Researchers from Uppsala and Magdeburg obtain an ERC Synergy Grant to advance cancer immunotherapy
Blood vessels as the key to more effective cancer immunotherapies
2024-11-05
(Press-News.org)
Targeting and customizing blood vessels in tumors to increase T cell infiltration and maintain their function may represent the next breakthrough in cancer therapy. The European Research Council has recognized this by awarding a prestigious Synergy Grant to the project VASC-IMMUNE, where three researchers, each possessing complementary expertise in this research topic, will synergize to advance the field. Professors Anna Dimberg and Magnus Essand are both from the Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology, Uppsala University and Professor Thomas Tüting is from the Department of Dermatology, University Hospital Magdeburg.
The successful implementation of immunotherapy over the last 10 years represents a true paradigm shift in cancer treatment. We know today that tumor-reactive T cells inside tumors can be made more potent through immune checkpoint blockade (e.g., anti-PD1 antibodies). These special medications release the ‘brakes’ of the immune system that prevent T cells from attacking the tumor and can therefore significantly improve the chances of survival for many cancer patients. We also know that immune checkpoint inhibitors tend not to work when T cells are absent in tumor tissues. Since T cells enter tumor tissues from the circulation, the tumor vasculature plays an important role in their recruitment. In this process, endothelial cells that form the vasculature interact in a reciprocal manner with immune cells. Together, they shape the composition and function of the vascular and immune landscapes in tumor tissues. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are incompletely understood.
The VASC-IMMUNE project addresses the interaction between endothelial and immune cells focusing on both melanoma, a malignant skin cancer where many patients benefit from immunotherapies, and glioblastoma, a malignant brain cancer where current immunotherapies so far have not been able to improve patient survival.
“We will utilize the fact that in melanoma some patients respond very well to immunotherapy, while others do not”, says Thomas Tüting. He continues, “we know that responders tend to have higher numbers of T cells in their tumor tissues. Many T cells are found near specialized endothelial cells together with other immune cell types in structures called immune hubs. By connecting detailed cellular and molecular investigations of the vascular and immune landscapes in carefully selected tumor material from responding and non-responding patients, we hope to identify factors in the vascular-immune crosstalk that governs the responsiveness to immunotherapies.”
“I have been studying glioblastoma vessels and their interaction with immune cells for many years”, says Anna Dimberg. “I am confident that comparing detailed comparison of the vascular and immune landscapes in melanoma and glioblastoma tissues will reveal transcriptional networks in endothelial cells that determine how tumor vessels interact with immune cells. Once we have learnt this, we will reprogram tumor vessel function utilizing important transcription factors that optimize the ability of endothelial cells to recruit T cells and support the formation of activating immune hubs in tumor tissues.”
However, targeting and transcriptionally reprogramming tumor vessels in cancer patients possess a significant challenge. The contribution of my research groups will be to develop a novel viral vector that can specifically target tumor vessels while sparing normal blood vessels”, says Magnus Essand. “We have already shown that this is possible in mouse models of glioblastoma and together, we will now translate this finding to human tumor vessels, not only in glioblastoma and melanoma but in tumor vessels in general. This is why the project has such great transformational potential.”
The 6-year project will start in the first half of 2025. The researchers expect to work closely and share data, expertise and personnel to advance the project and at the same time create a rich and stimulating environment for young researchers to grow.
The European Research Council (ERC) funds top international research in the EU. More information: https://erc.europa.eu/apply-grant/synergy-grant
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-05
Mosquitoes are much more blunt. Mating occurs for a few seconds in midair. And all it takes to woo a male is the sound of a female’s wingbeats. Imagine researchers’ surprise when a single change completely killed the mosquitoes’ libidos.
Now a study out of UC Santa Barbara reveals that this is really all there is to it. Researchers in Professor Craig Montell’s lab created deaf mosquitoes and found that the males had absolutely no interest in mating. “You could leave them together with the females ...
2024-11-05
INDIANAPOLIS – A commentary, published in the Journal of Neurotrauma, calls for traumatic brain injury to be recognized as a chronic condition as are diabetes, asthma, depression and heart failure.
