(Press-News.org) Embargoed: Not for Release Until 2:00 pm U.S. Eastern Time Friday, 01 November 2024.
Researchers at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) are collaborating with colleagues from Frankfurt/Main, Oxford and Würzburg to investigate how the complex, cooperative behaviour of honey bees (Apis mellifera) is genetically programmed so that it can be passed on to subsequent generations. As they explain in the scientific journal Science Advances, they found an answer in what is known as the doublesex gene (dsx).
Behavioural interactions between organisms are fundamental and often inherited. Every human being and every animal interacts with other individuals in its social group in one way or another through its behaviour. In the animal kingdom, this has considerable advantages in collective foraging for food, defence against predators and the rearing of offspring.
In some animals, such as honeybees, the social behaviour bonds are so strong that the individual members form a tight-knit society that function collectively as a single “superorganism”. Through their individual behaviour, thousands of worker bees protect the entire colony, feed it and care for the brood.
Professor Dr Martin Beye, who heads the Institute of Evolutionary Genetics at HHU and is the corresponding author of the study that has now been published in Science Advances, emphasises: “The behavioural repertoire of the individual bees and their function in the colony are not learned, but rather inherited. Until now, it was not known how such complex behaviours were genetically encoded.”
Together with colleagues from the universities in Frankfurt/Main, Oxford and Würzburg, the team of researchers at HHU led by Beye and first author Dr Vivien Sommer has now discovered that a special gene known as dsx specifies worker bee-specific behaviour.
Sommer: “The gene programmes whether a worker bee takes up a task in the colony and for how long. This includes collective tasks such as caring for the larvae or foraging for food and social exchanges on food sources, for example.”
The biologists used the CRISPR/Cas9 genetic scissors in their investigations to modify or switch off the dsx gene in selected bees. They attached a QR code to the manipulated bees, then monitored their behaviour in the hive with cameras. The resulting video sequences were analysed with the support of artificial intelligence to determine the bees’ individual behavioural patterns.
Sommer: “Our central question was whether and how the inherited behavioural patterns changed as a result of the gene modification. Such changes must be reflected in the nervous system of the worker bees where the specific behaviour is controlled.”
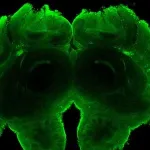
The researchers introduced green fluorescent protein (GFP) into the dsx sequence so that GFP was produced together with the dsx protein. The neuronal circuits could then be viewed using fluorescence microscopy, in both the unmodified bees and in those with genetic modifications. “We were able to use these tools to see exactly which neural pathways the dsx gene creates in the brain and how this gene in turn specifies the inherited behavioural patterns of honeybees,” explains doctoral researcher Jana Seiler, who is also a co-author of the study.
“Our findings indicate a fundamental genetic programme that determines the neuronal circuitry and behaviour of worker bees,” says Professor Dr Wolfgang Rössler from the Department of Behavioural Physiology and Sociobiology, who led the study at the University of Würzburg.
In the next step, the researchers now want to move from the level of the individual honeybee to the bee colony superorganism. Alina Sturm, who is also a doctoral researcher at HHU and study co-author, adds: “We hope to find the link between individual programming and the coordinated behaviour of many individuals.”
Original publication:
Vivien Sommer, Jana Seiler, Alina Sturm, Sven Köhnen, Anna Wagner, Christina Blut, Wolfgang Rössler, Stephen F. Goodwin, Bernd Grünewald, Martin Beye. Dedicated developmental programing for group-supporting behaviors in eusocial honeybees. Science Advances (2024).
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adp3953
END
Bee gene specifies collective behavior
Bee research: publication in Science Advances
2024-11-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Jennifer Bickel, M.D., named MD Anderson Vice President and Chief Wellness Officer
2024-11-01
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the selection of Jennifer Bickel, M.D., as the institution’s inaugural vice president and chief wellness officer (CWO). She will begin on January 6, 2025. Working closely with the senior vice president of people, culture and infrastructure, as well as the chief academic officer, she will spearhead initiatives that prioritize employee well-being, professional fulfillment and community resilience.
In her new role, Bickel will implement a three-component model focusing on a culture of wellness, efficiency ...
Evolutionary paths vastly differ for birds, bats
2024-11-01
ITHACA, N.Y. – New Cornell University research has found that, unlike birds, the evolution of bats’ wings and legs is tightly coupled, which may have prevented them from filling as many ecological niches as birds.
“We initially expected to confirm that bat evolution is similar to that of birds, and that their wings and legs evolve independently of one another. The fact we found the opposite was greatly surprising,” said Andrew Orkney, postdoctoral researcher in the laboratory of Brandon Hedrick, assistant professor biomedical sciences.
