(Press-News.org) Our ability to see starts with the light-sensitive photoreceptor cells in our eyes. A specific region of the retina, termed fovea, is responsible for sharp vision. Here, the color-sensitive cone photoreceptors allow us to detect even the smallest details. The density of these cells varies from person to person. Additionally, when we fixate on an object, our eyes make subtle, continuous movements, which also differ between individuals. Researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn have now investigated how sharp vision is linked to these tiny eye movements and the mosaic of cones. Using high-resolution imaging and micro-psychophysics, they demonstrated that eye movements are finely tuned to provide optimal sampling by the cones. The results of the study have now been published in the journal eLife.
Humans can fixate their gaze on an object to see it clearly thanks to a small region in the center of the retina. This area, known as the fovea (latin for "pit"), is made up of a tightly packed mosaic of light-sensitive cone photoreceptor cells. Their density reaches peaks of more than 200,000 cones per square millimeter— in an area about 200 times smaller than a quarter-dollar coin. The tiny foveal cones sample the portion of visual space visible to the eye and send their signals to the brain. This is analogous to the pixels of a camera sensor, with millions of photo‑sensitive cells spread across their surface.
However, there is an important difference: unlike the pixels of a camera sensor, the cones in the fovea are not uniformly distributed. Each eye has a unique density pattern in their fovea. Additionally, “unlike a camera, our eyes are constantly and unconsciously in motion,” explains Dr. Wolf Harmening, head of the AOVision Laboratory at the Department of Ophthalmology at UKB and a member of the Transdisciplinary Research Area (TRA) "Life & Health" at the University of Bonn. This happens even when we are looking steadily at a stationary object. These fixational eye movements convey fine spatial details by introducing ever-changing photoreceptor signals, which must be decoded by the brain. It is well known that one of the components of fixational eye movements, termed drift, can differ between individuals, and that larger eye movements can impair vision. How drift relates to the photoreceptors in the fovea, however, and our ability to resolve fine detail has not been investigated until now.
Using High-Resolution Imaging and Micro-Psychophysics
This is precisely what Harmening’s research team has now investigated by using an adaptive optics scanning light ophthalmoscope (AOSLO), the only one of its kind in Germany. Given the exceptional precision offered by this instrument, the researchers could examine the direct relationship between cone density in the fovea and the smallest details we can resolve. At the same time, they recorded the tiny movements of the eyes. To do this, they measured visual acuity of 16 healthy participants while performing a visually demanding task. The team tracked the path of the visual stimulus on the retina to later determine which photoreceptor cells contributed to vision in each participant. The researchers – including first author Jenny Witten from the Department of Ophthalmology at UKB, who is also a PhD student at the University of Bonn – used AOSLO video recordings to analyze how the participants’ eyes moved during a letter discrimination task.
Eye Movements are finely tuned to Cone Density
The study revealed that humans are able to perceive finer details than the cone density in the fovea would suggest. “From this, we conclude that the spatial arrangement of foveal cones only partially predicts resolution acuity,” reports Harmening. In addition, the researchers found that tiny eye movements influence sharp vision: during fixation, drift eye movements are precisely aligned to systematically move the retina synchronized with the structure of the fovea. “The drift movements repeatedly brought visual stimuli into the region where cone density was highest,” explains Witten. Overall, the results showed that within just a few hundred milliseconds, drift behavior adjusted to retinal areas with higher cone density, improving sharp vision. The length and direction of these drift movements played a key role.
According to Harmening and his team, these findings provide new insights into the fundamental relationship between eye physiology and vision: “Understanding how the eye moves optimally to achieve sharp vision can help us to better understand ophthalmological and neuropsychological disorders, and to improve technological solutions designed to mimic or restore human vision, such as retinal implants.”
Funding: This work was supported by the Emmy Noether Program of the German Research Foundation (DFG); the Carl Zeiss Foundation (HC-AOSLO); Novartis Pharma GmbH (EYENovative research award), and the Open Access Publication Fund of the University of Bonn.
Publication: Jenny L. Witten, Veronika Lukyanova, Wolf M. Harmening: Sub-cone visual resolution by active, adaptive sampling in the human foveolar; eLife; DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.98648.3
END
Subtle eye movements optimize vision
Researchers from Bonn uncover how tiny eye movements and the density of our photoreceptors aid in sharp vision
2024-10-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Maternal health expert professor Vicki Clifton reveals placenta's hidden role in mental health
2024-10-29
Brisbane, Queensland, Australia (October 29, 2024) - In a revealing Genomic Press Interview published in Brain Medicine on October 29, 2024, Professor Vicki Clifton shares transformative discoveries about the placenta's unexpected influence on maternal mental health, potentially revolutionizing our understanding of pregnancy-related anxiety and depression.
Professor Clifton's team at the Mater Research Institute-University of Queensland has identified 13 distinct glucocorticoid receptor isoforms in the placenta, with one particular variant ...
From concert piano to fear memory research: Dr. Raül Andero Galí bridges mouse-human studies
2024-10-29
Barcelona, Spain (October 29, 2024) - In a compelling new Genomic Press Interview published in Brain Medicine, Dr. Raül Andero Galí reveals how his early passion for classical piano shaped his unique approach to neuroscience research. As an ICREA Research Professor at the Autonomous University of Barcelona, Dr. Andero Galí leads groundbreaking studies that connect mouse and human fear responses, potentially revolutionizing treatments for PTSD and anxiety disorders.