To provide comprehensive care for traumatic brain injury throughout individuals’ lifespans, the authors propose that coordinated care models they and others have developed, tested and applied to various populations -- including older adults, individuals living with depression and post-intensive care unit survivors -- be adapted to improve communication and integration between brain injury specialists -- including ...
2024-11-05
SAN ANTONIO — November 5, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute’s Dr. James Walker has received the Distinguished Scientist Award from the Hypervelocity Impact Society. This honor recognizes individuals who have made a significant and lasting contribution to the field of hypervelocity science. Hypervelocity impact is typically viewed as impacts at speeds above 2 kilometers per second (4,475 miles per hour); for some materials, however, lower speed impacts display hypervelocity impact effects.
The ...
2024-11-05
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and obesity are at a higher risk of giving birth to smaller babies in terms of birth weight, length, and head circumference, according to a recent study conducted at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
One in eight women is affected by the hormone disorder PCOS. Common characteristics are elevated levels of male sex hormones, infrequent or irregular menstrual periods, and the formation of small cysts on the ovaries.
In the study, 390 children born to women ...
2024-11-05
Researchers are developing new ideas about the best ways to make lab-grown diamonds while minimizing other forms of carbon, such as soot. These diamonds aren’t destined for rings and necklaces, though. These are the kinds that are needed for the computers, optics and sensors of the future.
One new study, conducted by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) and Princeton University, investigated ways to reliably grow diamond at lower temperatures than those currently used. Diamond has properties ...
2024-11-05
The American Pediatric Society (APS) is pleased to announce Maria E. Trent, MD, MPH, as the 2025 David G. Nichols Health Equity Award recipient.
The David G. Nichols Health Equity Award, administered by the APS and endowed by the American Board of Pediatrics (ABP) Foundation, was created to recognize demonstrated excellence in advancing child and adolescent health, well-being, and equity through quality improvement, advocacy, practice, or research. This award recognizes Dr. Trent’s outstanding contributions to advancing child and adolescent health, well-being, and equity and the far-reaching impact of her work. The award will be presented to Dr. Trent ...
2024-11-05
A study published today in Astronomy & Astrophysics marks a significant milestone in our understanding of the formation and dynamical evolution of multiple stellar populations in globular clusters (spherical and very compact stellar agglomerates typically populated by 1–2 million stars). This pioneering study, conducted by a group of researchers from the National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), the University of Bologna, and Indiana University, is the first to perform a 3D kinematic analysis of multiple stellar populations for a representative sample of 16 globular clusters in our Galaxy. It provides ...
2024-11-05
Hydrogen gas is a promising energy source with several advantages - it is lightweight, storable, energy-dense, and environmentally friendly compared to fossil fuels, producing no pollutants or greenhouse gas emissions. As such, it has extensive applications across different fields, including transportation, architecture, power generation, and industries. However, hydrogen is highly flammable, and therefore its safe and widespread use requires reliable methods for detecting leaks and ensuring its purity. The need for reliable detection methods has necessitated the development of trace-gas sensing techniques. While several methods have been developed for hydrogen sensing, ...
2024-11-05
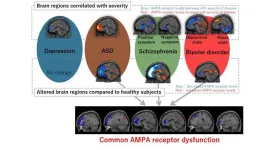
Even though psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are quite common, their diagnosis and treatment are challenging. While doctors today have a good idea of the clinical symptoms caused by these disorders, our overall understanding of their biological characteristics and underlying physiological causes remain obscure.
Experts agree that problems with synapses—the connections that allow communication between neurons—might be a defining feature ...
2024-11-05
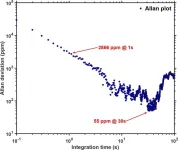
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden and at the University of Magdeburg in Germany have developed a novel type of nanomechanical resonator that combines two important features: high mechanical quality and piezoelectricity. This development could open doors to new possibilities in quantum sensing technologies.
Mechanical resonators have been used for centuries for a multitude of applications. A key aspect of these devices is their ability to vibrate at specific frequencies. A well-known example is the tuning fork. When struck, the tuning fork oscillates at its resonance frequency, producing a sound wave within our hearing range. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers from Uppsala and Magdeburg obtain an ERC Synergy Grant to advance cancer immunotherapy
Blood vessels as the key to more effective cancer immunotherapies