(Press-News.org) PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [November 7, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers focusing on maintaining evidence-based expert consensus driven guidelines for care—announces the publication of the expanded NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, Pancreatic, and Prostate. This closely follows the recent publication of the expanded NCCN Guidelines® for Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Colorectal, Endometrial, and Gastric.
Additional cancer types were added to the title and content for both guidelines. These updates account for the growing use of genetic testing in cancer prevention, screening, and treatment.
“These expanded guidelines reflect the recommendations from leading experts on genetic testing based on the latest scientific research across the cancer spectrum, consolidated into two convenient resources,” explained Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, Chief Executive Officer, NCCN. “This information is critical for guiding shared decision-making between health care providers and their patients, enhancing screening practices as appropriate, and potentially choosing options for prevention and targeted treatment choices. Genetic testing guidelines enable us to better care for people with cancer and their family members.”
The NCCN Guidelines include information on when genetic testing is recommended, and which type of testing may be best. They detail which hereditary conditions and genetic mutations are associated with elevated cancer risk and include follow-up on what to do for people who have them. Those next steps can include instructions for increased screening, or even preventive surgeries or other interventions.
“NCCN has played a major role in the field by creating guideline panels specifically devoted to the genetics of major cancers, and by developing scientifically based guidelines to help providers offer the best genetic-based care to their patients,” said Mary B. Daly, MD, PhD, FACP, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Chair of the NCCN Guidelines Panel for Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, Pancreatic, and Prostate. “These guideline panels are continuously active and engaged, constantly responding to new evidence as it becomes available to provide the most up-to-date information to NCCN Guidelines users. These updates include the spectrum of genes associated with genetic syndromes, the range of risk associated with each pathogenic variant, the improvements in screening and prevention strategies, the role of genetic data to inform cancer treatment, and the expansion of the role of genetic counseling as this field moves forward.”
“The recently updated NCCN Guidelines for Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Colorectal, Endometrial, and Gastric takes into account the latest published research and expert opinions from more than 30 experts on caring for individuals with risk for hereditary cancer,” said Samir Gupta, MD, UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center, Chair of the NCCN Guidelines Panel for Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Colorectal, Endometrial, and Gastric. “For the first time, we feature enhanced recommendations for evaluation for endometrial and gastric cancer risk, including: 1) new recommendations for consideration for hereditary cancer screening for all individuals with newly diagnosed endometrial cancer; 2) new recommendations for evaluation and management of CDH1 associated gastric cancer risk; 3) de-implementation of intense colorectal cancer screening for individuals with CHEK2 pathogenic variants; and 4) enhanced recommendations for managing gastric cancer risk in patients with APC pathogenic variants.”
The NCCN Guidelines are the recognized standard for clinical recommendations and policy in cancer care and the most frequently updated clinical practice guidelines available in any area of medicine. There are 88 separate subject-specific guidelines, which are maintained by more than 1,900 subject matter experts from across the 33 NCCN Member Institutions. Panels may also include primary care physicians and patient advocates. The NCCN Guidelines are available free-of-charge for non-commercial use at NCCN.org or via the Virtual Library of NCCN Guidelines® App.
# # #
About the National Comprehensive Cancer Network
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) is a not-for-profit alliance of leading cancer centers devoted to patient care, research, and education. NCCN is dedicated to improving and facilitating quality, effective, equitable, and accessible cancer care so all patients can live better lives. The NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) provide transparent, evidence-based, expert consensus recommendations for cancer treatment, prevention, and supportive services; they are the recognized standard for clinical direction and policy in cancer management and the most thorough and frequently-updated clinical practice guidelines available in any area of medicine. The NCCN Guidelines for Patients® provide expert cancer treatment information to inform and empower patients and caregivers, through support from the NCCN Foundation®. NCCN also advances continuing education, global initiatives, policy, and research collaboration and publication in oncology. Visit NCCN.org for more information.
END
Cancer genetic risk assessment guidelines expand to meet growing understanding of hereditary risk
National Comprehensive Cancer Network overhauls two major resources to help cancer care providers and other stakeholders stay current on cutting edge research into genetic/familial high-risk assessment.
2024-11-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Advances in screening and early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer
2024-11-07
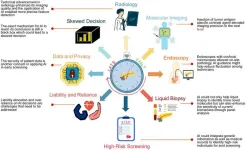
Pancreatic cancer (PC) presents substantial diagnostic challenges due to its aggressive nature and lack of early symptoms, leading to late detection and poor prognosis. According to recent cancer statistics, PC ranks as the fourth leading cause of cancer deaths globally, with increasing incidence, particularly in high-risk regions such as China. Factors such as a shortage of specific and reliable screening markers, along with a lower prevalence in the general population, make effective large-scale screening a formidable tasko assess advancements in diagnostic techniques, artificial intelligence integration, biomarker discoveries, ...
