Cerebral blood flow and arterial transit in older adults
“ATT may be more sensitive to age-related decline than CBF, and therefore useful for early detection and management of cerebrovascular impairment.”
2024-10-08
(Press-News.org)
“ATT may be more sensitive to age-related decline than CBF, and therefore useful for early detection and management of cerebrovascular impairment.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 8, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 18 on September 18, 2024, entitled, “Determinants of cerebral blood flow and arterial transit time in healthy older adults.”
This research paper highlights that brain health deteriorates with age, particularly in terms of cerebral blood flow (CBF) and arterial transit time (ATT), key markers of brain vascular health. This decline can impair cognitive function and limit independence in later life—an issue that will affect many as the global population continues to age rapidly.
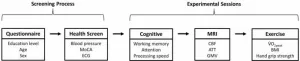
In their paper, researchers Jack Feron, Katrien Segaert, Foyzul Rahman, Sindre H. Fosstveit, Kelsey E. Joyce, Ahmed Gilani, Hilde Lohne-Seiler, Sveinung Berntsen, Karen J Mullinger, and Samuel J. E. Lucas from the University of Birmingham, University of Agder, and University of Nottingham aimed to identify modifiable determinants of CBF and ATT in healthy older adults (n = 78, aged 60–81 years). They also investigated the relationship between CBF, ATT, and cognitive function in older adults.
The researchers hypothesized that markers of superior general health—such as higher cardiorespiratory fitness, handgrip strength, and grey matter volume, or lower age, BMI, and blood pressure—would be associated with greater CBF and shorter ATT.
Results from multiple linear regressions revealed that a higher BMI was associated with lower global cerebral blood flow (CBF) (β = −0.35, P = 0.008) and longer global arterial transit time (ATT) (β = 0.30, P = 0.017). Additionally, global ATT increased with age (β = 0.43, P = 0.004), while higher cardiorespiratory fitness was linked to longer ATT in the parietal (β = 0.44, P = 0.004) and occipital (β = 0.45, P = 0.003) regions. However, neither global nor regional CBF or ATT were associated with processing speed, working memory, or attention.
“In conclusion, preventing excessive weight gain may help attenuate age-related declines in brain vascular health.”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.206112
Corresponding Author: Jack Feron - j.feron@bham.ac.uk
Keywords: aging, arterial transit time, cardiorespiratory fitness, cerebral blood flow, cognitive function
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
The journal Aging aims to promote 1) treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, 2) validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, and 3) prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. (Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.)
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker St, Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-08
The cells in your pancreas, like people, can only handle so much stress before they start to break down. Certain stressors, such as inflammation and high blood sugar, contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes by overwhelming these cells.
Researchers at The Jackson Laboratory (JAX) have now discovered that DNA sequence changes known to increase a person’s risk for diabetes are linked to how well pancreatic cells can handle two different kinds of molecular stress. In people with these DNA changes, the insulin-producing ...
2024-10-08
About The Study: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, aerobic physical activity was associated with modest short-term and long-term reductions of depression among adults with cancer. Future studies should discern the effectiveness of aerobic physical activity in combination with other strategies for managing depression across various populations of patients with cancer.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Sapna Oberoi, M.D., M.Sc., email soberoi@cancercare.mb.ca.
To access the embargoed study: ...
2024-10-08
About The Study: In this cohort study of a large primary care population served by an integrated health system, alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) hospitalizations were common, especially in male patients, younger age groups, and individuals with high-risk alcohol use. During hospitalizations, the burden of AWS was similar to or exceeded complications of other chronic diseases that receive greater medical attention.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Tessa L. Steel, M.D., M.P.H., email tessita@uw.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
2024-10-08
A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) challenges long-held assumptions about human cooperation. Traditionally, behavioral scientists and economists have primarily studied cooperation in public good contexts through repeated interactions, where individuals can build trust and reciprocal relationships, adjusting their behavior based on the actions of others. However, many real-world, naturally occurring situations, such as volunteering or donating ...
2024-10-08
Tsukuba, Japan—Maintaining soil health is crucial for sustainable agriculture. Recently, soil volatile organic compounds (VOCs) have emerged as promising indicators for assessing soil health. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of soil VOC profiles as indicators of soil health in soybean fields.
Soil samples were collected from soybean fields in Fukushima Prefecture, which exhibited diverse soil conditions, over the past three years. These samples were analyzed for VOC content in conjunction with data on soil physical properties, soil metabolome, soil ionome, and soil microbiome as well as rhizosphere chemicals ...
2024-10-08
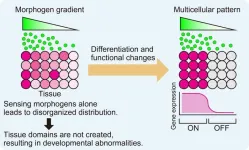
Researchers at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, demonstrate how morphogens combined with cell adhesion can generate tissue domains with a sharp boundary in an in vitro model system.
Recent advances that have enabled the growth of tissue cultures into organoids and embryoids have heightened interest as to how tissue growth is controlled during the natural processes of embryo development. It is known that the diffusion of signaling molecules called morphogens directs patterned tissue growth ...
2024-10-08
October 8, 2024 (Chicago) — The JAMA Network today announces the launch of JAMA+ AI, an engaging, interactive channel that amplifies the best of the JAMA Network’s content exploring the science of artificial intelligence and digital medicine and its application in health and health care.
JAMA+ AI is a window into the premier scientific content, educational reviews, and commentary on AI and medicine published across JAMA, JAMA Network Open, and the 11 JAMA specialty journals. JAMA+ AI builds on that content with new multimedia materials, including interviews ...
2024-10-08
CORVALLIS, Ore. – An international coalition led by Oregon State University scientists concludes in its annual report published today that the Earth’s worsening vital signs indicate a “critical and unpredictable new phase of the climate crisis” and that “decisive action is needed, and fast.”
The collaboration directed by OSU’s William Ripple and former postdoctoral researcher Christopher Wolf outlines areas where policy change is needed – energy, pollutants, nature, food and economy – in “The 2024 State of the Climate Report: Perilous Times on Planet Earth,” published ...
2024-10-08
A new report published in BioScience warns that the world is facing a climate emergency of unprecedented magnitude. The "2024 State of the Climate Report," by an international team of scientists led by Oregon State University's William Ripple and Christopher Wolf, presents alarming evidence that climate change is worsening at a dangerous pace.
In the report, the authors update 35 annually reported "planetary vital signs," which provide ongoing timeseries of human climate-related activities ...
2024-10-08
Measuring tiny magnetic fields, such as those generated by brain waves, enables many new novel opportunities for medical diagnostics and treatment. The research team led by Dr. Jan Jeske at Fraunhofer IAF is working on a globally innovative approach to precise magnetic field measurements: Laser Threshold Magnetometry. The researchers have now combined an NV diamond and a laser diode in a resonator, successfully demonstrating the sensor system with two active media for the first time. This outstanding paper has been published in Science Advances and represents a significant progress in the BMBF-funded research project NeuroQ.
Quantum ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cerebral blood flow and arterial transit in older adults
“ATT may be more sensitive to age-related decline than CBF, and therefore useful for early detection and management of cerebrovascular impairment.”