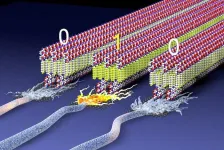
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, D.C. - As the Department of Energy (DOE) continues to accelerate a clean-energy future that includes fusion technology, a total of $49 million in funding for 19 projects was announced today in the Foundational Fusion Materials, Nuclear Science, and Technology programs.
The purpose of the funding is to reorient the laboratory-based foundational and basic science research programs to better align and support the new FES program vision.
“The Fusion Nuclear Science Foundational research program, in enabling research and development and furthering research in fusion nuclear science and fusion materials, is vital to addressing critical scientific gaps foundational to enabling fusion energy,” said Jean Paul Allain, DOE Associate Director of Science for Fusion Energy Sciences.
Fusion energy holds the potential to revolutionize the world’s energy supply by providing a virtually limitless, clean, and sustainable power source. Unlike current nuclear power, which relies on splitting atoms (fission), fusion mimics the process that powers the sun by combining atomic nuclei to release massive amounts of energy.
Fusion produces no long-lived radioactive waste, emits no carbon dioxide, and uses abundant fuels like hydrogen. If harnessed successfully, fusion energy could provide a safe, reliable solution to meet global energy demands while significantly reducing the environmental impact of power generation.
The projects funded under this initiative cover a wide range of cutting-edge research areas, each crucial to the development of fusion energy technology. For instance, scientists are testing new magnet designs that will help control the extremely hot plasma needed for fusion.
Other teams are working on materials that can withstand the damage caused by plasma, ensuring that systems used for maintaining the plasma remain functional and efficient. Some researchers are investigating blanket materials, which are designed to absorb heat from the plasma and turn it into usable energy, while also studying how these materials can be made durable enough to function in such an extreme environment.
Additionally, efforts are being made to improve fuel cycle systems, which help maintain the continuous flow of the fuel necessary for fusion reactions. Finally, advanced structural materials are being developed to construct stronger, more durable components that can endure the harsh conditions inside the fusion systems. Together, these projects aim to advance our understanding and capability in the pursuit of clean, sustainable fusion energy.
The projects were selected by competitive peer review under the DOE Lab Call: Opportunities in Foundational Fusion Materials, Nuclear Science, and Technology.
Total funding is $49 million for projects lasting up to three years in duration, with $7 million in Fiscal Year 2024 dollars and outyear funding contingent on congressional appropriations. The list of projects and more information can be found on the Fusion Energy Sciences program homepage.
Selection for award negotiations is not a commitment by DOE to issue an award or provide funding. Before funding is issued, DOE and the applicants will undergo a negotiation process, and DOE may cancel negotiations and rescind the selection for any reason during that time.
END
Department of Energy announces $49 million for research on foundational laboratory fusion
Projects address scientific gaps foundational to enabling fusion energy
2024-10-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Effects of exposure to alcohol in early pregnancy can be detected in the placenta
2024-10-09
A new study led by Pr. Serge McGraw, researcher at CHU Sainte-Justine and professor at Université de Montréal, shows that the effects of alcohol exposure on an embryo prior to implantation in the uterus can be detected in the late-gestation placenta. Using a mouse model well suited for this type of exposure, the researcher and his team observed significant molecular changes in the placenta, including the expression of numerous genes and DNA methylation, an epigenetic marker that influences gene expression by ...
Scientists caution no guarantees when it comes to overshooting 1.5°C
2024-10-09
Even if it is possible to reverse the rise of global temperatures after a temporary overshoot of 1.5°C, some climate damages inflicted at peak warming, including rising sea levels, will be irreversible, according to a new study published today in Nature.
The study is the culmination of a three-and-a-half-year project, backed by the European innovation fund HORIZON2020, looking at so-called ‘overshoot’ scenarios where temperatures temporarily exceed the Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C ...
