(Press-News.org) A new study published in the journal Science Advances [1] by researchers at the IBS Center for Climate Physics (ICCP) at Pusan National University in South Korea shows that the patchwork of different ecosystems found in mountainous regions played a key role in the evolution of humans.
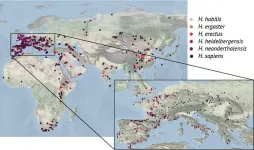
A notable feature of the archeological sites of early humans, members of the genus Homo known as hominins, is that they are often found in and near mountain regions. Using an extensive dataset of hominin fossils and artifacts, along with high-resolution landscape data and a 3-million-year-long simulation of Earth’s climate, the team of scientists from ICCP have provided a clearer picture of how and why early humans adapted to such rugged landscapes. In other words, they have helped explain why so many of our evolutionary relatives preferred being “steeplanders” as opposed to “flatlanders.”
Mountainous regions have enhanced biodiversity because the changes in elevation result in shifts of the climate, providing a range of environmental conditions under which different plant and animal species can thrive. The authors showed that steep regions usually exhibit a larger variety and density of ecosystems and vegetation types, known as biomes. Such biome diversity was a draw for early humans, as it provided increased food resources and resilience to climate change, an idea known as the Diversity Selection Hypothesis [2].
“When we analyzed the environmental factors that controlled where human species lived, we were surprised to see that terrain steepness was standing out as the dominant one, even more than local climate factors, such as temperature and precipitation.“ said Elke Zeller, PhD student from the IBS Center for Climate Physics and lead author of the study.
On the other hand, steep regions are more difficult to navigate than flatter terrain and require more energy to traverse. Hominins needed to gradually adapt to the challenges of rougher terrain in order to take advantage of the increased resources. The ICCP researchers examined how, over time, human adaptations changed the cost-benefit balance of living in rugged environments.
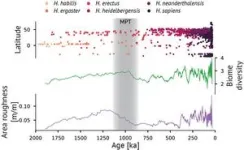
The adaptation towards steeper environments (Figs. 1 and 2) is visible for the earliest human species Homo habilis, Homo ergaster, and Homo erectus until about 1 million years ago, after which the topographic signal disappears for about 300,000 years. It reemerges again around 700,000 years ago with the advent of better adapted and more culturally advanced species such as Homo heidelbergensis and Homo neanderthalensis. These groups, which were able to control fire, also exhibited a much higher tolerance for colder and wetter climates.
“The decrease in topographic adaptation around 1 million years ago roughly coincides with large-scale reorganizations in our climate system, known as the Mid-Pleistocene Transition. It also lines up with evolutionary events such as a recently discovered ancestral genetic bottleneck, which drastically reduced human diversity, and the timing of the chromosome 2 merger in hominins. Whether this is all a coincidence, or whether the intensifying glacial climate shifts contributed to the genetic transitions in early humans, remains an open question,” said Axel Timmermann, Director of the IBS Center of Climate Physics and co-author of the study.
How humans have evolved over the past 3 million years and adapted to emerging environmental challenges is a hotly-debated research topic. The results of the South Korean research team provide a new piece in the puzzle of human evolution. Averaged over hundreds of thousands of years, across different species and continents, the data clearly show that our ancestors were “steeplanders.”
“Our results clearly show that over time hominins adapted to steep terrain and that this trend was likely driven by the regionally increased biodiversity. Our analysis suggests that it was beneficial for early human groups to populate mountainous regions, despite the increased energy consumption needed to scale these environments,” said Elke Zeller in summary.
[1] The evolving 3-dimensional landscape of human adaptation, Elke Zeller, Axel Timmermann, Science Advances, doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adq3613, (2024)
[2] Human adaptation to diverse biomes over the past 3 million years, Elke Zeller, Axel Timmermann, Kyung-Sook Yun, Pasquale Raia, Karl Stein and Jiaoyang Ruan, Science, vol. 380, 6645, pp. 604-608, doi: 10.1126/science.abq1288 (2023)
END
Early human species benefited from food diversity in steep mountainous terrain
2024-10-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers discover new insights into bacterial photosynthesis
2024-10-09
Researchers at the University of Liverpool and collaborators have discovered new understanding of bacterial photosynthesis.
Using cutting-edge techniques, investigators have unveiled intricate detailed images of the key photosynthetic protein complexes of purple bacteria. These images shed new light on how these microorganisms harness solar energy.
The study, published today, not only advances scientists’ understanding of bacterial photosynthesis but also has potential applications in the development of artificial photosynthetic systems for clean energy production.
Like plants, many ...
Former United States Air Force surgeon general to lead Military Health Institute at UT Health San Antonio
2024-10-09
The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) announces the appointment of retired Lt. Gen. Robert Miller, MD, MBA, MSS, FAAP, FACHE, FACPE, as the new Executive Director of the Military Health Institute at UT Health San Antonio. Miller will assume his role, effective October 15.
