(Press-News.org) BOSTON (Oct. 24, 2024) – In many cultures, it is common to burn incense for religious and cultural practices, including meditations, celebrations and spiritual and ancestral worship. A new medically challenging case being presented at this year’s American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting in Boston warns that, for those with allergies and asthma, health problems from burning incense can be a significant risk to adults and children.
“Our patient was an 87-year-old woman with history of asthma and COPD, on oxygen therapy, who presented with unexplained shortness of breath,” says Gomeo Lam, BA, lead author on the paper. “A detailed history revealed daily incense burning. We recommended she stop burning incense, which the patient did not want to do as burning joss stick incense daily allowed her to express homage and veneration for ancestors. We then advised she use electric incense devices, which resulted in improvement of her symptoms.”
The paper points out that burning incense poses health risks including headaches, respiratory dysfunction, dermatologic sensitivity and allergic reactions. Incense fumes contain carbon, sulfur, nitrogen oxides as well as formaldehyde, and other polycyclic aromatic volatile compounds which are carcinogenic. Per gram burned, particulate matter generated from incense is 45 mg versus 10 mg from cigarettes.
“People who burn incense may not realize that family members, including children, who are exposed to secondhand smoke, face health consequences,” says allergist Mary Lee-Wong, senior author of the study and ACAAI member. “Similar to tobacco smoke, thirdhand incense smoke may linger in furniture, clothing, and other articles, dissipating for months afterward.”
The authors point out that, besides health implications, incense combustion contributes to air pollution and can be a fire hazard. They recommend that when counseling patients who burn incense, health practitioners consider the sacred significance of incense burning, but also recognize that health risks from this practice cannot be overlooked. After screening patients for incense use, healthcare practitioners can recommend replacement with electric or aromatic vapors; simulated visuals; improved ventilation; and limiting burn time as approaches to mitigate harms and improve symptoms.
Abstract Title: HEALTH HAZARDS FROM CULTURAL PRACTICES: INCENSE BURNING (Abstract below - image included with online abstract)
Presenter: Gomeo Lam, BA
For more information about allergies and asthma, or to find an allergist in your area, visit AllergyandAsthmaRelief.org. The ACAAI Annual Scientific Meeting is Nov. 9-13. For more news and research from the ACAAI Scientific Meeting, go to our newsroom and follow the conversation on X/Twitter #ACAAI24.
About ACAAI
The American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI) is a professional medical organization of more than 6,000 allergists-immunologists and allied health professionals, headquartered in Arlington Heights, Ill. Founded in 1942, the College fosters a culture of collaboration and congeniality in which its members work together and with others toward the common goals of patient care, education, advocacy, and research. ACAAI allergists are board-certified physicians trained to diagnose allergies and asthma, administer immunotherapy, and provide patients with the best treatment outcomes. For more information and to find relief, visit AllergyandAsthmaRelief.org. Join us on Facebook, Pinterest, Instagram and X/Twitter.
M163
HEALTH HAZARDS FROM CULTURAL PRACTICES: INCENSE BURNING
G. Lam*1, A. Wu2, H. Bao3, S. Gomez4, M. Lee-Wong5, 1. Suwanee, GA; 2. Hempstead, NY; 3. Bronx, NY; 4. Brooklyn, NY; 5. New York, NY.
Introduction: Incense, as coils, cones, powders and sticks, is widely used for religious and cultural practices. Usage includes meditations, celebrations, deodorizations, in addition to spiritual and ancestral worship. Health problems from incense burning are numerous.
Case Description: An 87-year-old woman with history of asthma and COPD, on oxygen therapy, presents with unexplained shortness of breath. Detailed history taking disclosed temporal relationship with incense burning. Recommendation to stop burning incense was denied as burning joss stick incense daily allows patient to express homage and veneration for ancestors. Subsequently, advice to use electric incense devices resulted in improvement of patient's symptoms.
Discussion: Burning incense poses health risks including headaches, respiratory dysfunction, dermatologic sensitivity and allergic reactions. Incense fumes contain carbon, sulfur, nitrogen oxides as well as formaldehyde, and other polycyclic aromatic volatile compounds which are carcinogenic. Per gram burned, particulate matter generated from incense is 45 mg versus 10 mg from cigarettes. Studies report family members, including children, exposed to incense burning suffer from secondhand smoke health consequences. Like tobacco smoke, thirdhand incense smoke may linger in furniture, clothing, and other articles, dissipating for months afterwards. Besides health implications, incense combustion contributes to air pollution and can be a fire hazard. Understanding the role, cultural sensitivity and sacred significance of incense burning is vital but health risks from burning incense cannot be overlooked. Screening patients for incense use, in addition to replacement with electric or aromatic vapors, simulated visuals, improved ventilation, and limiting burn time can be explored with impacted patients.
END
Burning incense can pose health risks for those with allergies and asthma
Symptoms include headaches, respiratory dysfunction and skin sensitivity
2024-10-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: Parents’ understanding of atopic dermatitis may influence child’s diet
2024-10-24
BOSTON (Oct. 24, 2024) – Parents of children with atopic dermatitis (AD, also called eczema) know that the allergic condition can mean a heightened risk of developing food allergies. The desire to prevent food allergies causes some parents to consider elimination diets, cutting out certain foods from their child’s diet. A new study being presented at this year’s American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting in Boston showed that elimination diets in the case ...
