(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND, Ohio (Oct. 30, 2024)—Many studies suggest that an earlier age at menopause is more detrimental to a woman’s health, leading to an increased risk for adverse health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, osteoporosis, and depression, among others. However, a new study is linking a later age at natural menopause with a greater risk for asthma. Results of the study are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
Asthma is a common, chronic disease affecting more than 300 million people worldwide. The prevalence of asthma has been increasing over recent years, creating a substantial economic impact because it is one of the highest diseases for healthcare use. Adult-onset asthma is typically more severe and more difficult to treat than childhood asthma.
Multiple studies have suggested a possible link between asthma and sex hormones. Most notable is the fact that adult-onset asthma is more common in women than men. In childhood, asthma is more prevalent in boys. After puberty, however, asthma occurs more often in girls. Women also tend to have more severe asthma and are less likely to have remission of the disease.
Some studies have found a peak incidence of asthma at around age 40 years, which is commonly the age of the menopause transition, whereas other studies found a peak at the average age at menopause, which is 51 years. Both natural estrogen and synthetic estrogen, such as used in hormone therapy, offer similar risk profiles. Women using hormone therapy were shown to have a 63% increased risk of asthma, whereas women who stopped hormone therapy were two times more likely to quit asthma treatment. Higher body mass index also is shown to be a risk factor for women, but not men, because fat produces estrogen.
Unfortunately, research on the association between menopause and asthma incidence is limited and has yielded conflicting results. That is why this newest study, based on 10 years of follow-up data from more than 14,000 postmenopausal women, was designed to investigate the association between the age at natural menopause and incidence of asthma in nonsmoking postmenopausal women. The study researchers found that women with early menopause (which occurs between 40 and 44 years of age) are at a reduced risk of asthma, which led them to suggest a role of estrogen with asthma risk.
Study results are published in the article “The association between age at natural menopause and risk of asthma among postmenopausal women from the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging.”
“This study highlights sex-based differences in asthma, with women at a greater risk for asthma than men in adulthood. It also showed that women with later onset of menopause are at greater risk than those with early onset of menopause. Clinicians should be aware of this link and should monitor women with later age at natural menopause for asthma symptoms,” says Dr. Stephanie Faubion, medical director for The Menopause Society.
For more information about menopause and healthy aging, visit www.menopause.org.
The Menopause Society (formerly The North American Menopause Society) is dedicated to empowering healthcare professionals and providing them with the tools and resources to improve the health of women during the menopause transition and beyond. As the leading authority on menopause since 1989, the nonprofit, multidisciplinary organization serves as the independent, evidence-based resource for healthcare professionals, researchers, the media, and the public and leads the conversation about improving women’s health and healthcare experiences. To learn more, visit menopause.org.
END
Women entering menopause later in life at greater risk for asthma
New study suggests role of natural and synthetic estrogen in increasing risk of asthma
2024-10-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sinuses prevented prehistoric croc relatives from deep diving
2024-10-30
EMBARGOED: NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL 00.05 (UK TIME) WEDNESDAY 30 OCTOBER 2024
An international team of paleobiologists have found that the sinuses of ocean dwelling relatives of modern-day crocodiles prevented them from evolving into deep divers like whales and dolphins.
A new paper published today [30 October] in Royal Society Open Science suggests that thalattosuchians, which lived at the time of the dinosaurs, were stopped from exploring the deep due to their large snout sinuses.
Whales and dolphins (cetaceans) ...
Spirited away: Key protein aids transport within plant cells
2024-10-30
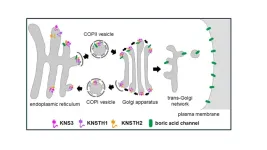
Botanists have come to understand the channels and transporters involved in the uptake and transport of nutrients, yet how are they positioned where they need to be?
For example, plants need boron, which is taken into the cells by molecules known as the boric acid channel. But how do the proteins that form the channel make it to the plasma membrane?
A research group led by Professor Junpei Takano of Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Agriculture identified a mutant line of Arabidopsis thaliana in which the boric acid channels are not properly transported to the plasma membrane. The cause was a deficiency in the protein KAONASHI3 (KNS3); the name ...
