(Press-News.org) Houston, Texas – In a comprehensive review published in the October 2024 issue of Genomic Psychiatry, researchers have unveiled crucial insights into how two types of hormone receptors collaborate to maintain brain health and potentially prevent neurodegenerative diseases.
The study, led by Professor Jan-Åke Gustafsson and colleagues at the University of Houston and Karolinska Institutet, demonstrates that liver X receptors (LXRs) and thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) work together in a previously unrecognized manner to regulate critical brain functions and protect against neurodegeneration.
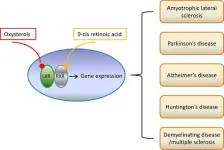
"Our analysis reveals that LXRs and TRs don't represent parallel pathways but rather constitute a single pathway through which the thyroid hormone endocrine system regulates cholesterol homeostasis," explains Professor Margaret Warner, one of the study's lead authors. "This discovery could fundamentally change how we approach treatment for various neurodegenerative conditions."
Key findings include:
• LXRs play a crucial role in regulating thyroid hormone function in the brain
• Both receptors are essential for normal brain development and maintenance
• Loss of LXR function leads to age-related neurodegeneration in multiple brain regions
• The receptors work together to maintain cholesterol balance in the brain
The review highlights several promising therapeutic implications:
1. Alzheimer's Disease: LXR activation could help reduce amyloid plaque formation and improve memory
2. Parkinson's Disease: LXR signaling appears to protect dopamine-producing neurons
3. ALS: LXRs influence motor neuron survival and function
4. Multiple Sclerosis: The receptors play crucial roles in myelin repair and maintenance
"What's particularly intriguing is the age-dependent nature of these protective effects," notes Dr. Xiaoyu Song, co-author of the study. "Understanding why certain neurons become vulnerable to degeneration as we age could be key to developing preventive treatments."
The research raises several compelling questions for future investigation:
How might targeting both receptor systems simultaneously enhance therapeutic outcomes? Could early intervention through these pathways prevent or delay the onset of neurodegenerative diseases? What role do different receptor variants play in different brain regions?
The full Genomic Psychiatry peer-reviewed article “Liver X and thyroid hormone receptors in neurodegeneration,” is available on 24 October 2024 in Genomic Psychiatry. The article is freely available online at https://gp.genomicpress.com/aop/ or https://url.genomicpress.com/yf5vx6bf
About Genomic Psychiatry – Genomic Psychiatry: Advancing Science from Genes to Society (ISSN: 2997-2388) represents a paradigm shift in genetics journals by interweaving advances in genomics and genetics with progress in all other areas of contemporary psychiatry. Genomic Psychiatry publishes peer-reviewed papers of the highest quality from any area within the continuum that goes from genes and molecules to neuroscience, clinical psychiatry, and public health.
END
Breakthrough review links hormone receptors to age-related brain disease prevention
Scientists uncover complex interplay between liver X and thyroid hormone receptors, offering new therapeutic possibilities for neurodegenerative disorders
2024-10-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New West Health-Gallup survey finds desire for better access to mental healthcare is nonpartisan issue
2024-10-24
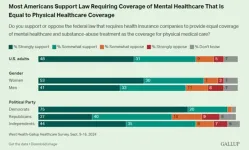
WASHINGTON, D.C. — OCTOBER 24, 2024 — Roughly four in five Americans say they either strongly (48%) or somewhat (31%) support a federal law that requires insurance companies to cover mental health at the same level they do medical or surgical care, including 95% of Democrats, 79% of independents and 67% of Republicans. Despite the widespread support, half of Americans (50%) have little to no trust that health insurers will comply with the law, according to a new West Health-Gallup survey released today.
In 2020, less than half of all adults with mental illness received treatment, according to the White House, leading the Biden ...
Cancer prevalence across vertebrate species decreases with gestation time, may increase with adult mass
2024-10-24
PHILADELPHIA – Cancer prevalence rates varied widely across vertebrate species and generally increased with higher adult mass and decreased with longer gestation time, according to results published in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
In 1977, Sir Richard Peto, FRS, FAACR, hypothesized that cancer prevalence in animals should correlate linearly with body size and lifespan, as larger animals have more cells in which to accumulate damage, and long-lived animals have more time to acquire mutations. He observed, however, that this did not seem to be the case based on ...
Epic voyage to uncover what causes tsunamis
2024-10-24
A team of international scientists, including two researchers from The Australian National University (ANU), will soon sail to the Japan Trench to discover more about what causes tsunamis.
