(Press-News.org) Newly discovered ancient birds from Late Cretaceous North America were hawk-sized and had powerful raptor-like feet, according to a study published October 9, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Alexander Clark of the University of Chicago, U.S. and colleagues.
The most diverse birds during the Cretaceous Period were a now-extinct group called enantiornithines, known from all over the world during this time. However, enantiornithines and other Mesozoic birds are mainly known from Lower Cretaceous deposits, with a relatively poor record from the Late Cretaceous. Thus, there is a general lack of understanding of trends in bird evolution toward the end of the Mesozoic Era.
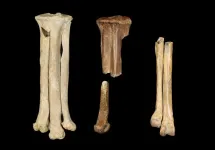
In this study, Clark and colleagues describe three new enantiornithine birds from fossils found in the Hell Creek Formation of Montana, dating to the latest Cretaceous Period (68 - 66 million years ago, shortly before the mass extinction that wiped out non-avian dinosaurs and enantiornithines). All three fossil birds are identified from lower leg bones. Two are new species named Magnusavis ekalakaensis and Avisaurus darwini, while the third is an unnamed species of Avisaurus.
These birds are all larger than Early Cretaceous enantiornithines, with Avisaurus darwini estimated to have weighed over one kilogram, roughly the size of a large hawk. Analysis of the leg bones of Avisaurus and its relatives reveals proportions and adaptations similar to hawks and owls, indicating powerful leg muscles and feet that could grip and potentially carry proportionally large prey, similar to some modern raptorial birds.
These fossils expand the known diversity of Late Cretaceous birds, confirm the trend toward large body size, and highlight how, over time, enantiornithines evolved a greater diversity of ecological roles. This study emphasizes how even fragmentary fossils can reveal important ecological information and be used to clarify evolutionary trends.
The authors add: “Avisaurids, a group of enantiornithine birds from the latest Cretaceous, exhibit hindlimb features indicating strong ankle flexion, which suggests the ability to carry heavy prey and behaviors similar to living raptorial birds.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0310686
Citation: Clark AD, Atterholt J, Scannella JB, Carroll N, O’Connor JK (2024) New enantiornithine diversity in the Hell Creek Formation and the functional morphology of the avisaurid tarsometatarsus. PLoS ONE 19(10): e0310686. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0310686
Author Countries: U.S.A.
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
END
Newly discovered Late Cretaceous birds may have carried heavy prey like extant raptors
New fossil species reveal diverse body sizes and lifestyles of birds before mass extinction
2024-10-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bat species richness in San Diego, C.A. decreases as artificial lights, urbanization, and unconserved land increase, with Townsend's big-eared bat especially affected
2024-10-09
Bat species richness in San Diego, C.A. decreases as artificial lights, urbanization, and unconserved land increase, with Townsend's big-eared bat especially affected
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0310812
Article Title: Quantification of threats to bats at localized spatial scales for conservation and management
Author Countries: U.S.A.
Funding: The United States Geological Survey Western Ecological Research Center and Ecosystems Mission Area provided funding and support, and the National ...
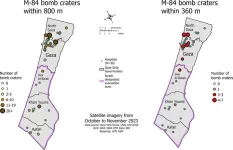
Satellite data shows massive bombs dropped in dangerous proximity to Gaza Strip hospitals in 2023
2024-10-09
Satellite data on the proximity of hundreds of M-84 bomb craters to hospitals in the Gaza Strip suggests that, as of November 2023, hospitals were not being given special protection from indiscriminate bombing, as mandated by international humanitarian law. That is one finding out of a new study published this week in PLOS Global Public Health by Dennis Kunichoff of Harvard University, and colleagues.
On October 7, 2023, Israel launched a major military campaign in the Gaza Strip in response to Hamas militant attacks in Israel. Among the munitions being used are United-States-provided Mark-84 (M-84) bombs, which are air-dropped explosive munitions that shoot more than 1000 pounds ...
Predatory birds from the same fossil formation as SUE the T. rex
2024-10-09
The Hell Creek Formation in what’s now the Dakotas, Montana, and Wyoming was once home to some of the world’s most beloved dinosaurs, like Triceratops and Tyrannosaurus rex (including SUE, one of the largest, most complete, and best-preserved T. rex specimens ever found). But these giant dinosaurs weren’t alone in their ecosystem, and in a paper in the journal PLOS ONE, scientists have described two new species of birds that lived alongside these dinosaurs 68 million years ago. The researchers ...