Vaccine refusal lower in minorities in new study
2024-10-24
BOSTON (Oct. 24, 2024) – Throughout the Covid pandemic, media widely reported that Black patients were more likely than White patients to refuse vaccines, including the influenza and Covid vaccines. A new study being presented at this year’s American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting in Boston showed that self-identified non-White patients were less likely to demonstrate vaccine-hesitancy than the self-identified White patient group.
“We found ...
Risk of developing EoE high when other allergic conditions factored in
2024-10-24
BOSTON (Oct. 24, 2024) – Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE), a disorder of the esophagus, is increasingly recognized as a major cause of swallowing difficulties in children and adults. It affects about one in 2,000 people and is part of a spectrum of allergic conditions. A new study being presented at this year’s American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting in Boston investigated the probability of patients with certain atopic (allergic) conditions developing EoE.
“We did a separate analysis of four common allergic conditions – asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis and food allergy – to determine ...
Study shows rates of sensitization in Chicago to outdoor allergens increased post-COVID
2024-10-24
BOSTON (Oct. 24, 2024) – People have heard for years that climate change is having a significant impact on plant vegetation patterns and influencing how pollen and mold produce. A new study being presented at this year’s American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) Annual Scientific Meeting in Boston showed that, in Chicago, there has been a significant increase in sensitization to pollens and molds in patients with nasal allergies.
“Our goal was to analyze changes in pollen sensitization patterns ...
Phase Two results with CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing support further development as treatment for hereditary angioedema (HAE)
2024-10-24
A single treatment with, a CRISPR-Cas9 based gene editing therapy, is enough to replace the daily medication of patients with hereditary angioedema (HAE), a condition characterized by severe, painful and sudden onset of swelling, sometimes resulting in death. Confirming the findings published earlier this year from researchers from Amsterdam UMC, the University of Auckland and Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. This phase two study is published today in the New England Journal of Medicine and presented at American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology's annual congress on the ...
Take aim at the pause!
2024-10-24
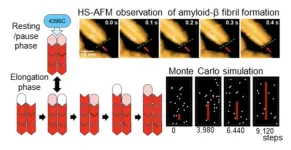
A collaborative research group, including researchers from Exploratory Research Center on Life and Living Systems and Institute for Molecular Science of National Institutes of Natural Sciences, as well as Nagoya City University, Nagoya University, and University of Tsukuba, has uncovered a new mechanism in the growth of amyloid β (Aβ) fibrils, which are closely associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Using advanced high-speed atomic force microscopy (HS-AFM), the team was able to observe Aβ fibril growth at the molecular ...
Pistachios may help improve eye health, new study finds
2024-10-24
A new study1 from researchers at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University has found that consuming pistachios daily may significantly improve eye health by increasing macular pigment optical density (MPOD), due to the plant pigment lutein, a key factor in protecting the eyes from blue (visible) light and age-related damage.
The randomized controlled trial showed that compared to eating a usual diet alone, eating 2 ounces (57 grams) of pistachios per day for 12 weeks as part of a usual diet resulted in a significant increase in MPOD in otherwise healthy middle-aged to older adults. MPOD is an important indicator of eye health, ...
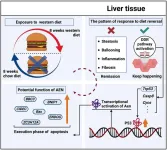
Transcriptomic landscape analysis reveals a persistent DNA damage response in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis post-dietary intervention
2024-10-24
Background and Aims
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its more advanced form, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, have emerged as the most prevalent liver diseases worldwide. Currently, lifestyle modification is the foremost guideline-recommended management strategy for MASLD. However, it remains unclear which detrimental signals persist in MASLD even after disease remission. Thus, we aimed to examine the persistent changes in liver transcriptomic profiles following ...
ECOG-ACRIN and Caris Life Sciences partner to interrogate landmark TAILORx breast cancer trial
2024-10-24
ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) and Caris Life Sciences®(Caris) announced today a multi-year research collaboration wherein Caris is pairing its highly sophisticated and comprehensive genomic, transcriptomic and proteomic profiling, advanced artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms with ECOG-ACRIN’s immense research capabilities. The first project is underway and leverages the tumor tissue samples from the Trial Assigning Individualized Options for Treatment (Rx) or TAILORx, breast cancer clinical trial. TAILORx is one of the world's largest breast cancer research resources. The TAILORx trial and its associated biospecimen ...
Ion-pairing: A new approach to lyotropic chromonic liquid crystal assembly
2024-10-24
Self-assembling molecules into organized structures is highly valuable for developing new materials. One notable class of these materials is lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals (LCLCs), which are molecular assemblies of amphiphilic π-electronic molecules, with water-absorbing and water-repelling parts. The term “lyotropic” refers to liquid crystal phases that depend on the concentration of the molecules in a solvent, while “chromonic” indicates that these molecules are stacked into columnar assemblies. In a solvent, these structures are stabilized by π–π interactions and hydrophobic effects. Examples of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
[Press-News.org] Burning incense can pose health risks for those with allergies and asthmaSymptoms include headaches, respiratory dysfunction and skin sensitivity