(Press-News.org) Research published in Nature Genetics on Oct.14, by Yale Cancer Center researchers at Yale School of Medicine, found a higher concentration of a specific kind of DNA — extrachromosomal or ecDNA — in more aggressive and advanced cancers that could mark them as targets for future therapies.
Using data available from The Cancer Genome Atlas, the International Cancer Genomics Consortium, the Hartwig Medical Foundation, and the Glioma Longitudinal Analysis Consortium, the researchers considered more than 8,000 tumor samples, divided between newly diagnosed untreated tumors and those that had been through previous treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation, and others. They found significantly higher amounts of ecDNA in tumors from previously treated patients, leading to the theory that ecDNA might give a survival advantage to those tumors.
“Our research suggests that ecDNA helps tumors become more aggressive,” said senior author of the paper, Roel Verhaak, the Harvey and Kate Cushing Professor of Neurosurgery at Yale School of Medicine and member of Yale Cancer Center. “EcDNA has a distinct mechanism and plays an important role, not just for breast or lung cancer, but across many cancer types.”
The study found that ecDNA is detected more often after taxol-based therapies such as docetaxel and paclitaxel, which is used for treatment of many cancer types. The researchers also noticed that when they looked at the same cancer over time, ecDNA was more likely to stick around than DNA changes on the regular chromosomes.
In the advanced cancers that were studied, ecDNA was prone to rapid mutations. Researchers say these "hypermutations" could be one of the reasons why cancer becomes so aggressive and difficult to treat as time goes on. The mutations in ecDNA may help cancer cells adapt and survive better than their normal counterparts. The hope is that this research can aid in the development of better cancer treatments.
“In the lab, we’re using drug libraries to find out what can specifically target ecDNA-containing cells,” said Verhaak. “We want to find vulnerabilities in tumors that have ecDNA, as ecDNA-targeting therapies could benefit as many as a third of all cancer patients.”
Verhaak said there are ongoing clinical trials involving therapies that are designed to specifically target ecDNA in tumors.
Yale Cancer Center’s Kevin Johnson joined Verhaak as a co-author on the study. Soyeon Kim and Hoon Kim, a former postdoctoral trainee in the Verhaak lab and now a professor at Sungkyunkwan University in Seoul, South Korea, contributed equally to the project.
This work was delivered as part of the eDyNAmiC team supported by the Cancer Grand Challenges partnership funded by Cancer Research UK (CGCATF-2021/100012; CGCATF-2021/100016 to S. Kim, K.C.J. and R.G.W.V.; and CGCATF-2021/100025 to V.B. and J.L.) and the National Cancer Institute (OT2CA278688; OT2CA278649 to S. Kim, K.C.J. and R.G.W.V.; and OT2CA278635 to V.B. and J.L.). This work was also supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants R01 CA237208, R21 NS114873 and R33 CA236681) and Cancer Center Support Grant (P30 CA034196 to R.G.W.V; U24CA264379 and R01GM114362 to V.B.), the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded bythe Korea government (MSIT; NRF-2019R1A5A2027340 and NRF- 2022M3C1A3092022 to H.K.), the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) grant funded by Ministry of Health & Welfare (HI19C1348 to S. Kim) and the Luxembourg National Research Fund (FNR; C20/BM/14646004/GLASSLUX to A.L., A.G. and S.P.N.).
END
Specific type of DNA could be a target of future cancer therapies
2024-10-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New Director of the Bates Center for the Study of the History of Nursing
2024-10-16
PHILADELPHIA (October 16, 2024) – J. Margo Brooks Carthon, PhD, RN, FAAN, the Tyson Family Endowed Term Chair for Gerontological Research; Professor of Nursing in the Department of Family and Community Health; and Associate Director of the Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research, has been appointed the new Director of the Barbara Bates Center for the Study of the History of Nursing (Bates Center), the preeminent history of nursing research center and archive. The Bates Center amplifies the importance of the history of nursing and healthcare to the development of crafting effective health policies and strategies to improve health for all.
“The ...
Scientists developing microchips with brain and lung tissue to study viral neuroinflammation
2024-10-16
Scientists are developing advanced tools to understand and treat neurological symptoms such as brain fog associated with respiratory diseases like influenza. The Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), part of the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response (ASPR) within the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), awarded a three-year contract to researchers at the University of Rochester to develop a technology to model respiratory disease effects on the brain ...
