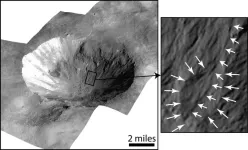
(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — October 21, 2024—A Southwest Research Institute researcher collaborated with a team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory to attempt to explain the presence of mysterious flow features that exist on the surfaces of airless celestial bodies, such as the asteroids Vesta and Ceres, explored recently by the NASA Dawn mission, or Jupiter’s moon Europa, which will soon be explored in detail by the NASA Europa Clipper mission that includes SwRI’s involvement.
In a new paper published in The Planetary Science Journal, its lead author, SwRI’s Dr. Michael J. Poston, and a team of researchers outline how post-impact conditions, such as from a meteoroid impact, could produce liquid brines that temporarily flow along the surface long enough to etch curved gullies and deposit fans of debris in the walls of newly formed craters.
“We wanted to investigate our previously proposed idea that ice underneath the surface of an airless world could be excavated and melted by an impact and then flow along the walls of the impact crater to form distinct surface features,” said project PI Dr. Jennifer Scully (JPL).
The team wanted to understand how long the liquid could potentially flow before refreezing, as most liquids lose stability in strong vacuum conditions.
The paper, “Experimental Examination of Brine and Water Lifetimes after Impact on Airless Worlds,” details the team’s findings after simulating the pressures that ice on Vesta, one of the largest asteroids in our solar system, experiences after a meteoroid impact and how long it takes the liquid released from the subsurface to refreeze.
The team modified a test chamber at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory to rapidly decrease pressure over a liquid sample to simulate the dramatic drop in pressure as the temporary atmosphere created after an impact on an airless body like Vesta dissipates. According to Poston, the pressure drop was so fast that test liquids immediately and dramatically expanded, ejecting material from the sample containers.
“Through our simulated impacts, we found that the pure water froze too quickly in a vacuum to effect meaningful change, but salt and water mixtures, or brines, stayed liquid and flowing for a minimum of one hour,” said Poston. “This is sufficient for the brine to destabilize slopes on crater walls on rocky bodies, cause erosion and landslides, and potentially form other unique geological features found on icy moons.”
These findings could also help to explain the origins of certain observed features on distant bodies, such as the smooth plains of Europa and the distinct “spider” feature in its Manannán crater, or the various gullies and fan-shaped debris deposits on Mars. The study could also help build a stronger case for the existence of subsurface water in seemingly inhospitable locations in the solar system.
“If the findings are consistent across these dry and airless or thin-atmosphere bodies, it demonstrates that water existed on these worlds in the recent past, indicating water might still be expelled from impacts,” said Poston. “There may still be water out there to be found.”
The study was funded through a grant from NASA’s Discovery Data Analysis Program as part of an ongoing project led by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/technical-divisions/space-science.
END
SwRI and JPL co-led study offers insights into mysterious features on airless worlds
Post-impact conditions could support temporary liquid brines that create flow formations
2024-10-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Artificial ‘nose’ can sniff out damaged fruit and spoiled meat
2024-10-21
Although smell has historically played an important role in the fight against diseases such as the plague and tuberculosis, the human nose is generally not sensitive enough to be used as a reliable diagnostic tool.
However, a new artificial ‘nose’ inspired by our sense of smell could now make it possible to detect undiagnosed disease, hazardous gases, and food that is starting to spoil.
And it is all made possible with technology that already exists.
Surrounded by antennas
What do your mobile phone, computer and TV have in common? Antennas.
“We are literally surrounded by technology that communicates using antenna technology,” said Michael ...
Tube spinning process: Recent advances and challenges
2024-10-21
Amidst the sustainable evolution of the economy and society, the issues of energy scarcity and environmental degradation have gained increasing prominence, making energy conservation and emission reduction the focal point of societal concern. Within this context, metal tubes fittings, as essential components, wield significant and extensive influence in domains such as aviation, aerospace, and new energy vehicles. Notably, the burgeoning prominence of advanced plastic forming methods, epitomized by the flexible medium forming process of tubes, has garnered ...
Enhancement of material microstructure and properties in Arc wire-based direct energy deposition: A short review
2024-10-21
In recent years, additive manufacturing technology has attracted considerable attention from various stakeholders. Among the different techniques, Arc wire-based direct energy deposition (DED) has experienced a notable increase in development, offering compelling advantages such as cost-effectiveness and high forming efficiency. However, a high deposition rate results in extremely high heat input and temperature inhomogeneity, leading to a deterioration in surface quality, a reduction in material properties, an increase in residual stresses and even distortion and cracking. Consequently, the current research agenda is focused on developing methods to ensure the quality ...
