(Press-News.org)
“Our finding that enhanced melting of Arctic sea-ice likely resulted in significant cooling in northern Europe in the earth’s past is alarming,” says Mohamed Ezat from the iC3 Polar Research Hub, lead author of the new study. “This reminds us that the planet’s climate is a delicate balance, easily disrupted by changes in temperature and ice cover.”
Ice-free summer conditions are expected to occur in the Arctic Ocean from the year 2050 onwards.
Earlier this month, dozens of climate scientists warned in an open letter that climate change is generating a “serious risk of a major ocean circulation change in the Atlantic [that] would have devastating and irreversible impacts”.
The Nordic Seas, located between Greenland and Norway, are a key area for oceanic heat transport and influence weather patterns far beyond their geographical boundaries.
During the early part of the Last Interglacial, over 100,000 years ago, global temperatures were warmer than present, ice volumes were smaller, and sea levels were significantly higher.
Mohammed Ezat’s research team has now linked the warming climate and enhanced melting of Arctic sea-ice during that era to changes in regional sea-surface temperature and ocean circulation.
As the sea-ice melted, it altered the salinity and density of the water and disrupted the normal flow of currents, leading to changes in circulation patterns and heat distribution across the ocean.
Understanding the dynamics of the Last Interglacial is crucial, he explains. Past warm periods in the earth’s history underscore the importance of feedback mechanisms in the climate system. As the Arctic continues to warm and sea-ice diminishes, further alterations in ocean currents and weather patterns may occur.
Ezat’s research team utilized a combination of biological, inorganic and organic geochemical tracers from sediment cores taken from the Nordic Seas. These cores act like time capsules, preserving information about past ocean conditions. By analyzing the chemical signatures within these sediments, the team was able to reconstruct past sea surface temperatures and salinity levels, sources of freshwater input and deep water formation processes.
Mohamed Ezat cautions that many questions still remain unanswered. “We can learn a lot from the still open question of the Last Interglacial cooling in the Norwegian Sea and potential responsible processes” he says. “We hope that our study provides a benchmark for climate modelers to utilize this time period to better constrain the impacts of ice changes on regional and global climate.”
The study used a multi-proxy approach (diatom, dinocyst, and planktic foraminiferal assemblages, sea ice biomarkers, planktic foraminiferal Na/Ca and Ba/Ca, and benthic foraminiferal assemblages) to reconstruct the development of sea ice, sea surface temperature, deep ocean convection as well as changes in freshwater input and their sources during the Last Interglacial period. It is available open access in Nature Communications.
END
San Diego, CA (October 26, 2024) — For kidney transplant recipients experiencing antibody-mediated rejection, the current standard of care involves removing donor-specific antibodies (DSAs) through plasmapheresis (PLEX)—a procedure that removes antibodies from the plasma portion of the blood. Results from a recent clinical trial reveal that an investigational drug called imlifidase, which cleaves and inactivates the type of antibodies that include DSAs, is more effective than PLEX. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney ...
San Diego, CA (October 26, 2024) — IgA nephropathy is an autoimmune kidney disease, and complement, a component of the innate immune system, plays a role in the condition’s pathogenesis. Investigators have developed and tested a novel gene therapy that enters kidney cells and enables them to block complement activation. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23– 27.
The gene therapy, called PS-002, uses a modified virus to treat kidney cells called podocytes. Administration of PS-002 in a mouse model of IgA nephropathy reduced signs of kidney dysfunction, lowered complement ...
San Diego, CA (October 26, 2024) — Chronic active antibody-mediated rejection (caAMR) is a common cause of allograft loss after transplantation, with no approved therapies. Clazakizumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6), stabilized kidney transplant recipients’ kidney function in a phase 2 trial. Investigators now have data from a phase 3 trial with clazakizumab. The findings from the Phase 3 IMAGINE trial, the largest placebo-controlled study in kidney transplant recipients with caAMR, will be ...
The results of numerous high-impact phase 3 clinical trials that could affect kidney-related medical care will be presented in-person at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23–27.
Hyponatremia, or a chronically low blood salt level, is the most common electrolyte disorder in hospitalized patients, and is associated with higher risks of death and re-hospitalization. In a recent trial, 2,173 hospitalized patients with hyponatremia from 9 centers across Europe were assigned to undergo either targeted correction of blood salt levels according to guidelines or to receive routine care for hyponatremia. The primary outcome was the combined ...
Background and objectives
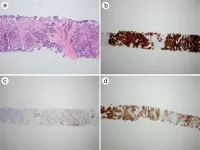
Mesothelioma is an aggressive tumor with a poor prognosis. Histological diagnosis of mesothelioma using limited tissue samples can be challenging. Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) is a transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in a variety of solid tumors. This study aimed to investigate the clinical utility of CAIX expression in the differential diagnosis of pleural mesothelioma from non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC).
Methods
Unstained tissue microarray slides composed of 56 cases of pleural mesothelioma and 82 cases of NSCLC were subjected to immunohistochemical staining using a mouse anti-human antibody against CAIX.
Results
Of the 38 epithelioid mesothelioma ...
Background and objectives
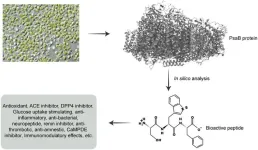
Chlorella vulgaris is a green, photosynthetic microalga in the phylum Chlorophyta. The goal of our study was to perform a bioinformatics analysis of Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A2, one of its photosynthesis-related proteins, and to hunt for potent bioactive peptides.
Methods
To generate peptides and estimate the safety and efficacy of each bioactive peptide, we employed the tools BIOPEP-UWM™, PeptideRanker, DBAASP, and ToxinPred. PepDraw was used to understand the physicochemical properties ...
Background and objectives
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection can cause multiple secondary digestive disorders. Some studies have found that polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor (TLR) genes, including TLR10 rs10004195, may be associated with increased susceptibility to H. pylori infection. Despite conflicting reports, we conducted a meta-analysis to clarify the relationship between these factors.
Methods
We conducted an exhaustive review, encompassing all relevant literature up to February 2024, using databases ...
Background and objectives
Nail psoriasis is common in patients with plaque psoriasis and is associated with morbidity, including onychomycosis, which can complicate psoriasis treatments and be difficult to differentiate. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry is a fast and simple technique for identifying microorganisms through protein analysis. This study aimed to determine the sensitivity and specificity of MALDI-TOF for diagnosing onychomycosis in patients with nail psoriasis, by using conventional mycological and histological methods as the reference standard.
Methods
A prospective study was conducted on 88 patients with ...
Background and Aims
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the misfolding and accumulation of the mutant variant of alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) within hepatocytes, which limits its access to the circulation and exposes the lungs to protease-mediated tissue damage. This results in progressive liver disease secondary to AAT polymerization and accumulation, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) due to deficient levels of AAT within the lungs. Our goal was to characterize the unique effects of COPD secondary to AATD on liver disease and gene expression.
Methods
A ...
Background and Aims
The effect of tenofovir amibufenamide (TMF) on blood lipid profiles in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) remains unclear. This study aimed to explore whether TMF affects blood lipids during 48 weeks in patients with CHB.
Methods
A total of 91 patients with CHB undergoing TMF treatment for 48 weeks were divided into two groups: Lipid Normal (n = 42) and Lipid Abnormal (n = 49), based on baseline blood lipid levels. Lipid indices, virological responses, and biochemical indicators were compared between the two groups. Clinical observations were ...