Miller joins UT Health San Antonio with more than 30 years of service in the United States Air Force, where he held several top leadership roles. Throughout his distinguished career, Miller served as command surgeon, director of education ...
Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior announces 2024 Best Article, Best Research Brief, and GEM Awards
2024-10-09
Philadelphia, October 9, 2024 – The Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior (JNEB) is pleased to announce the 2024 Best Article, Best Research Brief, and GEM (Great Educational Material) awards. These awards were presented at the Society for Nutrition Education and Behavior's (SNEB) 2024 International Conference, held July 29 – August 1 in Knoxville, TN, and hosted online. These awards recognize the authors of the outstanding articles in each category published in the prior year in JNEB, as judged by members of the ...
NYU Tandon School of Engineering study maps pedestrian crosswalks across entire cities, helping improve road safety and increase walkability
2024-10-09
As pedestrian fatalities in the United States reach a 40-year high, a novel approach to measuring crosswalk lengths across entire cities could provide urban planners with crucial data to improve safety interventions.
NYU Tandon School of Engineering researchers Marcel Moran and Debra F. Laefer published the first comprehensive, city-wide analysis of crosswalk distances in the Journal of the American Planning Association. Moran is an Urban Science Faculty Fellow at the Center for Urban Science + Progress (CUSP), and Laefer is a Professor of Civil and Urban Engineering and CUSP faculty member.
"In general, lots of important data related ...
Louis V. Gerstner, Jr. family donates $25 million to establish Gerstner Scholars Program in AI Translation at Mayo Clinic
2024-10-09
ROCHESTER, Minn. — A $25 million gift from the Louis V. Gerstner, Jr. family will establish the Gerstner Scholars Program in AI Translation at Mayo Clinic. Through this program, junior and early-career clinicians and clinician-investigators will collaborate with leading experts in artificial intelligence (AI), data science and informatics to drive breakthrough cures for patients.
“We are deeply grateful to Lou and Robin Gerstner for their long-standing friendship and support,” says Gianrico Farrugia, M.D., Mayo Clinic's president and CEO. “Lou’s remarkable generosity over many years has been instrumental in ...
UTIA entomologist elected president of SIP
2024-10-09
Juan Luis Jurat-Fuentes, professor in the Department of Entomology and Plant Pathology at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture, was elected to serve as president of the Society for Invertebrate Pathology (SIP). Jurat-Fuentes officially began his appointment at the society’s 56th annual meeting, held July 28 – August 1 in Vienna, Austria.
“Being elected by the SIP members as president is humbling and a great honor. I have big shoes to fill in this role as previous SIP executive councils were led by outstanding leaders,” Jurat-Fuentes said.
Jurat-Fuentes has a long history of ...
Rice bioengineers awarded $3.4M for project to end polio
2024-10-09
HOUSTON – (Oct. 9, 2024) – Rice University bioengineer Kevin McHugh has been awarded $3.4 million from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation for a project to incorporate protection against poliomyelitis (polio) into the combination vaccine that protects against five common and dangerous childhood diseases.
The research could help the polio eradication effort and play an instrumental role in improving access to immunization in low-resource settings ⎯ an important part of meeting sustainable development goals and achieving equity in health ...
Effects of environmental factors on Southeast Brazil’s coastal biodiversity surpass those of ecological processes
2024-10-09
Sea surface temperature, wave energy and freshwater discharge from rivers influence the abundance and size of the marine organisms that inhabit rocky shores along the coast of Southeast Brazil more than ecological processes such as competition and predation. In areas where the water is colder, such as the Lakes Region (Região dos Lagos) in Rio de Janeiro state, marine organisms are 25%-100% larger than in areas where it is warmer, such as the coast of São Paulo state.
These are the main conclusions of a study conducted by researchers affiliated with the Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP) in partnership with colleagues at the State University of Northern Rio de ...
Department of Energy announces $49 million for research on foundational laboratory fusion
2024-10-09
WASHINGTON, D.C. - As the Department of Energy (DOE) continues to accelerate a clean-energy future that includes fusion technology, a total of $49 million in funding for 19 projects was announced today in the Foundational Fusion Materials, Nuclear Science, and Technology programs.
The purpose of the funding is to reorient the laboratory-based foundational and basic science research programs to better align and support the new FES program vision.
“The Fusion Nuclear Science Foundational research program, ...
Effects of exposure to alcohol in early pregnancy can be detected in the placenta
2024-10-09
A new study led by Pr. Serge McGraw, researcher at CHU Sainte-Justine and professor at Université de Montréal, shows that the effects of alcohol exposure on an embryo prior to implantation in the uterus can be detected in the late-gestation placenta. Using a mouse model well suited for this type of exposure, the researcher and his team observed significant molecular changes in the placenta, including the expression of numerous genes and DNA methylation, an epigenetic marker that influences gene expression by ...