Metabolic dysregulation and metabolite imbalances in acute-on-chronic liver failure: Impact on immune status
2024-11-07
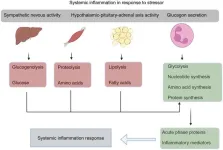
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is a life-threatening condition characterized by acute deterioration of liver function in patients with pre-existing chronic liver disease. It is often accompanied by multiorgan failure and systemic inflammation, with high short-term mortality rates. The triggers for ACLF include bacterial infections, acute alcoholic hepatitis, and ischemic hepatitis, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory mediators. These systemic inflammatory responses result in immune dysfunction, contributing to the progression of the disease.
Recent research has emphasized the metabolic changes ...
Elite coaches see compassion as a path to better performance
2024-11-07
It may sound like a contradiction to talk about compassion in the competitive world of elite sport. After all, isn't elite sport all about becoming hardened to resistance and adversity?
But this is a false dichotomy, according to a new study that analysed the views of 12 Danish high-performance coaches on the use of compassion in their work with elite athletes.
In fact, there is a broad consensus among the coaches, most of whom are head of national teams, about the benefits of using compassion, says the study's lead author, Emilia Backman from the Department of Psychology, University of Copenhagen.
"All of the high-performance ...
Microplastics impact cloud formation, likely affecting weather and climate
2024-11-07
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Scientists have spotted microplastics, tiny pieces of plastic smaller than 5 millimeters, in some of the most pristine environments on Earth, from the depths of the Mariana Trench to the snow on Mt. Everest to the mountaintop clouds of China and Japan. Microplastics have been detected in human brains, the bellies of sea turtles and the roots of plants. Now, new research led by Penn State scientists reveals that microplastics in the atmosphere could be affecting weather and climate.
The study, published today (Nov 7) in the journal Environmental Science and Technology: ...
ECOG-ACRIN and PrECOG announce multiple presentations at ASH 2024
2024-11-07
Researchers with the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) and PrECOG, LLC, will present a variety of abstracts that aim to improve treatments for patients with lymphoma and acute leukemias at the 66th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Meeting & Exposition. The meeting is set to occur in San Diego, California, and virtually December 7 - 10, 2024.
Promising results from a phase 2 study (PrE0905) in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and new data from the practice-changing E1910 phase ...
Off-the-shelf thermoelectric generators can upgrade CO2 into chemicals. The combination could help us colonize Mars
2024-11-07
Readily available thermoelectric generators operating under modest temperature differences can power CO2 conversion, according to a proof-of-concept study by chemists at the University of British Columbia (UBC).
The findings open up the intriguing possibility that the temperature differentials encountered in an array of environments—from a typical geothermal installation on Earth to the cold, desolate surface of Mars—could power the conversion of CO2 into a range of useful fuels and chemicals.
“The environment ...
What makes human culture unique?
2024-11-07
Why is human culture — the shared body of knowledge passed down across generations — so much more powerful than animal cultures?
“What’s special about our species?” is a question scientists have wrestled with for centuries, and now a scientist at Arizona State University has a new hypothesis that could change the way we perceive ourselves, and the world around us.
“Ten years ago it was basically accepted that it was the ability of human culture to accumulate and evolve that made us special, but new discoveries about animal behavior are challenging these ideas and forcing us to rethink what makes our cultures, ...
Researchers discover dozens of new genes associated with disc herniations
2024-11-07
Lumbar disc herniation is one of the most common structural changes in the lower back and the most common cause of radiating pain, or sciatica, in the leg.
Hereditary risk factors for disc herniations were investigated in a recently published international study led by a University of Oulu research group, utilising data from FinnGen, the Estonian Biobank, and the UK Biobank. The study analyzed the genetic and health data of 829,699 participants.
The study found 41 novel regions of the genome that modify the disease risk for disc herniations, in addition ...
Research shows caterpillar fungus can slow down growth of cancer cells
2024-11-07
New research into a chemical produced by a caterpillar fungus that has shown promise as a possible cancer treatment has revealed how it interacts with genes to interrupt cell growth signals. The discovery is an important step towards developing new drugs for the treatment of the disease.
The research into a chemical produced by a caterpillar fungus has revealed how it may work as a cancer treatment. It interrupts the cell growth signals that are overactive in cancer, an approach that could be less damaging to healthy ...
Tanning bed access and usage is driving higher rates of melanoma in specific regions
2024-11-07
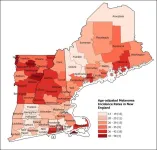
Philadelphia, November 7, 2024 – Melanoma accounts for only 1% of skin cancers in the United States but results in the largest number of skin cancer deaths. Investigators evaluated the potential link between the availability and use of tanning beds and the rising rates of melanoma in New England. They found compelling evidence linking tanning bed usage to increased melanoma risk. Their spatial epidemiologic study in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, published by Elsevier, provides critical insights to inform public health strategies and reduce melanoma incidence.
The incidence of melanoma in the US has been increasing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] Cancer genetic risk assessment guidelines expand to meet growing understanding of hereditary riskNational Comprehensive Cancer Network overhauls two major resources to help cancer care providers and other stakeholders stay current on cutting edge research into genetic/familial high-risk assessment.