(Press-News.org) In emergencies, children have distinct needs because of their unique physiological, emotional and developmental characteristics. But 83% of emergency departments nationwide are not fully prepared to meet those needs — which can be life-threatening for a child in cases of severe illness or injury.
A new Oregon Health & Science University-led study, published today in JAMA Network Open, found that bridging that gap, known as becoming “pediatric ready,” could prevent the deaths of more than 2,100 children each year with modest financial investment.
In Oregon specifically, an investment of just over $3 per child — a total cost of about $2.7 million annually — could save approximately 30 children’s lives each year when adjusted for population size.
“Few topics are more important than children and their health. We need to do everything we can to keep them alive, and improving pediatric ED readiness is one significant way to move the needle,” said Craig Newgard, M.D., M.P.H., professor of emergency medicine in the OHSU School of Medicine and lead author of the study. “This study builds on a growing body of research demonstrating that every hospital can and must be ready for children’s emergencies.
“For the first time, we have comprehensive national and state-by-state data that emphasizes both the urgency and feasibility of this work.”
Saving lives with readiness
The research team, co-led by Newgard and Nathan Kuppermann, M.D., chair of pediatrics and chief academic officer at Children’s National Hospital, analyzed data from 4,840 emergency departments, focusing on 669,019 children at risk for death upon seeking care. Using predictive models, they assessed how every emergency department achieving high pediatric readiness — defined as scoring at least 88 out of 100 on the National Pediatric Readiness Project, or NPRP, assessment — could impact mortality rates.
By applying the potential reduction in mortality associated with high readiness to the number of at-risk children and adjusting state-specific estimates for population size, the researchers identified the number of lives that could be saved each year: Of the 7,619 children who die annually while receiving emergency services, 2,143 lives could have been saved through universal high ED pediatric readiness.
The study authors emphasize that modest investment in health care dollars would be needed to eliminate these inequities in pediatric emergency care: The cost per child resident by state ranges from $0 to $12, a price tag lower than a single dose of most routine childhood vaccines.
They also outline several strategies to improve pediatric emergency care, such as integrating high pediatric readiness into hospital accreditation requirements and incentivizing readiness through performance-based reimbursement models.
“This research emphasizes the urgent need for widespread investment in pediatric readiness,” said Kate Remick, M.D., co-author of the study and emergency physician at the Dell School of Medicine at the University of Texas at Austin. “The National Pediatric Readiness Project has provided a roadmap for improvement. But we need the full engagement of clinicians, health care administrators, policymakers, and families to make universal pediatric readiness a reality.”
Ready, able to save a child’s life
On a high level, readiness of emergency departments represents the ability to care for acutely ill and injured children. In practice, achieving high pediatric ED readiness includes elements such as care coordination, personnel, quality improvement, safety, equipment, and policies and procedures.
To support hospitals’ efforts, the NPRP has developed free, open-access resources for ED providers and staff to help facilitate delivery of high-quality emergency care to all children. The Emergency Medical Services for Children Program also provides individualized resources, including program administrators in all 50 states who are able to guide hospitals through readiness work based on their state’s unique health care needs and landscape.
Understanding the significant geographic barriers many individuals face to receive care, upcoming research by Newgard and colleagues will focus on rural emergency care and how hospitals can better serve children living in rural and frontier areas. The research team will also continue to investigate the economic benefits of pediatric ED readiness, including long-term health system savings.
“The vast majority of kids — more than 80% — who present for care at emergency departments across the country are cared for outside of children’s hospitals, primarily in general community EDs,” Newgard said.
“What’s so impactful about the concept of readiness is that it’s designed to be inclusive of all hospitals regardless of size, resources, geography or other constraints,” he added. “It’s well within our reach to ensure every hospital is ready and able to save a child’s life.”
The research was supported by a Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) Emergency Medical Services for Children Targeted Issue grant (H34MC33243-01-01) and an HHS National Institutes of Health (NIH) Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) grant (R24 HD085927). The contents are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement, by HHS, HRSA, NIH, or the U.S. Government.
END
Investment in pediatric emergency care could save more than 2,100 young lives annually
2024-11-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The dynamic core of black holes
2024-11-01
Black holes continue to captivate scientists: they are purely gravitational objects, remarkably simple, yet capable of hiding mysteries that challenge our understanding of natural laws. Most observations thus far have focused on their external characteristics and surrounding environment, leaving their internal nature largely unexplored. A new study, conducted through a collaboration between the University of Southern Denmark, Charles University in Prague, Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati (SISSA) in Trieste, and Victoria University of Wellington ...