Cloud computing captures chemistry code
2024-10-21
RICHLAND, Wash.—Some computing challenges are so big that it’s necessary to go all in. That’s the approach a diverse team of scientists and computing experts led by the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, along with colleagues from Microsoft and other national laboratories and universities, are taking to democratize access to emerging cloud computing resources.
The effort, outlined in a recent peer-reviewed journal publication, provides a road map to moving scientific computing resources into a sustainable ecosystem that evolves as ...
Novel electrothermal model enables co-estimation of SOC and SOT
2024-10-21
For the main energy storage system for EVs, Li-ion batteries are extensively applied owing to their excellent overall performance The safe and efficient operation of the electric vehicle significantly depends on the accurate state-of-charge (SOC) and state-of-temperature (SOT) of Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. A recent breakthrough study presented by researchers from the Tongji University and Chongqing University introduces a co-estimation of state-of-charge and state-of-temperature for large-format lithium-ion batteries based on ...
Advanced online method for battery model parameter identification: Bias-compensated forgetting factor recursive least squares
2024-10-21
Lithium-ion power battery technology stands out as a pivotal component in advancement of new energy electric vehicles (EVs). Battery parameter identification, as one of the core technologies to achieve an efficient battery management system (BMS), is the key to predicting and managing the performance of Li-ion batteries. A recent breakthrough study presented by researchers from Hebei University of Technology proposes an online battery model parameters identification approach based on bias-compensated forgetting factor recursive least squares. This advanced method is expected to improve the accuracy of parameter identification under different noise.
The ...
Understanding the maturation of white blood cells to find new therapies against lymphoblastic leukaemia
2024-10-21
Over four hundred people, 80% of them being children under 14 years old, will be diagnosed with B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (B-ALL) next year in Spain, according to the latest projections from the Spanish network of cancer registries (REDECAN). Survival rates for this rapid-growing and aggressive type of blood cancer are high in youth, but fall rapidly with age, especially after 40, stressing the need for new therapeutic alternatives.
B-ALL arises when B-lymphocytes - the antibody producing cells of the immune system - fail to properly mature in the bone marrow, leading to the accumulation of immature progenitors ...
Sexual and gender-diverse individuals face more health challenges during COVID-19: Insights from a large-scale social media analysis
2024-10-21
A new study by researchers at Zhejiang University has highlighted the disproportionate health challenges faced by sexual and gender-diverse (SGD) individuals during the COVID-19 pandemic. By analyzing over 471 million tweets using advanced natural language processing (NLP) techniques, the study reveals that SGD individuals were more likely to discuss concerns related to social connections, mask-wearing, and experienced higher rates of COVID-19 symptoms and mental health issues than non-SGD individuals. The study has been published in the journal Health Data ...
First ever Hispanic thrifty food plan published
2024-10-21
A new study1 has unveiled the Hispanic Thrifty Food Plan (H-TFP), a culturally adapted and affordable diet specifically designed to align with the eating habits of U.S. Hispanic households. The research, led by Adam Drewnowski, PhD, from the University of Washington, used advanced dietary modeling to create a version of the USDA’s Thrifty Food Plan (TFP) that respects the distinctive food patterns of Hispanic communities.
The USDA's Thrifty Food Plan is the foundation for setting benefits under the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), but it has not traditionally accounted for the ...
Study reveals how fear memories transform over time, offering new insights into PTSD
2024-10-21
An innovative study, to be published in Nature Communications on October 21, 2024, reveals the mechanism behind two seemingly contradictory effects of fear memories: the inability to forget yet the difficulty to recall. Led by researchers from Sony Computer Science Laboratories, Inc., ATR Computational Neuroscience Laboratories, and the University of Tokyo, the study shows how fear experiences are initially remembered as broad, associative memories, but over time become integrated into episodic memories with a more specific timeline.
The researchers conducted experiments using functional ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
AI challenges lithography and provides solutions
Can AI make society less selfish?
UC Irvine researchers expose critical security vulnerability in autonomous drones
Changes in smoking status and their associations with risk of Parkinson’s, death
[Press-News.org] SwRI and JPL co-led study offers insights into mysterious features on airless worldsPost-impact conditions could support temporary liquid brines that create flow formations