Britain’s brass bands older than we thought and invented by soldiers from the Napoleonic Wars, new study reveals
2024-10-30
University of Cambridge media release
Britain’s brass bands older than we thought and invented by soldiers from the Napoleonic Wars, new study reveals
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 00:01 AM (UK TIME) ON WEDNESDAY 30TH OCTOBER 2024
Military musicians returning from the Napoleonic wars established Britain’s first brass bands earlier than previously thought, new research reveals. The study undermines the idea that brass bands were a civilian and exclusively northern creation.
It is widely believed that brass bands originated with coal miners and other industrial communities ...
The Lancet: Health threats of climate change reach record-breaking levels, as experts call for trillions of dollars spent on fossil fuels to be redirected towards protecting people’s health, lives and
2024-10-30
The Lancet: Health threats of climate change reach record-breaking levels, as experts call for trillions of dollars spent on fossil fuels to be redirected towards protecting people’s health, lives and livelihoods
New global findings in the 8th annual indicator report of the Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change reveal that people in every country face record-breaking threats to health and survival from the rapidly changing climate, with 10 of 15 indicators tracking health threats reaching ...
‘Weekend warrior’ exercise pattern may equal more frequent sessions for lowering cognitive decline risk
2024-10-29
Just one or two sessions of physical activity at the weekend—a pattern of exercise dubbed ‘weekend warrior’---may be just as likely to lower the risk of cognitive decline, which can often precede dementia, as more frequent sessions, concludes research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
And it may be more convenient and achievable for busy people as well, suggest the researchers.
It’s important to identify potentially modifiable risk factors for dementia because a 5-year delay in onset might halve its prevalence, they say, adding that nearly all the evidence to date comes from studies ...
Physical activity of any intensity linked to lower risk of death after dementia diagnosis
2024-10-29
Physical activity of any intensity after a diagnosis of dementia is associated with around a 30% lower risk of death, finds research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
The findings prompt the researchers to conclude that those affected should be encouraged to keep up or start an exercise routine, especially as average life expectancy after a diagnosis of dementia may be only around 4-5 years.
Previously published research has linked physical activity with a lower risk of death in people with the disease, but these studies have focused on a single point in time. So it’s not clear if changes in the amount or intensity of physical ...
Brain changes seen in lifetime cannabis users may not be causal
2024-10-29
Lifetime cannabis use is associated with several changes in brain structure and function in later life, suggests an observational study, but these associations may not be causal, finds a genetic analysis of the same data, published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
Some other unidentified factors may explain the differences found, say the researchers, who nevertheless emphasise that further research is needed to fully understand the effects of heavy use and cannabis potency on the brain.
Cannabis use has increased worldwide following its ...
For the love of suckers: Volunteers contribute to research on key freshwater fishes
2024-10-29
A new paper published today, led by Chicago’s Shedd Aquarium, reveals how volunteers across Illinois, Wisconsin and Michigan enabled researchers to gather seven years of data on the spawning migrations of suckers, an understudied yet essential group of freshwater fishes. Using observations collected by trained members of the public, the collaborative team of researchers have discovered that temperature is the primary trigger for sucker spawning migration, which can help inform conservation strategies in light of a changing climate.
“We believe that conservation of native, non-game fishes ...
Bill and Mary Anne Dingus commit $1M to fund Human Impacts on the Earth Fund at Rice
2024-10-29
Bill Dingus ’81, a Rice University alumnus, and his wife Mary Anne have pledged $1 million to support the university’s Human Impacts on the Earth Fund, dedicated to mitigating and addressing the negative environmental effects caused by human activities on the planet. Additionally, the Dingus family is matching other donors’ contributions to the fund up to $250,000.
The Dingus’ donation enables the launch of the Earth and Planetary Opportunities in Research (EXPLORE) program, a new initiative offered through the Department of Earth, Environmental and Planetary Sciences (EEPS) that allows undergraduates of any major hands-on experience in research projects ...
Most patients can continue GLP-1 anti-obesity drugs before surgery
2024-10-29
Most patients may continue to safely take glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists as prescribed before undergoing elective surgery and gastrointestinal endoscopies, according to new clinical guidance released today by five surgical and medical societies including the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA), American Gastroenterological Association (AGA), International Society of Perioperative Care of Patients with Obesity (ISPCOP), and Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES).
The guidance, published online in Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Women entering menopause later in life at greater risk for asthmaNew study suggests role of natural and synthetic estrogen in increasing risk of asthma