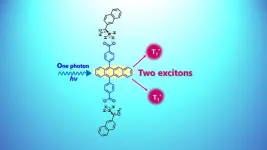
Improving energy production by boosting singlet fission process
2024-11-01
Fukuoka, Japan—In organic molecules an exciton is a particle bound pair of an electron (negative charge) and its hole (positive charge). They are held together by Coulombic attraction and can move within molecular assemblies. Singlet fission (SF) is a process where an exciton is amplified, and two triplet excitons are generated from a singlet exciton. This is caused by the absorption of a single particle of light, or photon, in molecules called chromophores (molecules that absorb specific wavelengths of light). Controlling the molecular orientation and arrangement of chromophores is crucial for achieving high SF efficiency in materials with strong potential for optical ...
Smoking cessation and incident cardiovascular disease
2024-11-01
About The Study: In this cohort study, smoking and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk exhibited a dose-dependent association, with light ex-smokers having a CVD risk similar to that of never-smokers relatively soon after smoking cessation. For heavy ex-smokers, greater than 25 years might be required for the residual CVD risk to align with that of never-smokers.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Seung Yong Shin, MD, PhD, email theshin04@korea.ac.kr.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Cannabis use during early pregnancy following recreational cannabis legalization
2024-11-01
About The Study: In this time-series study, recreational cannabis legalization implementation in California was associated with an increase in rates of cannabis use during early pregnancy, defined by both self-report and toxicology testing, driven by individuals living in jurisdictions that allowed adult-use retailers.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kelly C. Young-Wolff, PhD, MPH, email kelly.c.young-wolff@kp.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.3656)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
Research shows Cleveland Clinic’s therapeutic virtual yoga program can be effective for chronic low back pain
2024-11-01
Research Shows Cleveland Clinic’s Therapeutic Virtual Yoga Program Can Be Effective for Chronic Low Back Pain
Participants also reported better sleep quality and reduced use of pain medications
UNDER EMBARGO Friday, November 01, 2024, 11:00 a.m. ET, CLEVELAND: Cleveland Clinic researchers found that a 12-week therapeutic virtual yoga program for chronic low back pain can be a feasible, safe and effective treatment option. The findings are published in JAMA Network Open.
Chronic low back pain is very common — up to 20% of adults worldwide have long-lasting or recurrent lower back pain. In severe cases, ...
Closing in on Parkinson’s Disease proteins in extracellular vesicles in the blood
2024-11-01
Closing in on Parkinson’s Disease proteins in extracellular vesicles in the blood
Precision diagnostics for diseases that affect the brain and other organs brought closer by new ability to exclusively access contents of organ-derived extracellular vesicles in blood
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Brain disorders like Parkinson’s (PD) or Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) start to develop in patients much earlier than when their first clinical symptoms appear. Treating patients at these early stages could slow or even stop their ...
Regional and global experts convene in Accra, Ghana to update cancer treatment guidelines for Sub-Saharan Africa
2024-11-01
Accra, GHANA [October 29, 2024] — International oncology experts are gathering in Accra, Ghana for a series of meetings beginning today, to update cancer treatment recommendations in the NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Sub-Saharan Africa. This is the latest event from a longstanding collaboration between the African Cancer Coalition (ACC), American Cancer Society (ACS), and National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®), and the Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI) that collectively ...
China University of Geosciences (Beijing) unveils clues to an enigmatic geological process
2024-11-01
Cratons are fascinating yet enigmatic geological formations. Known to be relatively stable portions of the Earth’s continental crust, cratons have remained largely unchanged for billions of years. Although cratons have survived many geological events, some are undergoing decratonization—a process characterized by their deformation and eventual destruction. For example, the North China Craton (NCC), an ancient continental crust block, is known to have begun extensive decratonization during the Mesozoic era, largely due to tectonic and geochemical modifications and destabilization of its base (or ‘keel’). However, explaining the mechanisms ...
Fueling greener aviation with hydrogen
2024-11-01
Despite ongoing efforts to curb CO2 emissions with electric and hybrid vehicles, other forms of transportation remain significant contributors of greenhouse gases. To address this issue, old technologies are being revamped to make them greener, such as the reintroduction of sailing vessels in shipping and new uses for hydrogen in aviation. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering have used computer modeling to study the feasibility and challenges of hydrogen-powered aviation.
“While there is a long way to go for hydrogen aviation to be realized at scale, we hope that our ...
Education, occupation, and wealth affect the risk of cognitive impairment
2024-11-01
Socioeconomic factors such as education, occupation, and wealth influence the likelihood of developing cognitive impairment or dementia in later life and whether a person is likely to recover, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The research, published in Scientific Reports, followed 8,442 adults aged 50 and above in England over 10 years from 2008/09 to 2018/19, to examine how socioeconomic factors at the start of the study were associated with changes in cognitive status.
The researchers tracked how these people moved between various states: healthy, mild cognitive impairment, and dementia. They also considered the possibility ...