Nov. 14 AARP Author Q&A at GSA 2024 in Seattle: Debra Whitman, Global Aging Expert and Author of ‘The Second Fifty: Answers to the 7 Big Questions of Midlife and Beyond’
2024-10-31
(Press-News.org) Author Q&A: Debra Whitman, Global Aging Expert and Author of “The Second Fifty”
Date: Thursday, November 14
Time: 4:30 to 5:30 p.m. PT
Location: Seattle Convention Center Arch Building Room 305
Registration: GSA 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting media registration is required to attend this event.
During this meet-the-author media roundtable, Debra Whitman, executive vice president and chief public policy officer at AARP, will discuss her new book, “The Second Fifty: Answers to the 7 Big Questions of Midlife and Beyond.” The book walks people of all ages and circumstances through some of the biggest questions tied to aging: how long will I work, will I have enough money to last in retirement, and will I be healthy? Debra will discuss ways to live a healthier and more meaningful second half of life, and touch on topics like brain health, work, caregiving, saving for retirement, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits.
This event is organized and supported by AARP in conjunction with the GSA 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting. Light refreshments will be served.
###
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) is the nation's oldest and largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to research, education, and practice in the field of aging. The principal mission of the Society — and its 5,500+ members — is to advance the study of aging and disseminate information among scientists, decision makers, and the general public. GSA’s structure includes a nonpartisan public policy institute, the National Academy on an Aging Society, and GSA is also home to the National Center to Reframe Aging and the National Coordinating Center for the Resource Centers for Minority Aging Research.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-31
Groundbreaking research exploring the experiences of autistic psychiatrists has revealed that psychiatrists who are unaware that they themselves are autistic may fail to recognise the condition in their patients. The study, conducted by researchers from University College Dublin, London South Bank University, Brighton and Sussex Medical School, is the first of its kind to delve into the lives of neurodivergent psychiatrists. It was published today in BJPsych Open.
"Knowing that you are autistic can be positively life-changing," said the study author Dr Mary Doherty, Clinical Associate ...
2024-10-31
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists investigating animal viruses with potential to infect humans have identified a critical protein that could enable spillover of a family of organisms called arteriviruses.
In a new study, researchers identified a protein in mammals that welcomes arteriviruses into host cells to start an infection. The team also found that an existing monoclonal antibody that binds to this protein protects cells from viral infection.
Arteriviruses circulate broadly in many types of mammals around the world that serve as natural hosts – such as ...
2024-10-31
The visible universe — all the potatoes, gas giants, steamy romance novels, black holes, questionable tattoos, and overwritten sentences — accounts for only 5 percent of the cosmos.
A Virginia Tech-led team is hunting for the rest of it, not with telescopes or particle colliders, but by scrutinizing billion-year-old rocks for traces of dark matter.
In leading a transdisciplinary team from multiple universities on this unconventional search, physics’ Patrick Huber is also taking an unconventional step: from theoretical work into experimental work.
With support from a $3.5 million Growing Convergence Research ...
2024-10-31
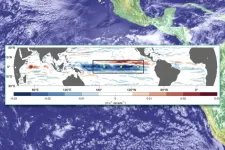
A new study published October 31, 2024, in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans has revealed significant acceleration in the upper-ocean circulation of the equatorial Pacific over the past 30 years. This acceleration is primarily driven by intensified atmospheric winds, leading to increased oceanic currents that are both stronger and shallower, with potential impacts on regional and global climate patterns, including the frequency and intensity of El Niño and La Niña events. The study provides a spatial view of these long-term trends from observations, adding at least ...
2024-10-31
Traditional city planning methods require significant technical expertise and manual work.
A Virginia Tech researcher is working to change that.
New research shows the potential of large language models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini, for assessing the human-made environment using street-view images.
By comparing LLM performance with traditional city planning deep learning methods, the study from the College of Natural Resources and Environment found that LLM-based performance is similar with established approaches. Unlike ...
2024-10-31
Irvine, Calif., Oct. 31, 2024 — By creating a new way for light and matter to interact, researchers at the University of California, Irvine have enabled the manufacturing of ultrathin silicon solar cells that could help spread the energy-converting technology to a vast range of applications, including thermoelectric clothing and onboard vehicle and device charging.
The development, subject of a paper recently published as the cover story in the journal ACS Nano, hinges on the UC Irvine researchers’ conversion of pure silicon from an indirect to a direct bandgap semiconductor through the way it interacts ...
2024-10-31
WHAT:
A clinical trial sponsored by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has launched to examine the safety and acceptability of a novel rectal HIV microbicide douche containing the antiretroviral drug tenofovir. This “on-demand” HIV prevention approach involves using the microbicide prior to a potential exposure from receptive anal intercourse.
Several forms of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) are in use in the United States and globally, namely daily oral pills, long-acting injections, and a monthly vaginal ring. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advises that gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with ...
2024-10-31
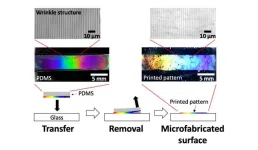
1. A team of researchers from NIMS and the University of Connecticut has developed a printing technique capable of forming a periodic nano/microstructure on the surface of a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) slab and easily transferring it onto the surface of a glass substrate. This technique enables us to create materials with useful functions—including water-repellency and the ability to generate structural colors—without expensive equipment and complex processes. In addition, the technique may be used to fabricate materials capable of realizing anti-fogging and/or generating structural colors on their surfaces—functions potentially useful in the development ...
2024-10-31
Reports of drug-related supply-chain issues were 40% less likely to result in drug shortages in Canada versus the United States, according to a new study from University of Pittsburgh researchers and published today in JAMA.
The analysis looked at drugs that had reports of supply-chain disruptions between 2017 and 2021 in both countries and found that within 12 months of an initial U.S. report, nearly half resulted in drug shortages in the U.S. versus about one-third in Canada. There was also a consistently lower ...
2024-10-31
About The Study: Drug-related reports of supply chain issues were 40% less likely to result in meaningful drug shortages in Canada compared with the U.S. These findings highlight the need for international cooperation between countries to curb the effects of drug shortages and improve resiliency of the supply chain for drugs.
Quote from corresponding author Katie J. Suda, PharmD, MS:
“Our U.S. drug supply chain is linked globally – shortages in one country can happen in another country – presenting an opportunity to compare and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nov. 14 AARP Author Q&A at GSA 2024 in Seattle: Debra Whitman, Global Aging Expert and Author of ‘The Second Fifty: Answers to the 7 Big Questions of Midlife and Beyond’