Both researchers ...
Political pros no better than public in predicting which messages persuade
2024-11-01
Political campaigns spend big bucks hiring consultants to craft persuasive messaging, but a new study coauthored by Yale political scientist Joshua L. Kalla demonstrates that political professionals perform no better than laypeople in predicting which messages will sway voters.
In the study, Kalla and his coauthors evaluated how well sample groups of political practitioners — professionals who work for political campaigns, polling firms, and advocacy organizations — and members of the public could predict the effectiveness of 172 campaign messages concerning 21 political issues, including legalizing marijuana, cancelling student debt, and increasing ...
Investment in pediatric emergency care could save more than 2,100 young lives annually
2024-11-01
In emergencies, children have distinct needs because of their unique physiological, emotional and developmental characteristics. But 83% of emergency departments nationwide are not fully prepared to meet those needs — which can be life-threatening for a child in cases of severe illness or injury.
A new Oregon Health & Science University-led study, published today in JAMA Network Open, found that bridging that gap, known as becoming “pediatric ready,” could prevent the deaths of more than 2,100 children each year with modest financial investment. ...
The dynamic core of black holes
2024-11-01
Black holes continue to captivate scientists: they are purely gravitational objects, remarkably simple, yet capable of hiding mysteries that challenge our understanding of natural laws. Most observations thus far have focused on their external characteristics and surrounding environment, leaving their internal nature largely unexplored. A new study, conducted through a collaboration between the University of Southern Denmark, Charles University in Prague, Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati (SISSA) in Trieste, and Victoria University of Wellington ...
Improving energy production by boosting singlet fission process
2024-11-01
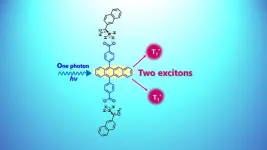
Fukuoka, Japan—In organic molecules an exciton is a particle bound pair of an electron (negative charge) and its hole (positive charge). They are held together by Coulombic attraction and can move within molecular assemblies. Singlet fission (SF) is a process where an exciton is amplified, and two triplet excitons are generated from a singlet exciton. This is caused by the absorption of a single particle of light, or photon, in molecules called chromophores (molecules that absorb specific wavelengths of light). Controlling the molecular orientation and arrangement of chromophores is crucial for achieving high SF efficiency in materials with strong potential for optical ...
Smoking cessation and incident cardiovascular disease
2024-11-01
About The Study: In this cohort study, smoking and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk exhibited a dose-dependent association, with light ex-smokers having a CVD risk similar to that of never-smokers relatively soon after smoking cessation. For heavy ex-smokers, greater than 25 years might be required for the residual CVD risk to align with that of never-smokers.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Seung Yong Shin, MD, PhD, email theshin04@korea.ac.kr.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Cannabis use during early pregnancy following recreational cannabis legalization
2024-11-01
About The Study: In this time-series study, recreational cannabis legalization implementation in California was associated with an increase in rates of cannabis use during early pregnancy, defined by both self-report and toxicology testing, driven by individuals living in jurisdictions that allowed adult-use retailers.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kelly C. Young-Wolff, PhD, MPH, email kelly.c.young-wolff@kp.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.3656)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
Research shows Cleveland Clinic’s therapeutic virtual yoga program can be effective for chronic low back pain
2024-11-01
Research Shows Cleveland Clinic’s Therapeutic Virtual Yoga Program Can Be Effective for Chronic Low Back Pain
Participants also reported better sleep quality and reduced use of pain medications
UNDER EMBARGO Friday, November 01, 2024, 11:00 a.m. ET, CLEVELAND: Cleveland Clinic researchers found that a 12-week therapeutic virtual yoga program for chronic low back pain can be a feasible, safe and effective treatment option. The findings are published in JAMA Network Open.
Chronic low back pain is very common — up to 20% of adults worldwide have long-lasting or recurrent lower back pain. In severe cases, ...
Closing in on Parkinson’s Disease proteins in extracellular vesicles in the blood
2024-11-01
Closing in on Parkinson’s Disease proteins in extracellular vesicles in the blood
Precision diagnostics for diseases that affect the brain and other organs brought closer by new ability to exclusively access contents of organ-derived extracellular vesicles in blood
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Brain disorders like Parkinson’s (PD) or Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) start to develop in patients much earlier than when their first clinical symptoms appear. Treating patients at these early stages could slow or even stop their ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
[Press-News.org] Bee gene specifies collective behaviorBee research: publication in Science Advances