Nature and plastics inspire breakthrough in soft sustainable materials
2024-10-09
Step aside hard, rigid materials. There is a new soft, sustainable electroactive material in town — and it’s poised to open new possibilities for medical devices, wearable technology and human-computer interfaces.
Using peptides and a snippet of the large molecules in plastics, Northwestern University materials scientists have developed materials made of tiny, flexible nano-sized ribbons that can be charged just like a battery to store energy or record digital information. Highly energy efficient, biocompatible and made from sustainable materials, the systems could give rise to new ...
New quantum timekeeper packs several clocks into one
2024-10-09
Imagine walking into a room where several different grandfather clocks hang on the walls, each ticking at a different pace.
Quantum physicists at the University of Colorado Boulder and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have essentially recreated that room at the scale of atoms and electrons. The team’s advancement could pave the way for new kinds of optical atomic clocks, devices that track the passage of time by measuring the natural “ticking” of atoms.
The group’s new clock is made from a few dozen strontium ...
Suicidal thoughts and behaviors among autistic transgender or gender-nonconforming US college students
2024-10-09
About The Study: This cross-sectional study addresses the dearth of information on how intersectionality in gender and autism status impacts the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors, and the results confirm the elevated risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors among transgender or gender nonconforming and autistic populations. Interventions are needed to support college students with these identities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Annabelle M. Mournet, MS, email amm883@psych.rutgers.edu.
To ...
The bright and dark sides of Pacific salmon biotransport
2024-10-09
Each year millions of Pacific salmon make a grand journey from the ocean to their freshwater spawning grounds at the end of their life cycles. This migration has rippling effects through food webs and ecosystems along the way. Whether they decompose or are consumed by other animals, these salmon deliver both nutrients and contaminants they have accumulated in their bodies after spending most of their lives growing at sea. A team of researchers from UConn, the University of South Dakota, the U.S. Geological Survey, Natural ...
New therapeutic strategy identified for triple negative breast cancer
2024-10-09
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) remains the most aggressive and deadly type of breast cancer, but new findings from cancer researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, are pointing the way toward therapeutic strategies that could be tested in clinical trials in the future. Using patient-derived samples in pre-clinical work, researchers discovered that by combining two therapeutic agents they could nudge TNBC cells into a more treatable state. Findings are published in Nature.
“When combined, these therapeutic agents ...
Scientists create first map of DNA modification in the developing human brain
2024-10-09
A UCLA-led study has provided an unprecedented look at how gene regulation evolves during human brain development, showing how the 3D structure of chromatin — DNA and proteins — plays a critical role. This work offers new insights into how early brain development shapes lifelong mental health.
The study, published in Nature, was led by Dr. Chongyuan Luo at UCLA and Dr. Mercedes Paredes at UC San Francisco, in collaboration with researchers from the Salk Institute, UC San Diego and Seoul National University. It created the first map of DNA modification in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex — two regions ...
Extended Timing: How neurons encode information on timescales that match learning
2024-10-09
New research from the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience published this week in Nature has identified a key step in how neurons encode information on timescales that match learning.
A timing mismatch
Learning takes seconds to minutes. However, the best-understood mechanisms of how the brain encodes information happen at speeds closer to neural activity—around 1000 times faster. These mechanisms, known as Hebbian plasticity, suggest that if two connected neurons are both active within a hundredth of a second, then the connection between the two neurons is strengthened. In this ...
Dual immunotherapy plus chemotherapy benefits specific subset of patients with lung cancer
2024-10-09
HOUSTON ―Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have demonstrated that patients with metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring specific mutations in the STK11 and/or KEAP1 tumor suppressor genes were more likely to benefit from adding the immunotherapy tremelimumab to a combination of durvalumab plus chemotherapy to overcome treatment resistance typically seen in this patient population.
Study results, published today in Nature, identify ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Department of Energy announces $49 million for research on foundational laboratory fusionProjects address scientific gaps foundational to enabling fusion energy