(Press-News.org) Spectrometers are technology for reading light that date back to the era of famed 17th-century physicist Isaac Newton. They work by breaking down light waves into their different colors — or spectra — to provide information about the makeup of the objects being measured.
UC Santa Cruz researchers are designing new ways to make spectrometers that are ultra-small but still very powerful, to be used for anything from detecting disease to observing stars in distant galaxies. Their inexpensive production cost makes them more accessible and customizable for specific applications.
The team of researchers, led by an interdisciplinary collaboration between UC Santa Cruz Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Holger Schmidt and Professor of Astronomy and Astrophysics Kevin Bundy, published the details of their device in a paper in APL Photonics, a premier journal in the field.
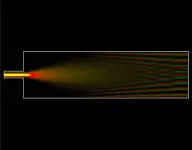
The researchers demonstrate a novel, extremely high-performance spectrometer that can measure light with a 0.05 nanometers wavelength resolution. That’s about 1.6 million times smaller than the width of a human hair, and the same resolution that can be achieved on a device 1,000 times bigger.
“That's essentially as good as a big, standard, expensive spectrometer,” said Schmidt, the senior author on the paper and a long-time expert in developing chips for light detection. “That’s really pretty impressive and very competitive.”
Miniature devices
Miniaturizing spectrometers is an active area of research, as spectrometers are used in many fields but can be as big as a three-story building and extremely expensive. However, miniaturized spectrometers often do not perform as well as bigger instruments, or they are very difficult and expensive to manufacture because they require extremely precise nanofabrication.
UC Santa Cruz researchers have created a device that is able to achieve high performance without such costly manufacturing. Their device is a miniature, high-powered waveguide which is mounted on a chip and used to guide light into a specific pattern, depending on its color.
Information from the chip is fed into a machine learning algorithm that reads the patterns created by different wavelengths of light in order to reconstruct the image with extremely high accuracy and precision — an approach is called “reconstructive” spectrometry.
This technique produces accurate results because the machine learning algorithms don’t require highly precise input to be able to distinguish the light patterns, and can constantly improve upon their own performance and optimize themselves to the hardware.
Because of this, the researchers can make the chips with relatively easy and inexpensive fabrication techniques, in a process that takes hours rather than weeks. The lightweight, compact chips for this project were designed at UCSC, and fabricated and optimized at Brigham Young University in partnership with Schmidt’s longtime collaborator Professor Aaron Hawkins and his undergraduate students.
“Compared to more sophisticated chip design, this only requires one photolithography mask which makes the fabrication much easier and much faster,” Hawkins said. “Someone with some basic capabilities could reproduce this and create a similar device tuned to their own needs.”
Reading the stars
The researchers envision that this technology can be used for a wide range of applications, though their preliminary focus is to create powerful instruments for astronomy research. Because their devices are relatively inexpensive, astronomers could specialize them to their specific research interests, which is practically impossible on much larger instruments that cost millions of dollars.
The research team is working to make the chips functional on the UC-operated Lick Observatory telescope, first to take in light from a star and later to study other astrological events. With such high accuracy on these devices, astronomers could start to understand phenomena such as the makeup of atmospheres on exoplanets, or probing the nature of dark matter in faint dwarf galaxies. The comparatively low cost of these devices would make it easier for scientists to optimize them for their specific research interests, something nearly impossible on traditional devices.
Leveraging long standing expertise at UC Santa Cruz in adaptive optics systems for astronomy, the researchers are collaborating to figure out how to best capture the faint glimmers of light from distant stars and galaxies and feed it through into the miniaturized spectrometer.
“In astronomy, when you try to put something on a telescope and get light through it, you always discover new challenges — it’s much harder than just doing it in the lab. The beauty of this collaboration is that we actually have a telescope, and we can try deploying these devices on the telescope with a good adaptive optics system,” Bundy said.
Uses for health and beyond
Beyond astronomy, the research team shows in this paper that the tool is capable of fluorescence detection, which is a noninvasive imaging technique used for many medical applications, such as cancer screening and infectious disease detection.
In the future, they plan to develop the technology for Raman scattering analysis. This is a technique that uses light scattering for the detection of any unique molecule, often used as a specialized test to look for a specific chemical substance, such as the presence of drugs in the human body or toxic pollutants in the environment. Because the system is so straightforward and does not require the use of heavy instrumentation or fluidics like other techniques, it would be convenient and robust for use in the field.
The researchers also demonstrate that the compact waveguides can be placed alongside each other to enhance the performance of the system, as each chip can measure a different spectra and provide more information about whatever light it is observing. In the paper the researchers demonstrate the power of four waveguides working together, but Schmidt envisions that hundreds of chips could be used at once.
This is the first device shown to be able to use multiple chips at once in this way. The researchers will continue to work to improve the sensitivity of the device to get even higher spectral resolution.
END
Ultra-small spectrometer yields the power of a 1,000 times bigger device
The tiny, relatively inexpensive devices could be used for customized astronomy research
2024-10-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rocky planets orbiting small stars could have stable atmospheres needed to support life
2024-10-23
Since its launch in late 2021, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has raised the possibility that we could detect signs of life on exoplanets, or planets outside our solar system.
Top candidates in this search are rocky, rather than gaseous, planets orbiting low-mass stars called M-dwarfs — easily the most common stars in the universe. One nearby M-dwarf is TRAPPIST-1, a star about 40 light years away that hosts a system of orbiting planets under intense scrutiny in the search for life on planets orbiting stars other than the sun.
Previous research questioned the habitability of planets orbiting TRAPPIST-1, finding that intense UV rays would burn away their ...
