
Researchers at McMaster University have identified a new therapeutic approach to preventing cancer from spreading to the brain.
In a new study, published recently in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, researchers Sheila Singh and Jakob Magolan discovered a critical vulnerability in metastatic brain cancer, which they say can be exploited with new drugs to prevent spread.
Singh, a professor in McMaster’s Department of Surgery and director of the Centre for Discovery in Cancer Research, says brain metastases are becoming increasingly prevalent and are extremely fatal, with 90 per cent of patients dying within one ...
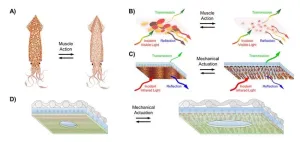
Squid-inspired fabric for temperature-controlled clothing
2024-10-01
WASHINGTON, October 1, 2024 – Too warm with a jacket on but too cold without it? Athletic apparel brands boast temperature-controlling fabrics that adapt to every climate with lightweight but warm products. Yet, consider a fabric that you can adjust to fit your specific temperature needs.
Inspired by the dynamic color-changing properties of squid skin, researchers from the University of California, Irvine developed a method to manufacture a heat-adjusting material that is breathable and washable and can be integrated into flexible fabric. They published their ...
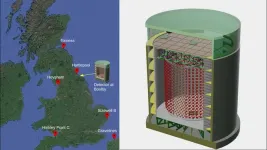
Using antimatter to detect nuclear radiation
2024-10-01
WASHINGTON, Oct. 1, 2024 – Nuclear fission reactors act as a key power source for many parts of the world and worldwide power capacity is expected to nearly double by 2050. One issue, however, is the difficulty of discerning whether a nuclear reactor is being used to also create material for nuclear weapons. Capturing and analyzing antimatter particles has shown promise for monitoring what specific reactor operations are occurring, even from hundreds of miles away.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Sheffield and the University of Hawaii developed ...
Modeling the minutia of motor manipulation with AI
2024-10-01
In neuroscience and biomedical engineering, accurately modeling the complex movements of the human hand has long been a significant challenge. Current models often struggle to capture the intricate interplay between the brain's motor commands and the physical actions of muscles and tendons. This gap not only hinders scientific progress but also limits the development of effective neuroprosthetics aimed at restoring hand function for those with limb loss or paralysis.
EPFL professor Alexander Mathis and his team have developed an AI-driven approach that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
[Press-News.org] A tool to enhance the taste and texture of sourdough and study the complexity of microbiomesSyracuse University researchers explore how acetic acid bacteria shapes emergent properties of sourdough, with implications across complex microbial systems