(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA (October 8, 2024)—The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has selected Salk Associate Professor Nicola Allen to receive a 2024 NIH Director’s Pioneer Award. The award recognizes exceptionally creative scientists pursuing highly innovative research and groundbreaking approaches to major challenges in biomedical, behavioral, or social sciences.
Allen will receive $3.5 million over five years to support her latest research, which investigates how plasticity in the adult brain could be enhanced. She focuses on manipulating proteins produced by star-shaped brain cells called astrocytes.
“Nicola’s work challenges traditional ideas about the many cell types that make up the brain, and her innovative thinking really shines in this research project,” says Salk President Gerald Joyce. “True to the name of the award, she is truly a pioneer, and all of us at Salk look forward to supporting her as she continues to push scientific boundaries in the years ahead.”
Allen studies astrocytes, an abundant cell type in the nervous system long thought to act as mere scaffolding for neurons. With Allen’s work and a growing body of research dedicated to astrocytes, scientists are finding these cells do so much more, like maintaining neuronal health as we age, balancing molecules in the brain’s extracellular space, and stabilizing synapses between neurons.
Allen has been especially focused on this last point, studying the role of synaptic dysfunction during aging and in neurological disorders such as autism spectrum and Alzheimer’s disease. Synapses are the tiny junctions that connect neurons in the brain to create circuits through which information can flow. In young brains, synapses fire quickly and exhibit plasticity—an ability to learn new tasks and easily repair lost connections. In older or otherwise dysfunctional brains, synapses can lose this plasticity. Emerging research has begun pointing to the proteins that surround neurons as the possible culprit for this decline in plasticity.
With her award, Allen plans to pin down this relationship between extracellular proteins and brain plasticity. Her plan is twofold: 1) creating a tool kit for modulating the brain’s protein environment called Targeted Degradation of Extracellular Proteins (TDEP), and 2) establishing an atlas containing all secreted proteins responsible for regulating plasticity. As a proof of concept, Allen will design TDEP to target only proteins secreted by astrocytes that are already known to reduce plasticity, which should demonstrate both the efficacy of TDEP and whether the removal of some proteins can revive plasticity. If successful, TDEP can then be adapted to target the many proteins identified in the atlas.
The tool kit and project goals promise a new therapeutic strategy for neurological disorders and injuries wherein boosted plasticity would be advantageous, like after a stroke or in Alzheimer’s disease.
“I am honored to receive this prestigious award from NIH, and excited to begin work on this project,” says Allen. “Through the support of this funding mechanism that targets innovative and bold ideas, we aim to make significant progress in developing tools to control brain plasticity.”
Allen’s additional recognitions include a Coins for Alzheimer’s Research Trust Award, Chan Zuckerberg Initiative Career Accelerator Award, World Economic Forum Young Scientist Award, Dana Foundation Neuroimaging Award, and Pew Biomedical Scholar Award.
Allen has also been involved in several Salk collaborations to explore different parts of the brain, including a 2018 American Heart Association-Allen Initiative-funded program to study Alzheimer’s disease and aging, a 2019 round of funding from the NIH Brain Research Through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies Initiative, and the recently launched 2024 NOMIS Foundation-funded Neuroimmunology Initiative, of which Allen is a co-lead.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH):
NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
About the Salk Institute for Biological Studies:
Unlocking the secrets of life itself is the driving force behind the Salk Institute. Our team of world-class, award-winning scientists pushes the boundaries of knowledge in areas such as neuroscience, cancer research, aging, immunobiology, plant biology, computational biology, and more. Founded by Jonas Salk, developer of the first safe and effective polio vaccine, the Institute is an independent, nonprofit research organization and architectural landmark: small by choice, intimate by nature, and fearless in the face of any challenge. Learn more at www.salk.edu.
END
Salk Institute’s Nicola Allen receives 2024 NIH Director’s Pioneer Award
2024-10-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The secret strength of our cell guards
2024-10-08
Proteins control most of the body’s functions, and their malfunction can have severe consequences, such as neurodegenerative diseases or cancer. Therefore, cells have mechanisms in place to control protein quality. In animal and human cells, chaperones of the Hsp70 class are at the heart of this control system, overseeing a wide array of biological processes. Yet, despite their crucial role, the precise molecular mechanism of Hsp70 chaperones has remained elusive for decades. Using a cutting-edge nanopore single-molecule technique, a team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with EPFL, has now made a significant breakthrough in determining how Hsp70 chaperones ...