The researchers will be on board the world’s most advanced drilling-equipped science vessel, Chikyu. It will drill directly into the Tōhoku-oki earthquake fault zone, where one of the most powerful earthquakes ever recorded in Japan occurred in 2011.
The stress accumulated at this junction over hundreds of years was suddenly released, causing the tectonic plate on which Japan sits to skip upwards and eastwards by up to 50 metres. This shallow slip displaced a vast area ...
USC Stem Cell mouse study sheds light on the secret to maintaining a youthful immune system
2024-10-24
What keeps some immune systems youthful and effective in warding off age-related diseases? In a new paper published in Cellular & Molecular Immunology, USC Stem Cell scientist Rong Lu and her collaborators point the finger at a small subset of blood stem cells, which make an outsized contribution to maintaining either a youthful balance or an age-related imbalance of the two main types of immune cells: innate and adaptive.
Innate immune cells serve as the body’s first line of defense, mobilizing a quick and general attack against invading germs. For germs that evade the body’s innate immune defenses, the second line of attack consists of adaptive immune ...
Suicide risk highest on Mondays and New Year’s Day
2024-10-23
Suicide risk is highest on Mondays and increased on New Year’s Day, whereas suicide risk on weekends and Christmas varies by country and region, finds an analysis of data from 26 countries published by The BMJ today.
The researchers say their results can help to better understand the short term variations in suicide risks and define suicide prevention action plans and awareness campaigns.
According to the World Health Organization, more than 700,000 people died due to suicide in 2019, accounting for approximately 1.3% of deaths, which was higher than the number of deaths by malaria, HIV/AIDS, and breast cancer.
Previous studies have shown that suicide ...
Gene signature shows promise to improve survival for breast cancer patients
2024-10-23
Using a gene signature technique to tailor chemotherapy for patients with early triple negative breast cancer shows promise as a way to improve disease-free survival, finds a clinical trial published by The BMJ today.
Triple negative breast cancer is an aggressive type of breast cancer that carries a higher risk of recurrence and death after standard treatment. As such, there is an urgent need for more effective chemotherapy strategies.
Multigene signatures are tests that analyse genes in a tumour sample to predict how well ...
Investigation finds “unexplained” millions in drug industry payments to the NHS
2024-10-23
Pharmaceutical companies have paid an estimated £156 million to NHS trusts in England between 2015 and 2022 without the public being told what the payments are for, reveals an investigation by The BMJ today.
The findings raise important questions about unrecognised conflicts of interest and have led to calls for a shake-up of current transparency rules.
The BMJ tracked all disclosed non-research payments to NHS trusts in England from 2015 to 2022 reported in Disclosure UK, a database run by the Association of the British Pharmaceutical Industry (ABPI), which requires participating companies to disclose cash payments and other benefits in ...
Maternal antibodies interfere with malaria vaccine responses
2024-10-23
Maternal antibodies passed across the placenta can interfere with the response to the malaria vaccine, which would explain its lower efficacy in infants under five months of age, according to research led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), in collaboration with seven African centers (CISM-Mozambique, IHI-Tanzania, CRUN-Burkina Faso, KHRC-Ghana, NNIMR-Ghana, CERMEL-Gabon, KEMRI-Kenya). The findings, published in Lancet Infectious Diseases, suggest that children younger than currently recommended by the WHO may benefit from the RTS,S and R21 malaria vaccines if they live in areas with low malaria transmission, ...
Teaching must be made more attractive as a profession to tackle shortages
2024-10-23
Teaching needs to be made more attractive to a wider pool of graduates to tackle shortages in the profession, according to new international research comparing 18 countries.
The worldwide comparison led by Durham University, UK, shows that the level of pay relative to other graduate professions, lack of resources and poor student behaviour all play a part in recruitment and retention issues.
Popular quick-fix strategies used across the world to attract and retain teachers, such as bursaries, scholarships and ...
Airbnb rentals linked to increased crime rates in London neighborhoods – study
2024-10-23
Latest research has revealed a “positive association” between the number of properties listed as Airbnb rentals and police-reported robberies and violent crimes in thousands of London neighbourhoods between 2015 and 2018.
In fact, the study from University of Cambridge and the University of Pennsylvania suggests that a 10% increase in active Airbnb rentals in the city would correspond to an additional 1,000 robberies per year across London.*
Urban sociologists say the rapid pace at which crime rises in conjunction with new rentals suggests that the link is related more to opportunities for crime, rather than loss ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
[Press-News.org] Breakthrough review links hormone receptors to age-related brain disease preventionScientists uncover complex interplay between liver X and thyroid hormone receptors, offering new therapeutic possibilities for neurodegenerative disorders