Sexist textbooks? Review of over 1200 English-language textbooks from 34 countries reveals persistent pattern of stereotypical gender roles and under-representation of female characters across countri
2024-10-09
Gender biases around male and female roles and under-representation of female characters appeared in textbooks from around the world, with male-coded words appearing twice as often as female-coded words on average, according to a study published October 9, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Lee Crawfurd from the Center for Global Development, United Kingdom, and colleagues.
School textbooks play an important role in shaping norms and attitudes in students—one reason why controversy ...
Interview with Lee Crawfurd, Center for Global Development, United Kingdom
2024-10-09
Interview with Lee Crawfurd
###
What first drew you to study gender bias in school textbooks, and why did you choose to investigate this topic?
I was raised by a gay feminist single mother who was a school teacher and loves to challenge gender stereotypes, so this is something I've always been interested in. This personal background, combined with recent advancements in computerized text analysis and the new availability of digital textbooks, led me to this line of research.
What are the key findings from your research?
It's not really news that there is some ...
Scientists show accelerating CO2 release from rocks in Arctic Canada with global warming
2024-10-09
Researchers from the Department of Earth Sciences at the University of Oxford have shown that weathering of rocks in the Canadian Arctic will accelerate with rising temperatures, triggering a positive feedback loop that will release more and more CO2 to the atmosphere. The findings have been published today in the journal Science Advances.
For sensitive regions like the Arctic, where surface air temperatures are warming nearly four times faster than the global average, it is particularly crucial to understand the potential contribution of atmospheric CO2 from weathering. ...
The changing geography of “energy poverty”
2024-10-09
A growing portion of Americans who are struggling to pay for their household energy live in the South and Southwest, reflecting a climate-driven shift away from heating needs and toward air conditioning use, an MIT study finds.
The newly published research also reveals that a major U.S. federal program that provides energy subsidies to households, by assigning block grants to states, does not yet fully match these recent trends.
The work evaluates the “energy burden” on households, which reflects the percentage of income needed to pay for energy necessities, from 2015 to 2020. Households with an energy burden greater ...
Why people think they’re right, even when they are wrong
2024-10-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – If you smugly believe you’re right in a disagreement with a friend or colleague, a new study suggests why you may actually be wrong.
Researchers found that people naturally assume they have all the information they need to make a decision or support their position, even when they do not.
The researchers called it the “illusion of information adequacy.”
“We found that, in general, people don’t stop to think whether there might be more information that would help them make a more informed decision,” said study co-author ...
New study shows how muscle energy production is impaired in type 2 diabetes
2024-10-09
A new study from Karolinska Institutet, published in Science Translational Medicine, shows that people with type 2 diabetes have lower levels of the protein that breaks down and converts creatine in the muscles. This leads to impaired function of the mitochondria, the 'powerhouses' of the cell.
Creatine is a natural compound in the body that is also found in foods such as meat and fish. It is also a popular supplement for improving exercise performance as it can make muscles work harder and longer before they become fatigued. Despite creatine's ...
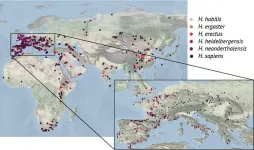
Early human species benefited from food diversity in steep mountainous terrain
2024-10-09
A new study published in the journal Science Advances [1] by researchers at the IBS Center for Climate Physics (ICCP) at Pusan National University in South Korea shows that the patchwork of different ecosystems found in mountainous regions played a key role in the evolution of humans.
A notable feature of the archeological sites of early humans, members of the genus Homo known as hominins, is that they are often found in and near mountain regions. Using an extensive dataset of hominin fossils and artifacts, along with high-resolution landscape data and a 3-million-year-long simulation of Earth’s climate, the team of scientists from ICCP have provided a clearer picture of how ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Newly discovered Late Cretaceous birds may have carried heavy prey like extant raptorsNew fossil species reveal diverse body sizes and lifestyles of birds before mass extinction