The intersection of stress and memory has captured Dr. Andero Galí's attention throughout his career. "All ...
Arctic whales research collaboration is signed by Heriot-Watt University and HX Expeditions (Hurtigruten Expeditions)
2024-10-29
Pioneering research to protect and conserve Arctic whale populations is to begin under a new five-year collaboration between Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh, Scotland and HX Expeditions (Hurtigruten Expeditions), a world leader in travel exploration.
The partners have signed a five-year Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), beginning in 2024, to research challenges facing marine life in the high Arctic – the most northern part of the Arctic region and one of the world’s most fragile ecosystems.
The agreement will see Heriot-Watt University and HX work together on the Whales & Arctic Vessels Project (WAVE), ...
Scientists develop tool to predict sepsis in apparently healthy newborns
2024-10-29
A genetic signature in newborns can predict neonatal sepsis before symptoms even start to show, according to a new study.
The study, led by UBC and SFU researchers in collaboration with the Medical Research Council (MRC) Unit The Gambia, has the potential to help healthcare workers diagnose babies earlier, including in lower- and middle-income countries (LMICs) where neonatal sepsis is of particular concern. The research, published today in eBiomedicine, is funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
“Neonatal sepsis is caused by the body’s irregular response ...
AI algorithm accurately detects heart disease in dogs
2024-10-29
Researchers have developed a machine learning algorithm to accurately detect heart murmurs in dogs, one of the main indicators of cardiac disease, which affects a large proportion of some smaller breeds such as King Charles Spaniels.
The research team, led by the University of Cambridge, adapted an algorithm originally designed for humans and found it could automatically detect and grade heart murmurs in dogs, based on audio recordings from digital stethoscopes. In tests, the algorithm detected heart murmurs with a sensitivity ...
What animal societies can teach us about ageing
2024-10-29
Red deer may become less sociable as they grow old to reduce the risk of picking up diseases, while older house sparrows seem to have fewer social interactions as their peers die off, according to new research which shows humans are not the only animals to change our social behaviour as we age.
A collection of 16 studies, including six from the University of Leeds, have been published today as part of a special issue of the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, investigating ageing and society across the natural world.
One study into red deer shows that ...
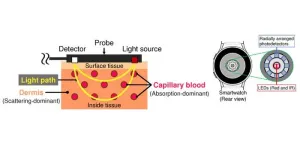
Enhancing the accuracy of wearables that measure blood glucose levels
2024-10-28
Diabetes is an increasingly pervasive disease, currently affecting over 500 million adults worldwide. Since there is as yet no cure for type 1 or type 2 diabetes, patients must regularly monitor their BGLs to keep them in check. Though BGL-measuring devices relying on painful finger pricks have been the gold standard for decades, modern technology is slowly opening doors to better alternatives.
Many researchers have proposed noninvasive methods to monitor BGLs using widely available wearable devices, such as smartwatches. For example, by placing the LEDs ...
Increasing social supports for new mothers with opioid use disorder
2024-10-28
Opioid use disorder (OUD) is a growing public health problem among pregnant and parenting people in the U.S. Between 1999 and 2014, the number of pregnant women with OUD increased by more than four times. This trend also coincides with a rise in pregnancy-associated maternal overdose mortality.
Researchers at Thomas Jefferson University, led by Meghan Gannon, PhD, MSPH, investigated how community-based supports, like doulas, can be integrated into health care for mothers who use opioids. Using a social network analysis, ...
Mitigating the neurotoxic effects of lead exposure
2024-10-28
Lead exposure is a risk to any human, but children are most vulnerable to the element’s neurotoxicity, which can lead to developmental delays, learning difficulties and mood changes among other symptoms. There has been some progress in reducing exposure and preventing neurotoxicity, but hundreds of thousands of American children are still affected.
A new study by Thomas Jefferson University neuroscientist Jay Schneider, PhD, suggests that the toxic effects of lead can be mitigated by attentive maternal care and an enriched environment ...
Developing kidneys from scratch
2024-10-28
To Alex Hughes, Assistant Professor in Bioengineering within Penn Engineering and in Cell and Developmental Biology within Penn Medicine, the kidney is a work of art. “I find the development of the kidney to be a really beautiful process,” says Hughes.
Most people only ever see the organ in cross-section, through textbooks or by dissecting animal kidneys in high school biology class: a bean-shaped slice with lots of tiny tubes. “I think that really undersells how amazing the structure is,” says ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
Heterogeneity of treatment effects of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss in adults
Within-person association between daily screen use and sleep in youth
Low-dose lithium for mild cognitive impairment
Catheter ablation and oral anticoagulation for secondary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
A new theory of brain development
Pilot clinical trial suggests low dose lithium may slow verbal memory decline
Bioprinting muscle that knows how to align its cells just as in the human body
A hair-thin fiber can read the chemistry of a single drop of body fluid
SwRI develops magnetostrictive probe for safer, more cost-effective storage tank inspections
National report supports measurement innovation to aid commercial fusion energy and enable new plasma technologies
Mount Sinai, Uniformed Services University join forces to predict and prevent diseases before they start
Science of fitting in: Do best friends or popular peers shape teen behavior?
USF study: Gag grouper are overfished in the Gulf; this new tool could help
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
[Press-News.org] Subtle eye movements optimize visionResearchers from Bonn uncover how tiny eye movements and the density of our photoreceptors aid in sharp vision