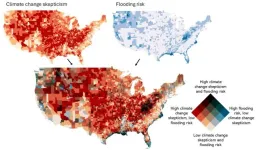
A 'worrying confluence' of flood risk, social vulnerability and climate change denial
2024-10-23
In certain parts of the United States, especially Appalachia, New England and the Northwest, the ability of residents to prepare for and respond to flooding is being undercut on three different levels.
This is according to a new study from the University of Michigan's School for Environment and Sustainability.
"It's a very worrying confluence that does keep me up," said Joshua Newell, a professor with the school's Center for Sustainable Systems and senior author of the study. "The communities that are most at risk of catastrophic flooding ...
Saving the bats: Researchers find bacteria, fungi on bat wings that could help fight deadly white-nose syndrome
2024-10-23
Saving the bats: Researchers find bacteria, fungi on bat wings that could help fight deadly white-nose syndrome
Hamilton, ON, Oct. 23, 2024 – Bacteria and fungi from the wings of bats could play a significant role in saving them from white-nose syndrome (WNS), a fungal disease affecting the skin of wings and muzzle, which has nearly wiped out vulnerable bat populations across North America.
Researchers at McMaster University have gathered and analyzed samples from the community of microorganisms, or microbiome, on the wings of several bat species ...
Project Cure CRC awards nearly $5 million in research funding
2024-10-23
Washington, D.C. – October 23, 2024 – Project Cure CRC, the breakthrough research fund of the leading nonprofit Colorectal Cancer Alliance (Alliance), has announced five new awardees of funds to advance urgent science in the colorectal cancer space. To date, 10 research grants have been awarded for a grand total of almost $5 million in critically needed funding.
Recipients of the most recent grants totaling almost $1 million include investigators from the University of California, San Francisco, Indiana University, University of Saskatchewan, Georgetown University, and Anglia Ruskin University. ...
New parasite discovered amid decline of California’s unique Channel Island fox
2024-10-23
California’s Channel Islands are home to the Channel Island fox (Urocyon littoralis), one of the smallest and most cherished species of island fox in the United States. Although no longer on the Endangered Species List, they remain a species of special concern due to their ecological importance.
In the 1990s, the San Miguel Island fox nearly went extinct, dropping to just 15 individuals. A recovery program restored their numbers by 2010. However, from 2014 to 2018, the population fell to 30% of its peak right after a new acanthocephalan parasite, commonly known as thorny-headed worms, was identified on the island. This also occurred while a multi-year draught heated San ...
Chemical Insights Research Institute publishes comprehensive guidance to protect community health impacted by wildland-urban interface fire events
2024-10-23
ATLANTA, Oct. 23, 2024 -- Chemical Insights Research Institute (CIRI) of UL Research Institutes has joined with UL Standards and Engagement to release new guidance for communities at risk for fires in wildland-urban interface (WUI) areas. An estimated 70,000 communities and 45 million residential buildings are at risk of destruction caused by wildfires. Additionally, WUI fires pose significant health risks. The smoke emitted by WUI fires likely contains a mixture of contaminants such as combustion gases, organic and inorganic metal complexes, volatile organic compounds and numerous reaction products. WUI wildfire plumes carry the risks of ...
New concussion sign identified by Mass General Brigham & Concussion Legacy Foundation scientists could identify up to 33% of undiagnosed concussions
2024-10-23
(Boston, MA) — Concussion researchers have recognized a new concussion sign that could identify up to 33% of undiagnosed concussions. After a hit to the head, individuals sometimes quickly shake their head back and forth. Although it has been depicted in movies, television, and even cartoons for decades, this motion has never been studied, named, and does not appear on any medical or sports organization’s list of potential concussion signs. A new study, led by Concussion Legacy Foundation (CLF) CEO and co-founder Chris Nowinski, PhD, says it should.
The study, published today in Diagnostics, reveals that when athletes exhibit this movement, ...
Dehydration linked to muscle cramps in IRONMAN triathletes
2024-10-23
PULLMAN, Wash. – As athletes prepare to dive into Hawaiian waters for the first part of the IRONMAN World Championship on Oct. 26, they may want to pay a little extra attention to the water inside their bodies.
Contrary to previous research, a Washington State University-led study of three decades of the IRONMAN’s top competition found a connection between dehydration and exercise-induced muscle cramps.
Based on medical data of more than 10,500 triathletes, the study, published in the Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine, found a strong link between dehydration and participants seeking treatment for muscle cramps during the competition. ...
Study: Marshes provide cost-effective coastal protection
2024-10-23
Images of coastal houses being carried off into the sea due to eroding coastlines and powerful storm surges are becoming more commonplace as climate change brings a rising sea level coupled with more powerful storms. In the U.S. alone, coastal storms caused $165 billion in losses in 2022.
Now, a study from MIT shows that protecting and enhancing salt marshes in front of protective seawalls can significantly help protect some coastlines, at a cost that makes this approach reasonable to implement.
The new findings are being reported in the journal Communications ...
New chemical treatment reduces number of plant pores that regulate water loss
2024-10-23
Researchers from Nagoya University Institute of Transformative Biomolecules (WPI-ITbM) in Japan and their colleagues have identified and derivatized a chemical compound that effectively regulates the density of stomata in model plants. Stomata are crucial for water regulation. As the environment grows increasingly unpredictable, managing water consumption for crops during droughts through chemical methods will become increasingly important. The results of their study were published in Nature Communications.
Manipulating protein interactions using chemical compounds is revolutionizing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
[Press-News.org] Ultra-small spectrometer yields the power of a 1,000 times bigger deviceThe tiny, relatively inexpensive devices could be used for customized astronomy research