Research shows caterpillar fungus can slow down growth of cancer cells
2024-11-07
(Press-News.org)
New research into a chemical produced by a caterpillar fungus that has shown promise as a possible cancer treatment has revealed how it interacts with genes to interrupt cell growth signals. The discovery is an important step towards developing new drugs for the treatment of the disease.
The research into a chemical produced by a caterpillar fungus has revealed how it may work as a cancer treatment. It interrupts the cell growth signals that are overactive in cancer, an approach that could be less damaging to healthy tissues than most currently available treatments.
Scientists from the University of Nottingham’s School of Pharmacy have been studying how a parasitic fungus that grows on caterpillars could work as a potential treatment for a range of diseases by studying cordycepin, one of the drugs found in these mushrooms. The research has been published in the journal FEBS Letters.
The caterpillar fungi are famous in Asia as a health food and traditional medicine. Cordycepin, which is produced by Cordyceps militaris, a pretty orange fungus that infects caterpillars, has shown promise as a cancer medicine in a range of studies, but until now it has been unclear how it works.
Using high-throughput techniques the research team measured the effects of cordycepin on the activity of thousands of genes in multiple cell lines. The research compared the effects of cordycepin with those from other treatments deposited in databases and showed that it works by acting on the growth inducing pathways of the cell in all cases.
By studying what happens to cordycepin inside the cell, the team confirmed that cordycepin is converted to cordycepin triphosphate, an analogue of the cell’s energy carrier ATP. Cordycepin triphosphate was shown to be the likely cause of the effects on cell growth, and therefore the molecule that can directly affect cancer cells.
Dr Cornelia de Moor in the School of Pharmacy has led this research, she explains: “We have been researching the effects of cordycepin on a range of diseases for a number of years and with each step we get closer to understanding how it could be used as an effective treatment. One of the exciting things to have been happening is that it has become easier and less expensive to do these very large experiments, so we were able to examine thousands of genes at the same time.
Our data confirms that cordycepin is a good starting point for novel cancer medicines and explains its beneficial effects. For instance, derivatives of cordycepin could aim to produce the triphosphate form of the drug to have the same effect. In addition, the data will help with monitoring the effects of cordycepin in patients, as our data indicate particular genes whose activity reliably responds to cordycepin, which could for instance be measured in blood cells.”
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-07
Philadelphia, November 7, 2024 – Melanoma accounts for only 1% of skin cancers in the United States but results in the largest number of skin cancer deaths. Investigators evaluated the potential link between the availability and use of tanning beds and the rising rates of melanoma in New England. They found compelling evidence linking tanning bed usage to increased melanoma risk. Their spatial epidemiologic study in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, published by Elsevier, provides critical insights to inform public health strategies and reduce melanoma incidence.
The incidence of melanoma in the US has been increasing ...
2024-11-07
Toronto, Canada, 7 November 2024 – From a curious young scientist investigating her grandfather's family wine to a leading expert in mitochondrial health and mental illness, Dr. Ana Cristina Andreazza's journey exemplifies the power of personal motivation in driving scientific innovation. As founder and Scientific Director of the Mitochondrial Innovation Initiative (Mito2i), Dr. Andreazza is revolutionizing our understanding of the connection between cellular energy production and mental health.
In an illuminating Genomic Press Interview, published in Brain Medicine on November 7, 2024, ...
2024-11-07
Bethesda, Maryland, USA, 7 November 2024 – Dr. Nora Volkow's mission to revolutionize addiction treatment began with a deeply personal observation: watching how excessive substance use could profoundly alter a person’s behavior while simultaneously triggering social rejection by others. As the first woman and Hispanic Director of the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), Dr. Volkow has dedicated her career to investigating how drugs affect the human brain and how these disruptions contribute to the behavioral/emotional ...
2024-11-07
Edinburgh, Scotland, 7 November 2024 – A groundbreaking 25-year research program has unveiled key insights into how our brains age and what factors influence cognitive performance throughout life. The findings, published on 7 November 2024 in Genomic Psychiatry, draw from the Lothian Birth Cohorts (LBC) studies, which uniquely tracked participants' cognitive abilities from childhood through their eighth decade of life.
Professor Ian Deary and Dr. Simon Cox from the University of Edinburgh present remarkable discoveries that challenge conventional wisdom about brain aging. Their research ...
2024-11-07
San Diego, California, 7 November 2024 – In a groundbreaking exploration of psychedelic medicine's potential for treating one of psychiatry's most challenging conditions, researchers at University of California, San Diego (UCSD) provided an analysis and further details of a trial published in Nature Medicine (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10427429/) that had shown how psilocybin therapy affects individuals with anorexia nervosa. In the new peer-reviewed Emerging Topic article in Psychedelics ...
2024-11-07
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology advances, the demand for higher-performing semiconductors is rapidly growing. The development of new materials and innovative structures to achieve high-performance semiconductors has become crucial. For the first time globally, a 4-inch heterostructure fabrication technology using plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) has been developed. This breakthrough enables the production of low-power, high-performance semiconductors, surpassing the capabilities of traditional silicon-based technology.
The research team led by Senior Researcher Hyeong-U Kim of the Semiconductor Manufacturing Research Center of the ...
2024-11-07
Robot-assisted heart surgery usually requires an assistant at the operating table to help the surgeon insert the robot arm through a small incision. The assistant has to constantly make sure the surgeon has enough room to operate via the robot arm. For greater independence on the surgeon’s side, an Osaka Metropolitan University-led group has developed a device that can secure the surgical field.
Graduate School of Medicine Professor Toshihiko Shibata and Associate Professor Yosuke Takahashi worked with colleagues and small and ...
2024-11-07
As bird populations dwindle across the globe, a new study from University of Vermont researchers suggests some species may be more flexible to habitat changes than previously understood, creating new opportunities for supporting populations through city planting efforts. The team’s findings were published in the Journal of Animal Ecology today.
While studies have found bird populations are on the decline—Canada and the United States have lost nearly three billion birds over the last half century—measuring ...
2024-11-07
Event Date: 15 November 2024 to 17 November 2024
Time: 9:00am - 6:30pm
Venue: Main Hall, Shaw Auditorium, HKUST
INTRODUCTION
The Molecular Frontiers Symposium, organized by the globally renowned Molecular Frontiers Foundation - founded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences - is recognized as one of the most influential scientific organizations worldwide.
For the first time in the organization’s history, the Foundation's annual flagship symposium will be held in Greater China, hosted at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology.
With the theme "Frontiers of New Knowledge in Science", the Symposium ...
2024-11-07
“How is plant growth controlled?” and “What is the basis of variation in stress tolerance in plants?” were among the 125 most challenging scientific questions, according to the journal Science in 2016.
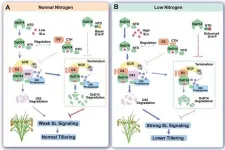
Strigolactone (SL) is an important plant hormone that plays essential roles in regulating branch number, a key growth and development trait for plants. Recently, scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have uncovered the mechanism behind SL perception and its key role in the tillering response to nitrogen.
The “gas and brake” mechanism of SL perception allows “smart and flexible” regulation of the duration ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Research shows caterpillar fungus can slow down growth of cancer cells