Discover science: Applications open for summer 2025 undergraduate internships
2024-10-16
WASHINGTON, DC – As the nation continues to build a diverse, clean-energy workforce, the Department of Energy (DOE) today announced that applications are being accepted for the Summer 2025 term of two undergraduate internship programs.
The Office of Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internships (SULI) program and the Community College Internships (CCI) program are unique opportunities open to all current and recent college undergraduates. Interns will learn about science and technology careers, team science, networking, and gain the experience needed to transition from internship to employment.
The application deadline for both programs is January 8, 2025, ...
Can electricity treat high blood pressure?
2024-10-16
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Several medications are available to treat high blood pressure, but more than 10 million Americans do not respond to the treatments, according to the American Heart Association. Using a bioelectronic device to deliver pulsed electricity to the body has proven to be a promising strategy to treat drug-resistant hypertension patients, according to Penn State researcher Tao Zhou, although he noted that its practical application in patient care has significant limitations.
Zhou, assistant professor of engineering science and mechanics and of biomedical engineering, received ...
Microplastics detected in dolphin breath
2024-10-16
U.S. researchers have detected microplastic particles in air exhaled by wild bottlenose dolphins, suggesting that inhalation may be a relevant route of exposure to these potentially harmful contaminants. Miranda Dziobak of the College of Charleston in South Carolina, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on October 16, 2024.
Around the world, humans and numerous other animals are exposed to tiny particles of plastic contaminants known as microplastics. In humans and rodents, microplastic exposure has been linked to adverse health impacts, such as oxidative stress and inflammation. Ingestion ...
Global north’s growing appetite for farmed salmon imperils communities’ access to local fish
2024-10-16
A new paper published today in Science Advances exposes the global aquaculture sector’s growing dependence on wild fish. Despite industry claims to the contrary, these findings highlight how the growing appetite for expensive farmed salmon can leave coastal communities struggling to access affordable local fish like sardines and anchovies. Instead, these small pelagic fish are frequently caught, processed, and “reduced” to fishmeal and fish oil, almost all of which is used to feed farmed fish. These ‘reduction fisheries’ account for 26% of global ocean catch.
“As the aquaculture industry grows, so does its ...
e-Flower records neuronal activity with electronic petals
2024-10-16
Neural spheroids — 3D clusters of brain cells — are emerging as essential tools for understanding neural networks and studying neurological diseases in the lab. EPFL’s e-Flower, a flower-shaped 3D microelectrode array (MEA), allows researchers to monitor the electrical activity of these spheroids in a way that was previously impossible. This breakthrough, published in Science Advances, lays the groundwork for more sophisticated research on brain organoids, which are complex, miniaturized models of brain tissues.
“The ...
Aquaculture uses far more wild fish than previously estimated, study finds
2024-10-16
A study published in the journal Science Advances suggests that global fish farming, or aquaculture, may rely on significantly larger quantities of wild-caught ocean fish than previously calculated. The study is part of a special issue focused on expanding contributions from the aquaculture industry to food systems with an aim towards sustainability.
These findings call into question long-held assumptions about the sustainability of the rapidly growing aquaculture industry and provides a range of plausible estimates for its impact on wild fish populations.
The research, led by an international team of scientists ...
Gene editing approach paves the way to first-in-human clinical trial for rare genetic disease
2024-10-16
A collaborative effort between investigators at the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, demonstrates the potential of precise genome editing technologies, called adenine base editors, to correct disease-causing mutations in stem cells from patients with X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (X-CGD), a rare genetic disorder characterized by high susceptibility to infections. The findings are published in Science Translational Medicine.
Patients with ...
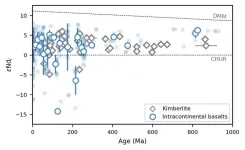
Compositional evolution of the upper mantle driven by plate tectonics
2024-10-16
On present-day Earth, plate subduction continuously modifies the chemical composition of the convecting mantle, and various mantle sources linked to these processes have been widely studied.
However, when did global chemical heterogeneity of the convecting mantle first emerge in Earth's geological history? And how might Earth’s geodynamic evolution have influenced the chemical composition of the convecting mantle over time?
Researchers from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS), along with collaborators from Australia, Switzerland and the USA, have tried to address these questions ...