DataSeer and AAAS partner to boost reporting standards
2024-10-08
DataSeer and the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) are pleased to announce two new pilot programs designed to support high-quality reporting across scientific disciplines. The first will generate pre-filled MDAR reports for authors – saving them time and boosting the quality of methods reporting – for AAAS’ flagship journal Science. The second will establish an Open Science Indicators baseline dataset, quantifying how and when authors at Science share their ...
Mizzou researchers awarded $8 million in grants to discover new bullying prevention strategies
2024-10-08
Students don’t have to be friends, but they should be friendly. In other words, they should learn to be respectful of one another while sharing the same space. For Chad Rose, a nationally renowned bullying prevention expert at the University of Missouri, this idea is central to his efforts to reduce school bullying, and in turn, school violence.
Bullying is a risk factor for violence, said Rose, the director of Mizzou’s Bully Prevention Lab who has spent the past 18 years researching the subject.
“After the Safe Schools initiative was launched in 1999 by the U.S. Department of Education, we began to see that children and teens who have experienced prolonged ...
Holographic 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize multiple industries, say Concordia researchers
2024-10-08
Researchers at Concordia have developed a novel method of 3D printing that uses acoustic holograms. And they say it’s quicker than existing methods and capable of making more complex objects.
The process, called holographic direct sound printing (HDSP), is described in a recent article in the journal Nature Communications. It builds on a method introduced in 2022 that described how sonochemical reactions in microscopic cavitations regions — tiny bubbles — create extremely high temperatures and pressure for trillionths of a second to harden resin into complex ...
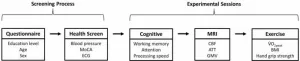
Cerebral blood flow and arterial transit in older adults
2024-10-08
“ATT may be more sensitive to age-related decline than CBF, and therefore useful for early detection and management of cerebrovascular impairment.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 8, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 18 on September 18, 2024, entitled, “Determinants of cerebral blood flow and arterial transit time in healthy older adults.”
This research paper highlights that brain health deteriorates with ...
How diabetes risk genes make cells less resilient to stress
2024-10-08
The cells in your pancreas, like people, can only handle so much stress before they start to break down. Certain stressors, such as inflammation and high blood sugar, contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes by overwhelming these cells.
Researchers at The Jackson Laboratory (JAX) have now discovered that DNA sequence changes known to increase a person’s risk for diabetes are linked to how well pancreatic cells can handle two different kinds of molecular stress. In people with these DNA changes, the insulin-producing ...
Aerobic physical activity and depression among patients with cancer
2024-10-08
About The Study: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, aerobic physical activity was associated with modest short-term and long-term reductions of depression among adults with cancer. Future studies should discern the effectiveness of aerobic physical activity in combination with other strategies for managing depression across various populations of patients with cancer.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Sapna Oberoi, M.D., M.Sc., email soberoi@cancercare.mb.ca.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Incidence of hospitalizations involving alcohol withdrawal syndrome
2024-10-08
About The Study: In this cohort study of a large primary care population served by an integrated health system, alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) hospitalizations were common, especially in male patients, younger age groups, and individuals with high-risk alcohol use. During hospitalizations, the burden of AWS was similar to or exceeded complications of other chronic diseases that receive greater medical attention.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Tessa L. Steel, M.D., M.P.H., email tessita@uw.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
Study: One-time cooperation decisions unaffected by increased benefits to society
2024-10-08
A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) challenges long-held assumptions about human cooperation. Traditionally, behavioral scientists and economists have primarily studied cooperation in public good contexts through repeated interactions, where individuals can build trust and reciprocal relationships, adjusting their behavior based on the actions of others. However, many real-world, naturally occurring situations, such as volunteering or donating ...
Soil volatile organic compound profiles as indicators for soil evaluation in soybean fields
2024-10-08
Tsukuba, Japan—Maintaining soil health is crucial for sustainable agriculture. Recently, soil volatile organic compounds (VOCs) have emerged as promising indicators for assessing soil health. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of soil VOC profiles as indicators of soil health in soybean fields.
Soil samples were collected from soybean fields in Fukushima Prefecture, which exhibited diverse soil conditions, over the past three years. These samples were analyzed for VOC content in conjunction with data on soil physical properties, soil metabolome, soil ionome, and soil microbiome as well as rhizosphere chemicals ...