Study reveals how fear memories transform over time, offering new insights into PTSD
2024-10-21
(Press-News.org)
An innovative study, to be published in Nature Communications on October 21, 2024, reveals the mechanism behind two seemingly contradictory effects of fear memories: the inability to forget yet the difficulty to recall. Led by researchers from Sony Computer Science Laboratories, Inc., ATR Computational Neuroscience Laboratories, and the University of Tokyo, the study shows how fear experiences are initially remembered as broad, associative memories, but over time become integrated into episodic memories with a more specific timeline.
The researchers conducted experiments using functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) and machine learning algorithms to track brain activity as participants experienced simulated threatening events, such as a car accident. They found that immediately after a fear-inducing event, the brain relies on associative memories, generalizing the fear regardless of event sequences. However, the following day, the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex takes over a role initially led by the hippocampus to integrate the event's sequence into fear memory, reducing the scope of fear.
The study also highlights that individuals with high anxiety, who are at greater risk for PTSD, may struggle with this memory integration. Their brains show weaker integration of time-based episodic memories through the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which may lead to persistent, overwhelming fear linked to associative cues. This insight opens new avenues for PTSD interventions by targeting the brain’s ability to integrate episodic memories after trauma.
"Our findings reveal a previously unknown phenomenon in how the brain prioritizes and processes fear memories", said lead author Dr. Aurelio Cortese from Advanced Telecommunications Research Institute (ATR). "This time-dependent rebalancing between brain regions may explain why some individuals develop PTSD while others don't", explained the last author Dr. Ai Koizumi from Sony Computer Science Laboratories, Inc.
The study's findings have the potential to reshape our understanding of PTSD and fear memory processing, offering novel perspectives for developing more effective interventions.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-21
Guideline Highlights:
Each year in the U.S., over half a million people have a first stroke; however, up to 80% of strokes may be preventable.
The new primary prevention of stroke guideline from the American Stroke Association urges health care professionals to screen people for stroke risk factors, including high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol, high blood sugar and obesity.
Increasing public awareness and knowledge about healthy lifestyle changes, such as smoking cessation, increased physical activity, improved dietary habits and better sleep, may also help people reduce their stroke risk.
The new guideline highlights the American Heart ...
2024-10-21
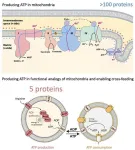
It is one of the most fundamental questions in science: how can lifeless molecules come together to form a living cell? Bert Poolman, Professor of Biochemistry at the University of Groningen, has been working on this problem for over twenty years. He aims to understand life by trying to reconstruct it; he is building simplified artificial versions of biological systems that can be used as components for a synthetic cell. Poolman recently published two papers in Nature Nanotechnology and Nature Communications. In the first paper, he describes a system for energy conversion ...
2024-10-21
In one of the largest-ever studies of DNA and brain volume, researchers have identified 254 genetic variants that shape key structures in the “deep brain,” including those that control memory, motor skills, addictive behaviors and more. The findings were just published in the journal Nature Genetics.
The study is powered by the Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis (ENIGMA) consortium, an international effort based at the Keck School of Medicine of USC, which unites more than 1,000 research labs across 45 countries to hunt for genetic variations that affect the brain’s structure and function.
“A lot of brain diseases are known to be partially ...
2024-10-21
Food production is one of the pillars of human civilization and underlies many of the changes caused by humans on planet’s landscapes. Producing food and getting it to people’s plates entails a significant expenditure of energy and resources. Unfortunately, approximately one third of all food produced globally is not consumed and discarded. Hence, to build sustainable societies, it is essential to minimize food waste.
In Japan, based on estimates reported by governmental institutions, an astonishing 2.47 megatons of food waste was generated in ...
2024-10-21
Many women who receive chemotherapy experience a decreased ability to remember, concentrate, and/or think—commonly referred to as “chemo-brain” or “brain fog”—both short- and long-term. In a recent clinical trial of women initiating chemotherapy for breast cancer, those who simultaneously started an aerobic exercise program self-reported greater improvements in cognitive function and quality of life compared with those receiving standard care. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
The study, called the Aerobic exercise and ...
2024-10-21
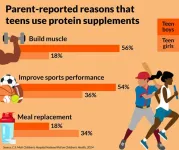
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Protein bars, shakes and powders are increasingly popular among adults – but many teens may be jumping on the bandwagon too.
Two in five parents say their teen consumed protein supplements in the past year, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health. The trend was more common among teen boys who were also more likely to take protein supplements every day or most days, parents reported.
“Protein is part of a healthy diet but it can be hard for parents to tell if ...
2024-10-21
SAN DIEGO, California, 21 October 2024. In an illuminating Genomic Press Interview published today, Dr. Stephanie Knatz Peck, Associate Clinical Professor of Psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD), unveils her groundbreaking work in eating disorder treatment and psychedelic research. The interview, featured in the journal Psychedelics, offers an intimate look at Dr. Knatz Peck's journey from personal struggle with an eating disorder to becoming a leading innovator in the field.
Dr. Knatz Peck's research ...
2024-10-21
In stalk-eyed flies, longer eyestalks attract the ladies. Females prefer males with longer eyestalks, and other males are less likely to fight them for access to females. But some males have a copy of the X chromosome which always causes short eyestalks. Scientists investigating why this mutation hasn’t died out, despite sexual selection, have discovered that the flies could be compensating for their shorter eyestalks with increased aggression.
“It's the first time I'm aware of that there's ...
2024-10-21
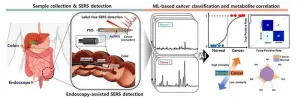
A research team led by Dr. Ho Sang Jung of the Advanced Bio and Healthcare Materials Research Division at the Korea Institute of Materials Science has developed an innovative sensor material that amplifies the optical signals of cancer metabolites in body fluids (saliva, mucus, urine, etc.) and analyzes them using artificial intelligence to diagnose cancer.
This technology quickly and sensitively detects metabolites and changes in cancer patients' body fluids, providing a non-invasive way to diagnose cancer instead of traditional blood draws or biopsies. In collaboration with Professor Soo Woong ...
2024-10-21
Inuit children in Nunavut, Canada, are being overdiagnosed for macrocephaly and underdiagnosed for microcephaly, two neurological conditions measured by head size, because of reliance on World Health Organization (WHO) growth curves, according to new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230905.
“Clinicians must be able to identify children with potential medical issues appropriately, without underdiagnosis or overdiagnosis at the extremes of head circumference measurements,” writes Dr. Kristina Joyal, a pediatric neurologist, University of Manitoba and University of Saskatchewan, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study reveals how fear memories transform over time, offering new insights into PTSD